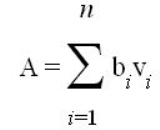
Expectancy-value theory
Encyclopedia
Expectancy-value theory was originally created in order to explain and predict individual's attitudes toward object
s and actions. Originally the work of psychologist
Martin Fishbein, the theory
states that attitudes are developed and modified based on assessments about beliefs and values. Primarily, the theory attempts to determine the mental
calculation
s that take place in attitude development. Expectancy-value theory has been used to develop other theories and is still utilized today in numerous fields of study.
.
(TRA). Later Ajzen posited the theory of planned behavior
(TPB) in his book Attitudes, Personality, and Behavior (1988). Both TRA and TPB address predictive and explanatory weaknesses with EVT and are still prominent theories in areas such as health communication research, marketing, and economics. Although not used as much since the early 1980s, EVT is still utilized in research within fields as diverse as audience research (Palmgreen & Rayburn, 1985) advertising (Shoham, Rose, & Kahle 1998; Smith & Vogt, 1995), child development (Watkinson, Dwyer, & Nielsen, 2005), education (Eklof, 2006; Ping, McBride, & Breune, 2006), health communication (Purvis Cooper, Burgoon, & Roter, 2001; Ludman & Curry, 1999), and organization communication (Westaby, 2002).
Watch videos on expectancy-value theory and more for free
Object
Object may refer to:* Object , a thing, being or concept** Entity, something that is tangible and within the grasp of the senses* As used in object relations theories of psychoanalysis, that to which a subject relates....
s and actions. Originally the work of psychologist
Psychologist
Psychologist is a professional or academic title used by individuals who are either:* Clinical professionals who work with patients in a variety of therapeutic contexts .* Scientists conducting psychological research or teaching psychology in a college...
Martin Fishbein, the theory
Theory
The English word theory was derived from a technical term in Ancient Greek philosophy. The word theoria, , meant "a looking at, viewing, beholding", and referring to contemplation or speculation, as opposed to action...
states that attitudes are developed and modified based on assessments about beliefs and values. Primarily, the theory attempts to determine the mental
Mental
Mental, a word referring to aspects of, or things related to, the mind; or in anatomy, the skull, e.g. the mental foramen, can also mean:* a slang, pejorative term used to describe people who act like lunatics, which is itself an outdated term for people with mental disorders* Mental , a 2009...
calculation
Calculation
A calculation is a deliberate process for transforming one or more inputs into one or more results, with variable change.The term is used in a variety of senses, from the very definite arithmetical calculation of using an algorithm to the vague heuristics of calculating a strategy in a competition...
s that take place in attitude development. Expectancy-value theory has been used to develop other theories and is still utilized today in numerous fields of study.
History
Dr. Martin Fishbein is credited with developing the expectancy-value theory (EVT) in the early to mid-1970s. It is sometimes referred to as Fishbein's expectancy-value theory or simply expectancy-value model. The primary work typically cited by scholars referring to EVT is Martin Fishbein and Icek Ajzen's 1975 book called Belief, Attitude, Intention, and Behavior: An Introduction to Theory and Research. The seed work of EVT can be seen in Fishbein's doctoral dissertation, A Theoretical and Empirical Investigation of the Interrelation between Belief about an Object and the Attitude toward that Object (1961, UCLA) and two subsequent articles in 1962 and 1963 in the journal Human Relations. Fishbein's work drew on the writings of researchers such as Ward Edwards, Milton J. Rosenberg, Edward Tolman, and John B. WatsonJohn B. Watson
John Broadus Watson was an American psychologist who established the psychological school of behaviorism. Watson promoted a change in psychology through his address Psychology as the Behaviorist Views it which was given at Columbia University in 1913...
.
Concepts
EVT has three basic components. First, individuals respond to novel information about an item or action by developing a belief about the item or action. If a belief already exists, it can and most likely will be modified by new information. Second, individuals assign a value to each attribute that a belief is based on. Third, an expectation is created or modified based on the result of a calculation based on beliefs and values. For example, a student finds out that a professor has a reputation for being humorous. The student assigns a positive value to humor in the classroom, so the student has the expectation that their experience with the professor will be positive. When the student attends class and finds the professor humorous, the student calculates that it is a good class. EVT also states that the result of the calculation, often called the “attitude”, stems from complex equations that contain many belief/values pairs. Fishbein and Ajzen (1975) represented the theory with the following equation where attitudes (a) are a factorial function of beliefs (b) and values (v).Current Usage
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Fishbein and Ajzen expanded expectancy-value theory into the theory of reasoned actionTheory of reasoned action
The theory of reasoned action , developed by Martin Fishbein and , derived from previous research that started out as the theory of attitude, which led to the study of attitude and behavior...
(TRA). Later Ajzen posited the theory of planned behavior
Theory of planned behavior
In psychology, the theory of planned behavior is a theory about the link between attitudes and behavior. It was proposed by Icek Ajzen as an extension of the theory of reasoned action. It is one of the most predictive persuasion theories...
(TPB) in his book Attitudes, Personality, and Behavior (1988). Both TRA and TPB address predictive and explanatory weaknesses with EVT and are still prominent theories in areas such as health communication research, marketing, and economics. Although not used as much since the early 1980s, EVT is still utilized in research within fields as diverse as audience research (Palmgreen & Rayburn, 1985) advertising (Shoham, Rose, & Kahle 1998; Smith & Vogt, 1995), child development (Watkinson, Dwyer, & Nielsen, 2005), education (Eklof, 2006; Ping, McBride, & Breune, 2006), health communication (Purvis Cooper, Burgoon, & Roter, 2001; Ludman & Curry, 1999), and organization communication (Westaby, 2002).
External links
Watch videos on expectancy-value theory and more for free

