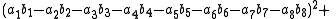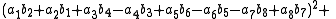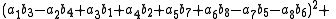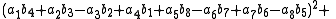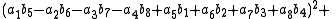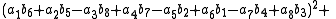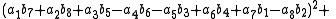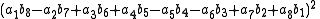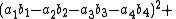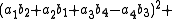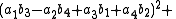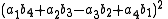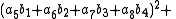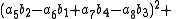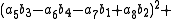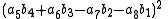Degen's eight-square identity
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, Degen's eight-square identity establishes that the product of two numbers, each of which being a sum of eight squares, is itself a sum of eight squares. Namely:
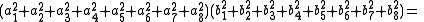
First discovered by Ferdinand Degen around 1818, the identity was independently rediscovered by John Thomas Graves
(1843) and Arthur Cayley
(1845). The latter two derived it while working on an extension of quaternion
s called octonion
s. In algebraic terms
the identity means that the norm
of product of two octonions equals the product of their norms: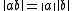 . Similar statements are true for quaternions (Euler's four-square identity
. Similar statements are true for quaternions (Euler's four-square identity
), complex numbers (the Brahmagupta-Fibonacci two-square identity
) and real numbers. However, in 1898 Adolf Hurwitz
proved that there is no similar identity for 16 squares (sedenions) or any other number of squares except for 1,2,4 and 8.
Note that each quadrant reduces to a version of Euler's four-square identity
:
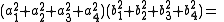
and,
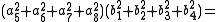
and similarly for the other two quadrants.
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, Degen's eight-square identity establishes that the product of two numbers, each of which being a sum of eight squares, is itself a sum of eight squares. Namely:
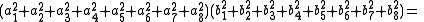
First discovered by Ferdinand Degen around 1818, the identity was independently rediscovered by John Thomas Graves
John T. Graves
John Thomas Graves was an Irish jurist and mathematician. He was a friend of William Rowan Hamilton, and is credited both with inspiring Hamilton to discover the quaternions and with personally discovering the octonions, which he called the octaves...
(1843) and Arthur Cayley
Arthur Cayley
Arthur Cayley F.R.S. was a British mathematician. He helped found the modern British school of pure mathematics....
(1845). The latter two derived it while working on an extension of quaternion
Quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternions are a number system that extends the complex numbers. They were first described by Irish mathematician Sir William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space...
s called octonion
Octonion
In mathematics, the octonions are a normed division algebra over the real numbers, usually represented by the capital letter O, using boldface O or blackboard bold \mathbb O. There are only four such algebras, the other three being the real numbers R, the complex numbers C, and the quaternions H...
s. In algebraic terms
Normed division algebra
In mathematics, a normed division algebra A is a division algebra over the real or complex numbers which is also a normed vector space, with norm || · || satisfying the following property:\|xy\| = \|x\| \|y\| for all x and y in A....
the identity means that the norm
Norm (mathematics)
In linear algebra, functional analysis and related areas of mathematics, a norm is a function that assigns a strictly positive length or size to all vectors in a vector space, other than the zero vector...
of product of two octonions equals the product of their norms:
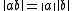 . Similar statements are true for quaternions (Euler's four-square identity
. Similar statements are true for quaternions (Euler's four-square identityEuler's four-square identity
In mathematics, Euler's four-square identity says that the product of two numbers, each of which being a sum of four squares, is itself a sum of four squares. Specifically:=\,...
), complex numbers (the Brahmagupta-Fibonacci two-square identity
Brahmagupta-Fibonacci identity
In algebra, Brahmagupta's identity, also called Fibonacci's identity, implies that the product of two sums each of two squares is itself a sum of two squares. In other words, the set of all sums of two squares is closed under multiplication...
) and real numbers. However, in 1898 Adolf Hurwitz
Adolf Hurwitz
Adolf Hurwitz was a German mathematician.-Early life:He was born to a Jewish family in Hildesheim, former Kingdom of Hannover, now Lower Saxony, Germany, and died in Zürich, in Switzerland. Family records indicate that he had siblings and cousins, but their names have yet to be confirmed...
proved that there is no similar identity for 16 squares (sedenions) or any other number of squares except for 1,2,4 and 8.
Note that each quadrant reduces to a version of Euler's four-square identity
Euler's four-square identity
In mathematics, Euler's four-square identity says that the product of two numbers, each of which being a sum of four squares, is itself a sum of four squares. Specifically:=\,...
:
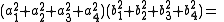
and,
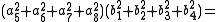
and similarly for the other two quadrants.
External links
- Degen's eight-square identity on MathWorldMathWorldMathWorld is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at...
- The Degen-Graves-Cayley Eight-Square Identity
- A Collection of Algebraic Identities