Feature model
Encyclopedia
Feature model is a compact representation of all the products of the Software Product Line (SPL) in terms of "features". Feature models are visually represented by means of feature diagrams. Feature models are widely used during the whole product line development process and are commonly used as input to produce other assets such as documents, architecture definition, or pieces of code.
A SPL is a family of related programs. When the units of program construction are features—increments in program functionality or development—every program in an SPL is identified by a unique and legal combination of features, and vice versa.
Feature models were first introduced in the Feature-Oriented Domain Analysis
(FODA) method by Kang in 1990.. Since then, feature modeling has been widely adopted by the software product line community and a number of extensions have been proposed.
or system". The focus of SPL development is on the systematic and efficient creation of similar programs. FODA is an analysis devoted to identification of features in a domain to be covered by a particular SPL.
In addition to the parental relationships between features, cross-tree constraints are allowed. The most common are:
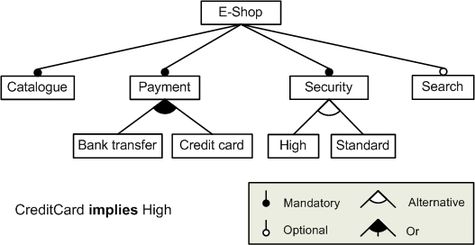
As an example, the figure below illustrates how feature models can be used to specify and build configurable on-line shopping systems. The software of each application is determined by the features that it provides. The root feature (i.e. E-Shop) identifies the SPL. Every shopping system implements a catalogue, payment modules, security policies and optionally a search tool. E-shops must implement a high or standard security policy (choose one), and can provide different payment modules: bank transfer, credit card or both of them. Additionally, a cross-tree constraint forces shopping systems including the credit card payment module to implement a high security policy.
-like multiplicities of the form [n,m] with n being the lower bound and m the upper bound. These are used to limit the number of sub-features that can be part of a product whenever the parent is selected.
If the upper bound is m the feature can be cloned as many times as we want (as long as the other constraints are respected). This notation is useful for products extensible with an arbitrary number of components.
. The satisfying valuations of this formula correspond to the feature configurations permitted by the feature diagram.
For instance, if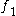 is a mandatory sub-feature of
is a mandatory sub-feature of 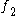 , the formula will contain the constraint
, the formula will contain the constraint  .
.
The following table provides a translation of the basic primitives. The semantics of a diagram is a conjunct of the translations of the elements contained in the diagram. We assume that the diagram is a rooted tree.
and CSP solvers
.
of another).
A SPL is a family of related programs. When the units of program construction are features—increments in program functionality or development—every program in an SPL is identified by a unique and legal combination of features, and vice versa.
Feature models were first introduced in the Feature-Oriented Domain Analysis
Feature-oriented domain analysis
Feature oriented domain analysis is a domain analysis method which introduced feature modelling to domain engineering. FODA was developed in 1990 following several U.S. Government research projects...
(FODA) method by Kang in 1990.. Since then, feature modeling has been widely adopted by the software product line community and a number of extensions have been proposed.
Background
A "feature" is defined as a "prominent or distinctive user-visible aspect, quality, or characteristic of a software systemSoftware system
A software system is a system based on software forming part of a computer system . The term "software system" is often used as a synonym of computer program or software; is related to the application of systems theory approaches in software engineering context and are used to study large and...
or system". The focus of SPL development is on the systematic and efficient creation of similar programs. FODA is an analysis devoted to identification of features in a domain to be covered by a particular SPL.
Model
A feature model is a model that defines features and their dependencies, typically in the form of a feature diagram + left-over (a.k.a. cross-tree) constraints. But also it could be as a table of possible combinations.Diagram
A feature diagram is a visual notation of a feature model, which is basically an and-or tree. Other extensions exist: cardinalities, feature cloning, feature attributes, discussed below.Configuration
A feature configuration is a set of features which describes a member of an SPL: the member contains a feature if and only if the feature is in its configuration. A feature configuration is permitted by a feature model if and only if it does not violate constraints imposed by the model.Feature modeling notations
Current feature modeling notations may be divided into three main groups, namely:- Basic feature models
- Cardinality-based feature models
- Extended feature models
Basic feature models
Relationships between a parent feature and its child features (or subfeatures) are categorized as:- Mandatory – child feature is required.
- Optional – child feature is optional.
- Or – at least one of the sub-features must be selected.
- Alternative (xor) – one of the sub-features must be selected
In addition to the parental relationships between features, cross-tree constraints are allowed. The most common are:
- A requires B – The selection of A in a product implies the selection of B.
- A excludes B – A and B cannot be part of the same product.
As an example, the figure below illustrates how feature models can be used to specify and build configurable on-line shopping systems. The software of each application is determined by the features that it provides. The root feature (i.e. E-Shop) identifies the SPL. Every shopping system implements a catalogue, payment modules, security policies and optionally a search tool. E-shops must implement a high or standard security policy (choose one), and can provide different payment modules: bank transfer, credit card or both of them. Additionally, a cross-tree constraint forces shopping systems including the credit card payment module to implement a high security policy.

Cardinality-based feature models
Some authors propose extending basic feature models with UMLUnified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
-like multiplicities of the form [n,m] with n being the lower bound and m the upper bound. These are used to limit the number of sub-features that can be part of a product whenever the parent is selected.
If the upper bound is m the feature can be cloned as many times as we want (as long as the other constraints are respected). This notation is useful for products extensible with an arbitrary number of components.
Extended feature models
Others suggest adding extra-functional information to the features using "attributes". These are mainly composed of a name, a domain, and a value.Semantics
The semantics of a feature model is the set of feature configurations that the feature model permits. The most common approach is to use mathematical logic to capture the semantics of a feature diagram. Each feature corresponds to a boolean variable and the semantics is captured as a propositional formulaPropositional formula
In propositional logic, a propositional formula is a type of syntactic formula which is well formed and has a truth value. If the values of all variables in a propositional formula are given, it determines a unique truth value...
. The satisfying valuations of this formula correspond to the feature configurations permitted by the feature diagram.
For instance, if
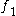 is a mandatory sub-feature of
is a mandatory sub-feature of 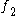 , the formula will contain the constraint
, the formula will contain the constraint  .
.The following table provides a translation of the basic primitives. The semantics of a diagram is a conjunct of the translations of the elements contained in the diagram. We assume that the diagram is a rooted tree.
| Feature Diagram Primitive | Semantics |
|---|---|
 is the root feature is the root feature |
 |
 optional sub-feature of optional sub-feature of 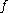 |
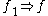 |
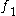 mandatory sub-feature of mandatory sub-feature of 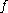 |
 |
 alternative sub-features of alternative sub-features of  |
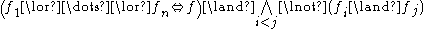 |
 or sub-features of or sub-features of  |
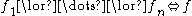 |
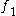 excludes excludes  |
 |
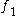 requires requires  |
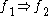 |
Configuring feature models
A product of the SPL is declaratively specified by selecting or deselecting features according to user's preferences. Such decisions must respect the constraints imposed by the feature model. A "configurator" is a tool that assists the user during a configuration process. For instance by automatically selecting or deselecting features that must or must not, respectively, be selected for the configuration to be completed successfully. Current approaches use unit propagationUnit propagation
Unit propagation or the one-literal rule is a procedure of automated theorem proving that can simplify a set of clauses.-Definition:...
and CSP solvers
Constraint satisfaction problem
Constraint satisfaction problems s are mathematical problems defined as a set of objects whose state must satisfy a number of constraints or limitations. CSPs represent the entities in a problem as a homogeneous collection of finite constraints over variables, which is solved by constraint...
.
Properties and analyses
An analysis of a feature model targets certain properties of the model which are important for marketing strategies or technical decisions. A number of analyses are identified in the literature. Typical analyses determine whether a feature model is void (represents no products), whether it contains dead features (features that cannot be part of any product) or what is the number of products of the software product line represented by the model. Other analyses focus on comparing several feature models (e.g. to check whether a model is a specialization or refactoring or generalizationGeneralization
A generalization of a concept is an extension of the concept to less-specific criteria. It is a foundational element of logic and human reasoning. Generalizations posit the existence of a domain or set of elements, as well as one or more common characteristics shared by those elements. As such, it...
of another).
Tools
Some tools supporting the editing and/or analyses of feature models are:- Ahead Tool suite
- Eclipse Modeling Framework Feature Model Project
- FaMa Tool Suite
- Feature Model Plug-in
- Feature Modeling Tool, a plug-in for Visual Studio 2008
- FAMILIAR
- FeatureIDE
- Hydra
- MOSKitt Feature Modeler
- Pure::Variants
- Requiline
- S2T2 Configurator
- SPLOT (Software Product Line Online Tools)
- ToolDAy - Tool for Domain Analysis
- XFeature
- ZIPC Feature
See also
- Domain analysisDomain analysisIn software engineering, domain analysis, or product line analysis, is the process of analyzing related software systems in a domain to find their common and variable parts. It is a model of wider business context for the system. The term was coined in the early 1980s by James Neighbors. Domain...
- Domain engineeringDomain engineeringDomain engineering, also called product line engineering, is the entire process of reusing domain knowledge in the production of new software systems. It is a key concept in systematic software reuse. A key idea in systematic software reuse is the application domain, a software area that contains...
- Feature-oriented Programming - a paradigm for software product line synthesis
- Product Family EngineeringProduct Family EngineeringProduct family engineering , also known as product line engineering, is a synonym for "domain engineering" created by the Software Engineering Institute, a term coined by James Neighbors in his 1980 dissertation at University of California, Irvine...
- Software Product Lines

