Distributed Antenna System
Encyclopedia
Concept
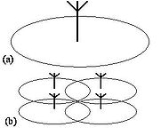
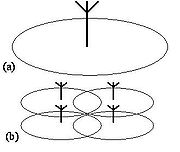
As illustrated in the figure, the idea is to split the transmitted power among several antennaAntenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
elements, separated in space so as to provide coverage over the same area as a single antenna but with reduced total power and improved reliability. A single antenna radiating at high power (a) is replaced by a group of low-power antennas to cover the same area (b). The idea was described in a paper by Saleh et al. in 1987. These antennas have recently been employed by several service providers in many areas around the United States. It should be noted that these antenna must be installed at 200 m from any public building
The idea works because less power is wasted in overcoming penetration and shadowing losses, and because a line-of-sight
Line-of-sight propagation
Line-of-sight propagation refers to electro-magnetic radiation or acoustic wave propagation. Electromagnetic transmission includes light emissions traveling in a straight line...
channel is present more frequently, leading to reduced fade depths
Fading
In wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
and reduced delay spread.
A distributed antenna system can be implemented using passive splitter
DSL filter
A DSL filter is an analog low-pass filter installed between analog devices and a plain old telephone service telephone line, in order to prevent interference between such devices and a digital subscriber line service operating on the same line...
s and feeders, or active repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
amplifier
Amplifier
Generally, an amplifier or simply amp, is a device for increasing the power of a signal.In popular use, the term usually describes an electronic amplifier, in which the input "signal" is usually a voltage or a current. In audio applications, amplifiers drive the loudspeakers used in PA systems to...
s can be included to overcome the feeder losses. In systems where equalization is applied, it may be desirable to introduce delays between the antenna elements. This artificially increases delay spread in areas of overlapped coverage, permitting quality improvements via time diversity.
If a given area is covered by many distributed antenna elements rather than a single antenna, then the total radiated power is reduced by approximately a factor N1–n/2 and the power per antenna is reduced by a factor Nn/2 where a simple power law
Power law
A power law is a special kind of mathematical relationship between two quantities. When the frequency of an event varies as a power of some attribute of that event , the frequency is said to follow a power law. For instance, the number of cities having a certain population size is found to vary...
path loss model with path loss exponent n is assumed. As an alternative, the total area covered could be extended for a given limit of effective radiated power, which may be important to ensure compliance with safety limits on radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
into the human body.

