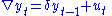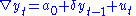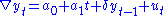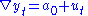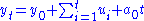Dickey-Fuller test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the Dickey–Fuller test tests whether a unit root
is present in an autoregressive model. It is named after the statistician
s D. A. Dickey
and W. A. Fuller
, who developed the test in 1979.
where yt is the variable of interest, t is the time index, ρ is a coefficient, and ut is the error
term. A unit root is present if ρ = 1. The model would be non-stationary in this case.
The regression model can be written as
where ∇ is the first difference operator
. This model can be estimated and testing for a unit root is equivalent to testing δ = 0 (where δ = ρ − 1). Since the test is done over the residual term rather than raw data, it is not possible to use standard t-distribution to provide critical values. Therefore this statistic
τ has a specific distribution
simply known as the Dickey–Fuller table.
There are three main versions of the test:
1. Test for a unit root:
2. Test for a unit root with drift:
3. Test for a unit root with drift and deterministic time trend:
Each version of the test has its own critical value which depends on the size of the sample. In each case, the null hypothesis
is that there is a unit root, δ = 0. The tests have low statistical power
in that they often cannot distinguish between true unit-root processes (δ = 0)and near unit-root processes (δ is close to zero). This is called the "near observation equivalence" problem.
The intuition behind the test is as follows. If the series y is stationary
(or trend stationary), then it has a tendency to return to a constant (or deterministically trending) mean. Therefore large values will tend to be followed by smaller values (negative changes), and small values by larger values (positive changes). Accordingly, the level of the series will be a significant predictor of next period's change, and will have a negative coefficient. If, on the other hand, the series is integrated, then positive changes and negative changes will occur with probabilities that do not depend on the current level of the series; in a random walk
, where you are now does not affect which way you will go next.
It is notable that
may be rewritten as
with a deterministic trend coming from and a stochastic intercept term coming from
and a stochastic intercept term coming from  , resulting in what is referred to as a stochastic trend.
, resulting in what is referred to as a stochastic trend.
There is also an extension of the Dickey–Fuller (DF) test called the augmented Dickey-Fuller test
(ADF), which removes all the structural effects (autocorrelation) in the time series and then tests using the same procedure.
 term estimated, then the power of the unit root test can be substantially reduced as a trend may be captured through the random-walk with drift model. On the other hand, inappropriate inclusion of the intercept or time trend term reduces the power of the unit root test, and sometimes that reduced power can be substantial.
term estimated, then the power of the unit root test can be substantially reduced as a trend may be captured through the random-walk with drift model. On the other hand, inappropriate inclusion of the intercept or time trend term reduces the power of the unit root test, and sometimes that reduced power can be substantial.
Use of prior knowledge about whether the intercept and deterministic time trend should be included is of course ideal but not always possible. When such prior knowledge is unavailable, various testing strategies (series of ordered tests) have been suggested, e.g. by Dolado, Jenkinson, and Sosvilla-Rivero (1990) and by Enders (2004), often with the ADF extension to remove autocorrelation. Elder and Kennedy (2001) present a simple testing strategy that avoids double and triple testing for the unit root that can occur with other testing strategies, and discusses how to use prior knowledge about the existence or not of long-run growth (or shrinkage) in y. Hacker and Hatemi-J (2010) provide simulation results on these matters, including simulations covering the Enders (2004) and Elder and Kennedy (2001) unit-root testing strategies. Simulation results are presented in Hacker (2010) which indicate that using an information criterion
such as the Schwarz information criterion may be useful in determining unit root and trend status within a Dickey-Fuller framework.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Dickey–Fuller test tests whether a unit root
Unit root
In time series models in econometrics , a unit root is a feature of processes that evolve through time that can cause problems in statistical inference if it is not adequately dealt with....
is present in an autoregressive model. It is named after the statistician
Statistician
A statistician is someone who works with theoretical or applied statistics. The profession exists in both the private and public sectors. The core of that work is to measure, interpret, and describe the world and human activity patterns within it...
s D. A. Dickey
D. A. Dickey
David Alan Dickey is an American statistician who has specialised in time series analysis. He is a William Neal Reynolds Professor in the Department of Statistics at North Carolina State University. The Dickey–Fuller test is named for him and Wayne Arthur Fuller.David Dickey is listed as a ISI...
and W. A. Fuller
Wayne Arthur Fuller
Wayne Arthur Fuller is a prominent American statistician who has specialised in econometrics, survey sampling and time series analysis. He was on the staff of Iowa State University from 1959 , becoming a Distinguished Professor in 1983....
, who developed the test in 1979.
Explanation
A simple AR(1) model iswhere yt is the variable of interest, t is the time index, ρ is a coefficient, and ut is the error
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
term. A unit root is present if ρ = 1. The model would be non-stationary in this case.
The regression model can be written as
where ∇ is the first difference operator
Finite difference
A finite difference is a mathematical expression of the form f − f. If a finite difference is divided by b − a, one gets a difference quotient...
. This model can be estimated and testing for a unit root is equivalent to testing δ = 0 (where δ = ρ − 1). Since the test is done over the residual term rather than raw data, it is not possible to use standard t-distribution to provide critical values. Therefore this statistic
Statistic
A statistic is a single measure of some attribute of a sample . It is calculated by applying a function to the values of the items comprising the sample which are known together as a set of data.More formally, statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function...
τ has a specific distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
simply known as the Dickey–Fuller table.
There are three main versions of the test:
1. Test for a unit root:
2. Test for a unit root with drift:
3. Test for a unit root with drift and deterministic time trend:
Each version of the test has its own critical value which depends on the size of the sample. In each case, the null hypothesis
Null hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
is that there is a unit root, δ = 0. The tests have low statistical power
Statistical power
The power of a statistical test is the probability that the test will reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is actually false . The power is in general a function of the possible distributions, often determined by a parameter, under the alternative hypothesis...
in that they often cannot distinguish between true unit-root processes (δ = 0)and near unit-root processes (δ is close to zero). This is called the "near observation equivalence" problem.
The intuition behind the test is as follows. If the series y is stationary
Stationary process
In the mathematical sciences, a stationary process is a stochastic process whose joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time or space...
(or trend stationary), then it has a tendency to return to a constant (or deterministically trending) mean. Therefore large values will tend to be followed by smaller values (negative changes), and small values by larger values (positive changes). Accordingly, the level of the series will be a significant predictor of next period's change, and will have a negative coefficient. If, on the other hand, the series is integrated, then positive changes and negative changes will occur with probabilities that do not depend on the current level of the series; in a random walk
Random walk
A random walk, sometimes denoted RW, is a mathematical formalisation of a trajectory that consists of taking successive random steps. For example, the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas, the search path of a foraging animal, the price of a fluctuating stock and the...
, where you are now does not affect which way you will go next.
It is notable that
may be rewritten as
with a deterministic trend coming from
 and a stochastic intercept term coming from
and a stochastic intercept term coming from  , resulting in what is referred to as a stochastic trend.
, resulting in what is referred to as a stochastic trend.There is also an extension of the Dickey–Fuller (DF) test called the augmented Dickey-Fuller test
Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
In statistics and econometrics, an augmented Dickey–Fuller test is a test for a unit root in a time series sample. It is an augmented version of the Dickey–Fuller test for a larger and more complicated set of time series models....
(ADF), which removes all the structural effects (autocorrelation) in the time series and then tests using the same procedure.
Dealing with uncertainty about including the intercept and deterministic time trend terms
Which of the three main versions of the test should be used is not a minor issue. The decision is important for the size of the unit root test (the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis of a unit root when there is one) and the power of the unit root test (the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis of a unit root when there is not one). Inappropriate exclusion of the intercept or deterministic time trend term leads to bias in the coefficient estimate for δ, leading to the actual size for the unit root test not matching the reported one. If the time trend term is inappropriately excluded with the term estimated, then the power of the unit root test can be substantially reduced as a trend may be captured through the random-walk with drift model. On the other hand, inappropriate inclusion of the intercept or time trend term reduces the power of the unit root test, and sometimes that reduced power can be substantial.
term estimated, then the power of the unit root test can be substantially reduced as a trend may be captured through the random-walk with drift model. On the other hand, inappropriate inclusion of the intercept or time trend term reduces the power of the unit root test, and sometimes that reduced power can be substantial.Use of prior knowledge about whether the intercept and deterministic time trend should be included is of course ideal but not always possible. When such prior knowledge is unavailable, various testing strategies (series of ordered tests) have been suggested, e.g. by Dolado, Jenkinson, and Sosvilla-Rivero (1990) and by Enders (2004), often with the ADF extension to remove autocorrelation. Elder and Kennedy (2001) present a simple testing strategy that avoids double and triple testing for the unit root that can occur with other testing strategies, and discusses how to use prior knowledge about the existence or not of long-run growth (or shrinkage) in y. Hacker and Hatemi-J (2010) provide simulation results on these matters, including simulations covering the Enders (2004) and Elder and Kennedy (2001) unit-root testing strategies. Simulation results are presented in Hacker (2010) which indicate that using an information criterion
Information criterion
-Statistics:* Akaike information criterion , a measure of the goodness fit of an estimated statistical model* Bayesian information criterion , also known as the Schwarz information criterion, a statistical criterion for model selection...
such as the Schwarz information criterion may be useful in determining unit root and trend status within a Dickey-Fuller framework.
External links
- Statistical tables for unit-root tests – Dickey–Fuller table
- How to do a "Regular" Dickey-Fuller Test Using Excel