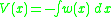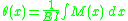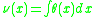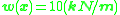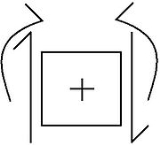
Direct integration of a beam
Encyclopedia
Direct integration is a structural analysis
method for measuring internal shear, internal moment, rotation, and deflection of a beam.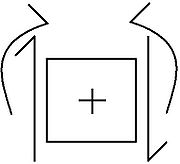 For a beam with an applied weight
For a beam with an applied weight 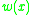 , taking downward to be positive, the internal shear force is given by taking the negative integral of the weight:
, taking downward to be positive, the internal shear force is given by taking the negative integral of the weight:
The internal moment M(x) is the integral of the internal shear:
The angle of rotation
from the horizontal,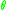 , is the integral of the internal moment divided by the product of the Young's modulus
, is the integral of the internal moment divided by the product of the Young's modulus
and the area moment of inertia
:
Integrating the angle of rotation obtains the vertical displacement :
:
shown at right supported by a fixed pin at the left and a roller at the right. There are no applied moments, the weight is a constant 10 kN, and - due to symmetry - each support applies a 75 kN vertical force to the beam. Taking x as the distance from the pin,
Integrating
,
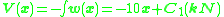
where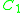 represents the applied loads. For these calculations, the only load having an effect on the beam is the 75 kN load applied by the pin, applied at x=0, giving
represents the applied loads. For these calculations, the only load having an effect on the beam is the 75 kN load applied by the pin, applied at x=0, giving
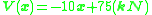
Integrating the internal shear,
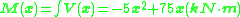 where, because there is no applied moment,
where, because there is no applied moment, 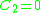 .
.
Assuming a EI value of 1 kN m
m m (for simplicity, real E
m (for simplicity, real E
I
values for structural members such as steel
are normally greater by powers of ten)
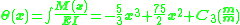 * and
* and
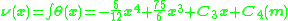
Because of the vertical supports at each end of the beam, the displacement ( ) at x = 0 and x = 15m is zero. Substituting (x = 0, v(0) = 0) and (x = 15m, v(15m) = 0) , we can solve for constants
) at x = 0 and x = 15m is zero. Substituting (x = 0, v(0) = 0) and (x = 15m, v(15m) = 0) , we can solve for constants 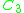 =-1406.25 and
=-1406.25 and 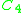 =0, yielding
=0, yielding
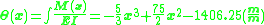 and
and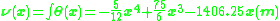
For the given EI value, the maximum displacement, at x=7.5m, is approximately 500 times the length of the beam. For a more realistic situation, such as a uniform load of 1kN and an EI value of 5,000 kN per square meter, the displacement would be approximately 1 cm.
Structural analysis
Structural analysis is the determination of the effects of loads on physical structures and their components. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, vehicles, machinery, furniture, attire, soil strata, prostheses and...
method for measuring internal shear, internal moment, rotation, and deflection of a beam.

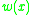 , taking downward to be positive, the internal shear force is given by taking the negative integral of the weight:
, taking downward to be positive, the internal shear force is given by taking the negative integral of the weight:
The internal moment M(x) is the integral of the internal shear:
-
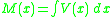 =
= 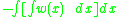
The angle of rotation
Angle of rotation
In mathematics, the angle of rotation is a measurement of the amount, the angle, that a figure is rotated about a fixed point, often the center of a circle....
from the horizontal,
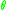 , is the integral of the internal moment divided by the product of the Young's modulus
, is the integral of the internal moment divided by the product of the Young's modulusYoung's modulus
Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and is a quantity used to characterize materials. It is defined as the ratio of the uniaxial stress over the uniaxial strain in the range of stress in which Hooke's Law holds. In solid mechanics, the slope of the stress-strain...
and the area moment of inertia
Second moment of area
The second moment of area, also known as the area moment of inertia, moment of inertia of plane area, or second moment of inertia is a property of a cross section that can be used to predict the resistance of beams to bending and deflection, around an axis that lies in the cross-sectional plane...
:
Integrating the angle of rotation obtains the vertical displacement
 :
:
Integrating
It must be noted that each time an integration is carried out, a constant of integration needs to be obtained. These constants are determined by using either the forces at supports, or at free ends.- For internal shear and moment, the constants can be found by analyzing the beam's free body diagramFree body diagramA free body diagram, also called a force diagram, is a pictorial representation often used by physicists and engineers to analyze the forces acting on a body of interest. A free body diagram shows all forces of all types acting on this body. Drawing such a diagram can aid in solving for the unknown...
.
- For rotation and displacement, the constants are found using conditions dependent on the type of supports. For a cantilever beam, the fixed support has zero rotation and zero displacement. For a beam supported by a pin and roller, both the supports have zero displacement.
Sample calculations
Take the beamBeam (structure)
A beam is a horizontal structural element that is capable of withstanding load primarily by resisting bending. The bending force induced into the material of the beam as a result of the external loads, own weight, span and external reactions to these loads is called a bending moment.- Overview...
shown at right supported by a fixed pin at the left and a roller at the right. There are no applied moments, the weight is a constant 10 kN, and - due to symmetry - each support applies a 75 kN vertical force to the beam. Taking x as the distance from the pin,
Integrating
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
,
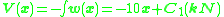
where
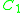 represents the applied loads. For these calculations, the only load having an effect on the beam is the 75 kN load applied by the pin, applied at x=0, giving
represents the applied loads. For these calculations, the only load having an effect on the beam is the 75 kN load applied by the pin, applied at x=0, giving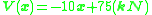
Integrating the internal shear,
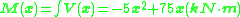 where, because there is no applied moment,
where, because there is no applied moment, 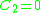 .
.Assuming a EI value of 1 kN
 m
m m (for simplicity, real E
m (for simplicity, real EYoung's modulus
Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and is a quantity used to characterize materials. It is defined as the ratio of the uniaxial stress over the uniaxial strain in the range of stress in which Hooke's Law holds. In solid mechanics, the slope of the stress-strain...
I
Second moment of area
The second moment of area, also known as the area moment of inertia, moment of inertia of plane area, or second moment of inertia is a property of a cross section that can be used to predict the resistance of beams to bending and deflection, around an axis that lies in the cross-sectional plane...
values for structural members such as steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
are normally greater by powers of ten)
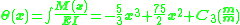 * and
* and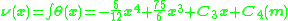
Because of the vertical supports at each end of the beam, the displacement (
 ) at x = 0 and x = 15m is zero. Substituting (x = 0, v(0) = 0) and (x = 15m, v(15m) = 0) , we can solve for constants
) at x = 0 and x = 15m is zero. Substituting (x = 0, v(0) = 0) and (x = 15m, v(15m) = 0) , we can solve for constants 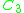 =-1406.25 and
=-1406.25 and 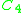 =0, yielding
=0, yielding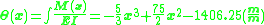 and
and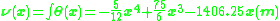
For the given EI value, the maximum displacement, at x=7.5m, is approximately 500 times the length of the beam. For a more realistic situation, such as a uniform load of 1kN and an EI value of 5,000 kN per square meter, the displacement would be approximately 1 cm.
- Note that for the rotation
 the units are meters divided by meters (or any other units of length which reduce to unity). This is because rotation is given as a slopeSlopeIn mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
the units are meters divided by meters (or any other units of length which reduce to unity). This is because rotation is given as a slopeSlopeIn mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
, the vertical displacement divided by the horizontal change.