Ethernet Powerlink
Encyclopedia
Ethernet Powerlink is a deterministic
real-time protocol for standard Ethernet
. It is an open protocol managed by the Ethernet POWERLINK Standardization Group (EPSG). It was introduced by Austrian automation company B&R
in 2001.
This protocol has nothing to do with power distribution via Ethernet cabling or power over Ethernet
(PoE), power line communication
or Bang & Olufsens PowerLink cable.
Modern implementations reach cycle-times of under 200 µs and a time-precision (jitter
) of less than 1 µs.
Working groups focus on tasks like safety, technology, marketing, certification and end users. The EPSG cooperates with standardization bodies and associations, like the CAN in Automation (CiA
) Group and the IEC.
(IEEE 802.3). Since the end of 2006, Ethernet Powerlink with Gigabit Ethernet
supported a transmission rate ten times higher (1,000 Mbit/s) usng somewhat better cable (Cat6). Higher speeds are possible in theory since with standard modules and FPGAs.
Repeating hubs instead of switches within the Real-time domain is recommended to minimise delay and jitter. Ethernet Powerlink uses IAONA's Industrial Ethernet Planning and Installation Guide for clean cabling of industrial networks and both industrial Ethernet connectors 8P8C (commonly known as RJ45) and M1 are accepted.
/CD mechanism of non-switched Ethernet, which caused non-deterministic Ethernet behaviour, is avoided by the Ethernet Powerlink scheduling mechanism.
The basic cycle consists of the following phases:
The time frame which includes Preq-n and Pres-n is called time slot for the addressed node.
The quality of the Real-Time behaviour depends on the precision of the overall basic cycle time. The length of individual phases can vary as long as the total of all phases remain within the basic cycle time boundaries. Adherence to the basic cycle time is monitored by the Managing Node. The duration of the isochronous and the asynchronous phase can be configured.
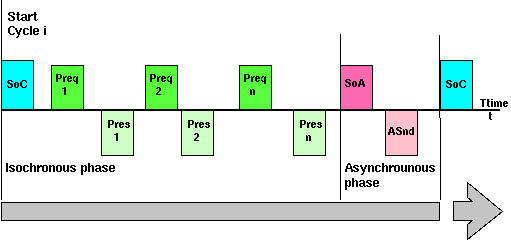
Picture 1: Frames above the time line are sent by the MN, below the time line by different CNs.
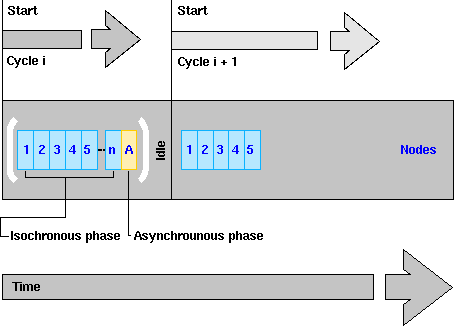
Picture 2: Time slots for nodes and the asynchronous time slot
Multiplex for Bandwidth Optimization
In addition to transferring isochronous data during each basic cycle, some nodes are also able to share transfer slots for better bandwidth utilization. For that reason, the isochronous phase can distinguish between transfer slots dedicated to particular nodes, which have to send their data in every basic cycle, and slots shared by nodes to transfer their data one after the other in different cycles. Therefore less important yet still time-critical data can be transferred in longer cycles than the basic cycle. Assigning the slots during each cycle is at the discretion of the Managing Node.
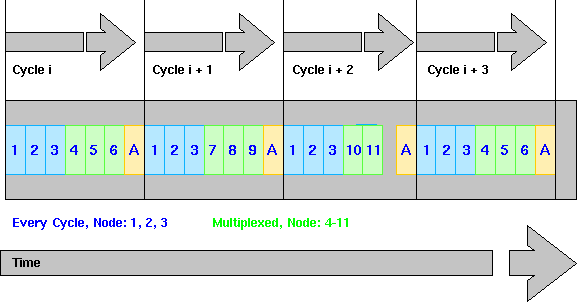
Picture 3: Time slots in EPL multiplexed mode.
. The protocol fulfills the requirements of SIL
3. Error detection techniques have no impact on existing transport layers.
Deterministic algorithm
In computer science, a deterministic algorithm is an algorithm which, in informal terms, behaves predictably. Given a particular input, it will always produce the same output, and the underlying machine will always pass through the same sequence of states...
real-time protocol for standard Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
. It is an open protocol managed by the Ethernet POWERLINK Standardization Group (EPSG). It was introduced by Austrian automation company B&R
B&R
B&R is an Austrian company founded as a Ges.m.b.H in 1979 by Erwin Bernecker and Josef Rainer. Bernecker + Rainer Industrie-Elektronik Ges.m.b.H., with development and production headquarters in Eggelsberg , is currently one of the largest private companies in the field of automation and process...
in 2001.
This protocol has nothing to do with power distribution via Ethernet cabling or power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet or PoE technology describes a system to pass electrical power safely, along with data, on Ethernet cabling. The IEEE standard for PoE requires category 5 cable or higher for high power levels, but can operate with category 3 cable for low power levels...
(PoE), power line communication
Power line communication
Power line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
or Bang & Olufsens PowerLink cable.
Overview
Ethernet Powerlink expands Ethernet with a mixed polling and timeslicing mechanism. This:- Guaranteed transfer of time-critical data in very short isochronic cycles with configurable response time
- Time-synchronisation of all nodes in the network with very high precision of sub-microseconds
- Transmission of less timecritical data in a reserved asynchronous channel
Modern implementations reach cycle-times of under 200 µs and a time-precision (jitter
Jitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
) of less than 1 µs.
Standardization
Powerlink was standardized by the Ethernet Powerlink Standardization Group (EPSG), founded in June 2003 as an independent association.Working groups focus on tasks like safety, technology, marketing, certification and end users. The EPSG cooperates with standardization bodies and associations, like the CAN in Automation (CiA
CAN in Automation
CAN in Automation is the international users' and manufacturers' organization that develops and supports CAN-based higher-layer protocols....
) Group and the IEC.
Physical layer
The original physical layer specified was 100Base-X Fast EthernetFast Ethernet
In computer networking, Fast Ethernet is a collective term for a number of Ethernet standards that carry traffic at the nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s, against the original Ethernet speed of 10 Mbit/s. Of the fast Ethernet standards 100BASE-TX is by far the most common and is supported by the...
(IEEE 802.3). Since the end of 2006, Ethernet Powerlink with Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a term describing various technologies for transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second , as defined by the IEEE 802.3-2008 standard. It came into use beginning in 1999, gradually supplanting Fast Ethernet in wired local networks where it performed...
supported a transmission rate ten times higher (1,000 Mbit/s) usng somewhat better cable (Cat6). Higher speeds are possible in theory since with standard modules and FPGAs.
Repeating hubs instead of switches within the Real-time domain is recommended to minimise delay and jitter. Ethernet Powerlink uses IAONA's Industrial Ethernet Planning and Installation Guide for clean cabling of industrial networks and both industrial Ethernet connectors 8P8C (commonly known as RJ45) and M1 are accepted.
Data Link Layer
The standard Ethernet Data Link Layer is extended by an additional bus scheduling mechanism which secures that at a time only one node is accessing the network. The schedule is divided into an isochronous phase and an asynchronous phase. During the isochronous phase, time-critical data is transferred, while the asynchronous phase provides bandwidth for the transmission of non time-critical data. The Managing Node (MN) grants access to the physical medium via dedicated poll request messages. As a result, only one single node (CN) has access to the network at a time, which avoids collisions, present on older Ethernet hubs before switches. The CSMACarrier Sense Multiple Access
Carrier Sense Multiple Access is a probabilistic Media Access Control protocol in which a node verifies the absence of other traffic before transmitting on a shared transmission medium, such as an electrical bus, or a band of the electromagnetic spectrum."Carrier Sense" describes the fact that a...
/CD mechanism of non-switched Ethernet, which caused non-deterministic Ethernet behaviour, is avoided by the Ethernet Powerlink scheduling mechanism.
Basic Cycle
After system start-up is finished, the Real-Time domain is operating under Real-Time conditions. The scheduling of the basic cycle is controlled by the Managing Node (MN). The overall cycle time depends on the amount of isochronous data, asynchronous data and the number of nodes to be polled during each cycle.The basic cycle consists of the following phases:
- Start Phase: The Managing Node is sending out a synchronization message to all nodes. The frame is called SoC - Start of Cycle.
- Isochronous Phase: The Managing Node calls each node to transfer time-critical data for process or motion control by sending the Preq - Poll Request - frame. The addressed node answers with the Pres - Poll Response - frame. Since all other nodes are listening to all data during this phase, the communication system provides a producer-consumer relationship.
The time frame which includes Preq-n and Pres-n is called time slot for the addressed node.
- Asynchronous Phase: The Managing Node grants the right to one particular node for sending ad-hoc data by sending out the SoA - Start of Asynchronous - frame. The addressed node will answer with ASnd. Standard IP-based protocols and addressing can be used during this phase.
The quality of the Real-Time behaviour depends on the precision of the overall basic cycle time. The length of individual phases can vary as long as the total of all phases remain within the basic cycle time boundaries. Adherence to the basic cycle time is monitored by the Managing Node. The duration of the isochronous and the asynchronous phase can be configured.

Picture 1: Frames above the time line are sent by the MN, below the time line by different CNs.

Picture 2: Time slots for nodes and the asynchronous time slot
Multiplex for Bandwidth Optimization
In addition to transferring isochronous data during each basic cycle, some nodes are also able to share transfer slots for better bandwidth utilization. For that reason, the isochronous phase can distinguish between transfer slots dedicated to particular nodes, which have to send their data in every basic cycle, and slots shared by nodes to transfer their data one after the other in different cycles. Therefore less important yet still time-critical data can be transferred in longer cycles than the basic cycle. Assigning the slots during each cycle is at the discretion of the Managing Node.

Picture 3: Time slots in EPL multiplexed mode.
Ethernet Powerlink Safety
Today, machines, plants and safety systems are stuck in a rigid scheme made up of hardware-based safety functions. The consequences of this are cost-intensive cabling and limited diagnostic options. The solution is the integration of safety relevant application data into the standard serial control protocol. Ethernet Powerlink Safety (EPLsafety). EPLsafety allows both publish/subscriber and client/server communication. Safety relevant data is transmitted via an embedded data frame inside of standard communication messages. Measures to avoid any undetected failures due to systematic or stochastic errors are an integral part of the security protocol. EPLsafety is in conformance with IEC 61508IEC 61508
IEC 61508 is an international standard of rules applied in industry. It is titled "Functional Safety of Electrical/Electronic/Programmable Electronic Safety-related Systems"....
. The protocol fulfills the requirements of SIL
Safety Integrity Level
Safety Integrity Level is defined as a relative level of risk-reduction provided by a safety function, or to specify a target level of risk reduction. In simple terms, SIL is a measurement of performance required for a Safety Instrumented Function ....
3. Error detection techniques have no impact on existing transport layers.

