
Die deterioration doubling
Encyclopedia
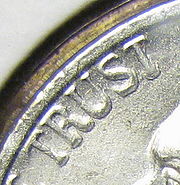
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
coins
COinS
ContextObjects in Spans, commonly abbreviated COinS, is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The...
that results from degradation
Elegant degradation
Elegant degradation is a term used in engineering to describe what occurs to machines which are subject to constant, repetitive stress.Externally, such a machine maintains the same appearance to the user, appearing to function properly. Internally, the machine slowly weakens over time. Eventually,...
of the die used to strike the coin.
Due to a combination of improper preparation and treatment of the die
Die (manufacturing)
A die is a specialized tool used in manufacturing industries to cut or shape material using a press. Like molds, dies are generally customized to the item they are used to create...
s, excessive wear, and overuse, die deterioration doubling has occurred on nearly every series issued by the US mint
Mint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins for currency.The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. One difference is that the history of the mint is usually closely tied to the political situation of an era...
in recent times. Certain coins are more susceptible to it than others, due to various factors, but it does occur on most series of coins.
Annealing Errors
During the annealingAnnealing (metallurgy)
Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
process of die making, two main errors can occur, resulting in less than perfect dies. It is impossible to tell without expensive and lengthy tests whether these errors occurred, but they will lead to significantly weaker dies and a higher tendency to deteriorate quickly. The first thing which can happen to a die in this process what metallurgists
Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their intermetallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are called alloys. It is also the technology of metals: the way in which science is applied to their practical use...
call decarburization
Decarburization
Decarburization is the process opposite to carburization, namely aimed at decreasing the content of carbon in metals . Decarburization occurs when Carbon in the metal reacts with gasses present in the atmosphere...
. Decarburization is the result of an improper mix of metals and chemicals in the annealing furnace where the dies are sent to soften. If there is not enough ambient carbon in the furnace, the steel will give up some of its carbon and will become soft. The result is a thin surface of inadequate metal whose chemical composition has been altered and is below standard.
Another less obvious error can also occur when heating the dies. After being taken out of the annealing furnace, the dies must cool for 24 to 36 hours. They are usually given an oil bath to cool them more quickly, but the dies must still cool for a period of several hours. When the dies are cooling, if they are not stored properly or not allowed to fully cool before being used, the result is a much softer die. When the die is subjected to the hubbing
Hubbing
Hubbing is a metalworking process that is used to make dies. It is a cold-working process, which means that it occurs well below the melting temperature of the metal being worked.-Process:...
press again and work hardened again, it will be softer and more susceptible to wear. If the die is softer because it was not fully cooled, it will not harden to the same standard as a die which has received proper treatment. However, there will not be a noticeable difference between a good die and a bad die; the change in the structure of the die does is not apparent until it is used for a period of time.
Overuse of Dies
In modern presses, a die strikes approximately 120 coins a minute. This is a large amount of coins produced in a short time, and obviously the die cannot last forever. However, the process of wearing the die is only hastened by the metals used in coins. NickelNickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
, one of the main metals used in today’s coins, is quite hard and causes wear quickly. Copper has been used for centuries because of its malleability and the ease with which it makes coins. However, it too wears the dies when they are used for too long. An infamous example is the 1955 "poorman’s double die." This coin is sold as a replacement for the 1955 doubled die cent
1955 doubled die cent
The 1955 doubled die cent is a die variety that occurred during production of the one cent coin at the United States Mint in 1955. This variety is often mistakenly referred to as an error...
, but it is no more than Die Deterioration Doubling, caused by wear on the dies.
When a coin is struck, the planchet
Planchet
A planchet is a round metal disk that is ready to be struck as a coin. An older word for planchet is flan. They are also referred to as blanks.-History:The preparation of the flan or planchet has varied over the years...
is not heated. Although the planchet would be softer and more malleable, the extra time and expense would prove too great for the Mint. The planchet is therefore struck at room temperature, and the only thing which makes the coin form is the tremendous pressure used to strike it. With a metal such as nickel, which is harder than a normal coin metal like silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
, gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
or copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
, the pressure must be greater. When a nickel coin, or any coin, is struck, the metal must "flow" into the contours of the front and back dies. It is through the atoms of the metal flowing into the dies that flow lines are created. However, when metal flows over a sharp corner in the die, like the edges of a mintmark or words, it tends to roll the detail out. It wears on the die, and a little detail is lost with every strike. Die Deterioration Doubling is most prevalent on the date and mintmark because these fine details are alone in the middle of the field, and the metal must flow into these without the help of other valleys nearby. When the metal rolls into the mintmark or date, it wears away the corner of the die, and after long enough will appear on the coin as Die Deterioration Doubling.
In addition, the mint has a practice of polishing the dies and using them longer. When a die begins to show evidence of wear, a mint technician will polish the die and reuse it. However, the die is still rapidly deteriorating, and polishing it cannot avoid the problem of wear. So, after many thousand coins in rapid succession, the wear on the die has gotten so bad that it appears as Die Deterioration Doubling.
Identification
Die deterioration doubling is a result of a few simple causes, but it can be difficult to positively identify. There are a number of different features which appear similar, but the characteristic traits of each are easy to identify with practice. Die deterioration doubling is often mistaken for hub doubling. The causes of the two types of doubling are different, but their appearance on the finished coin is often similar. Die deterioration doubling appears most often around the mintmark and date because they are alone in the field. When it occurs in other features, like an image of a bustBust (sculpture)
A bust is a sculpted or cast representation of the upper part of the human figure, depicting a person's head and neck, as well as a variable portion of the chest and shoulders. The piece is normally supported by a plinth. These forms recreate the likeness of an individual...
, it looks more like a weak strike than doubling.
Close examination of affected features show that the doubling is extremely irregular. This is because the coin metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
does not flow from just one direction, but flows and produces wear on the die from all sides. There is no definite shape, and it can take on several different but similar appearances. It often looks like a thin metal shelf or spreading spot. It can also make lettering appear thick and twisted. There are no crisp lines affected, but things generally look bloated, enlarged, blurry, twisted, and damaged. This is different from hub doubling, because hub doubling appears as a crisp secondary image, rotated minutely from the original. When casually glancing at a coin, the difference is not easy to tell, but when magnified
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
, the difference is obvious on most coins. Another easy way to tell hub doubling from die deterioration doubling is the presence of notched serif
Serif
In typography, serifs are semi-structural details on the ends of some of the strokes that make up letters and symbols. A typeface with serifs is called a serif typeface . A typeface without serifs is called sans serif or sans-serif, from the French sans, meaning “without”...
s; the small flairs on the ends of letters will appear distinctly separated with the former, whereas they appear just blurry and washed out with the latter.
Types of die deterioration doubling
There really are two different kinds of DDD: Inside and Outside Abraded Die Doubling. This is because Die Deterioration Doubling manifests itself in two different ways. The two classes look different, and are caused by wear in two different places. Inside Abraded Die Doubling is caused by wear around the edges and inside the actual detail affected. It appears as an enlarged, irregular outline of the element overlapping the original design element. Outside Abraded Die Doubling is caused by actual wear in the field of the die. The field of a die is the highest point, so when a mint technician polishes the die or the metal flow of a coin wears it away, the field is the first thing to be worn down. The difference here is that Outside doubling does not overlap any of the original design, but rather appears like an irregular shelf around the object.Numismatic Interest
Many beginning numismatistsNumismatics
Numismatics is the study or collection of currency, including coins, tokens, paper money, and related objects. While numismatists are often characterized as students or collectors of coins, the discipline also includes the broader study of money and other payment media used to resolve debts and the...
buy coins thinking they are very valuable, but really are not worth more than a little over face value
Face value
The Face value is the value of a coin, stamp or paper money, as printed on the coin, stamp or bill itself by the minting authority. While the face value usually refers to the true value of the coin, stamp or bill in question it can sometimes be largely symbolic, as is often the case with bullion...
due to a die deterioration doubling. This common error fools a number of people into believing that it is a much rarer, and more valuable, form of doubling. It goes by a number of names, such as the "poorman’s double die."
Jefferson nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
s and Lincoln cent
Cent (currency)
In many national currencies, the cent is a monetary unit that equals 1⁄100 of the basic monetary unit. Etymologically, the word cent derives from the Latin word "centum" meaning hundred. Cent also refers to a coin which is worth one cent....
s especially exhibit a large number of affected coins, throughout the entire history of the coin. The 1955 "poorman’s double die" is actually outside abraded die doubling, and a high percentage of 1999 coins exhibit this error. Because of the large numbers of these coins in circulation, they are not worth more than a few cents over normal value. Nevertheless, die deterioration doubling can deceive the beginning numismatist with the high hopes of discovering a new variety and making a fortune.

