
Decimal32 floating-point format
Encyclopedia
In computing
, decimal32 is a decimal floating-point computer numbering format that occupies 4 bytes (32 bits) in computer memory.
It is intended for applications where it is necessary to emulate decimal rounding exactly, such as financial and tax computations.
Decimal32 supports 7 decimal digits of significand
and an exponent range of −95 to +96, i.e. to ±. (Equivalently, to .) Because the significand is not normalized, most values with less than 7 significant digits have multiple possible representations; , etc. Zero has 192 possible representations (384 if you include both signed zeros).
Decimal32 floating point is a relatively new decimal floating-point format, formally introduced in the 2008 version of IEEE 754.
The standard does not specify how to signify which representation is used,
for instance in a situation where decimal32 values are communicated between systems.
In one representation method, based on binary integer decimal
,
the significand is represented as binary coded positive integer.
The other, alternative, representation method is based on
densely packed decimal
for most of the
significand (except the most significant digit).
Both alternatives provide exactly the same range of representable numbers: 7 digits of significand and possible exponent values.
In both cases, the most significant 4 bits of the significand (which actually only have 10 possible values) are combined with the most significant 2 bits of the exponent (3 possible values) to use 30 of the 32 possible values of a 5-bit field. The remaining combinations encode infinities
and NaN
s.
If the leading 4 bits of the significand is between 0 and 7, the number begins as follows
s 00 xxxx Exponent begins with 00, significand with 0mmm
s 01 xxxx Exponent begins with 01, significand with 0mmm
s 10 xxxx Exponent begins with 10, significand with 0mmm
If the leading 4 bits of the significand are binary 1000 or 1001 (decimal 8 or 9), the number begins as follows:
s 1100 xx Exponent begins with 00, significand with 100m
s 1101 xx Exponent begins with 01, significand with 100m
s 1110 xx Exponent begins with 10, significand with 100m
The following bits (xxx in the above) encode the additional exponent bits and the remainder of the most significant digit, but the details vary depending on the encoding alternative used. There is no particular reason for this difference, other than historical reasons in the eight-year long development of IEEE 754-2008.
The final combinations are used for infinities and NaNs, and are the same for both alternative encodings:
s 11110 x ±Infinity (see Extended real number line
)
s 111110 quiet NaN (sign bit ignored)
s 111111 signaling NaN (sign bit ignored)
In the latter cases, all other bits of the encoding are ignored. Thus, it is possible to initialize an array to NaNs by filling it with a single byte value.
As described above, the encoding varies depending on whether the most significant 4 bits of the significand are in the range 0 to 7 (00002 to 01112), or higher (10002 or 10012).
If the 2 bits after the sign bit are "00", "01", or "10", then the
exponent field consists of the 8 bits following the sign bit, and the
significand is the remaining 23 bits, with an implicit leading 0 bit:
s 00eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
s 01eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
s 10eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
This includes subnormal numbers where the leading significand digit is 0.
If the 4 bits after the sign bit are "1100", "1101", or "1110", then the 8-bit exponent field is shifted 2 bits to the right (after both the sign bit and the "11" bits thereafter), and the represented significand is in the remaining 21 bits. In this case there is an implicit (that is, not stored) leading 3-bit sequence "100" in the true significand.
s 11 00eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
s 11 01eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
s 11 10eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
The "11" 2-bit sequence after the sign bit indicates that there is an implicit "100" 3-bit
prefix to the significand. Compare having an implicit 1 in the significand of normal
values for the binary formats. Note also that the "00", "01", or "10" bits are part of the exponent field.
Note that the leading bits of the significand field do not encode the most significant decimal digit; they are simply part of a larger pure-binary number. For example, a significand of is encoded as binary , with the leading 4 bits encoding 7; the first significand which requires a 24th bit is 223 =
In the above cases, the value represented is
If the four bits after the sign bit are "1111" then the value is an infinity or a NaN, as described above:
s 11110 xx...x ±infinity
s 111110 x...x a quiet NaN
s 111111 x...x a signalling NaN
0 and 9 (3 or 4 binary bits), and the rest of the significand uses the densely packed decimal
encoding.
Unlike the binary integer significand version, where the exponent changed position and came before the significand, this encoding combines the leading 2 bits of the exponent and the leading digit (3 or 4 bits)
of the significand into the five bits that follow the sign bit.
This six bits after that are the exponent continuation field, providing the less-significant bits of the exponent.
The last 20 bits are the significand continuation field, consisting of 2 10-bit "declets".
Each declet encodes three decimal digits using the DPD encoding.
If the first two bits after the sign bit are "00", "01", or "10", then those are
the leading bits of the exponent, and the three bits after that are interpreted as
the leading decimal digit (0 to 7):
s 00 TTT (00)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 01 TTT (01)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 10 TTT (10)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
If the 4 bits after the sign bit are "1100", "1101", or "1110", then the
second two bits are the leading bits of the exponent, and the last bit is
prefixed with "100" to form the leading decimal digit (8 or 9):
s 1100 T (00)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 1101 T (01)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 1110 T (10)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
The remaining two combinations (11110 and 11111) of the 5-bit field
are used to represent ±infinity and NaNs, respectively.
The DPD/3BCD transcoding for the declets is given by the following table.
b9...b0 are the bits of the DPD, and d2...d0 are the three BCD digits.
The 8 decimal values whose digits are all 8s or 9s have four codings each.
The bits marked x in the table above are ignored on input, but will always be 0 in computed results.
(The 8×3 = 24 non-standard encodings fill in the gap between 103=1000 and 210=1024.)
In the above cases, with the true significand as the sequence of decimal digits decoded, the value represented is
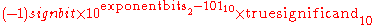
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
, decimal32 is a decimal floating-point computer numbering format that occupies 4 bytes (32 bits) in computer memory.
It is intended for applications where it is necessary to emulate decimal rounding exactly, such as financial and tax computations.
Decimal32 supports 7 decimal digits of significand
Significand
The significand is part of a floating-point number, consisting of its significant digits. Depending on the interpretation of the exponent, the significand may represent an integer or a fraction.-Examples:...
and an exponent range of −95 to +96, i.e. to ±. (Equivalently, to .) Because the significand is not normalized, most values with less than 7 significant digits have multiple possible representations; , etc. Zero has 192 possible representations (384 if you include both signed zeros).
Decimal32 floating point is a relatively new decimal floating-point format, formally introduced in the 2008 version of IEEE 754.
Representation of decimal32 values
IEEE 754 allows two alternative representation methods for decimal32 values.The standard does not specify how to signify which representation is used,
for instance in a situation where decimal32 values are communicated between systems.
In one representation method, based on binary integer decimal
Binary Integer Decimal
The IEEE 754-2008 standard includes an encoding format for decimal floating point numbers in which the significand and the exponent can be encoded in two ways, referred to in the draft as binary encoding and decimal encoding....
,
the significand is represented as binary coded positive integer.
The other, alternative, representation method is based on
densely packed decimal
Densely Packed Decimal
Densely packed decimal is a system of binary encoding for decimal digits.The traditional system of binary encoding for decimal digits, known as Binary-coded decimal , uses four bits to encode each digit, resulting in significant wastage of binary data bandwidth...
for most of the
significand (except the most significant digit).
Both alternatives provide exactly the same range of representable numbers: 7 digits of significand and possible exponent values.
In both cases, the most significant 4 bits of the significand (which actually only have 10 possible values) are combined with the most significant 2 bits of the exponent (3 possible values) to use 30 of the 32 possible values of a 5-bit field. The remaining combinations encode infinities
Infinity
Infinity is a concept in many fields, most predominantly mathematics and physics, that refers to a quantity without bound or end. People have developed various ideas throughout history about the nature of infinity...
and NaN
NaN
In computing, NaN is a value of the numeric data type representing an undefined or unrepresentable value, especially in floating-point calculations...
s.
If the leading 4 bits of the significand is between 0 and 7, the number begins as follows
s 00 xxxx Exponent begins with 00, significand with 0mmm
s 01 xxxx Exponent begins with 01, significand with 0mmm
s 10 xxxx Exponent begins with 10, significand with 0mmm
If the leading 4 bits of the significand are binary 1000 or 1001 (decimal 8 or 9), the number begins as follows:
s 1100 xx Exponent begins with 00, significand with 100m
s 1101 xx Exponent begins with 01, significand with 100m
s 1110 xx Exponent begins with 10, significand with 100m
The following bits (xxx in the above) encode the additional exponent bits and the remainder of the most significant digit, but the details vary depending on the encoding alternative used. There is no particular reason for this difference, other than historical reasons in the eight-year long development of IEEE 754-2008.
The final combinations are used for infinities and NaNs, and are the same for both alternative encodings:
s 11110 x ±Infinity (see Extended real number line
Extended real number line
In mathematics, the affinely extended real number system is obtained from the real number system R by adding two elements: +∞ and −∞ . The projective extended real number system adds a single object, ∞ and makes no distinction between "positive" or "negative" infinity...
)
s 111110 quiet NaN (sign bit ignored)
s 111111 signaling NaN (sign bit ignored)
In the latter cases, all other bits of the encoding are ignored. Thus, it is possible to initialize an array to NaNs by filling it with a single byte value.
Binary integer significand field
This format uses a binary significand from 0 to 107−1 = = 98967F16 = . The encoding can represent binary significands up to 10×220−1 = = 9FFFFF16 = , but values larger than 107−1 are illegal (and the standard requires implementations to treat them as 0, if encountered on input).As described above, the encoding varies depending on whether the most significant 4 bits of the significand are in the range 0 to 7 (00002 to 01112), or higher (10002 or 10012).
If the 2 bits after the sign bit are "00", "01", or "10", then the
exponent field consists of the 8 bits following the sign bit, and the
significand is the remaining 23 bits, with an implicit leading 0 bit:
s 00eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
s 01eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
s 10eeeeee (0)TTTtttttttttttttttttttt
This includes subnormal numbers where the leading significand digit is 0.
If the 4 bits after the sign bit are "1100", "1101", or "1110", then the 8-bit exponent field is shifted 2 bits to the right (after both the sign bit and the "11" bits thereafter), and the represented significand is in the remaining 21 bits. In this case there is an implicit (that is, not stored) leading 3-bit sequence "100" in the true significand.
s 11 00eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
s 11 01eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
s 11 10eeeeee (100)Ttttttttttttttttttttt
The "11" 2-bit sequence after the sign bit indicates that there is an implicit "100" 3-bit
prefix to the significand. Compare having an implicit 1 in the significand of normal
values for the binary formats. Note also that the "00", "01", or "10" bits are part of the exponent field.
Note that the leading bits of the significand field do not encode the most significant decimal digit; they are simply part of a larger pure-binary number. For example, a significand of is encoded as binary , with the leading 4 bits encoding 7; the first significand which requires a 24th bit is 223 =
In the above cases, the value represented is
- (−1)sign × 10exponent−101 × significand
If the four bits after the sign bit are "1111" then the value is an infinity or a NaN, as described above:
s 11110 xx...x ±infinity
s 111110 x...x a quiet NaN
s 111111 x...x a signalling NaN
Densely packed decimal significand field
In this version, the significand is stored as a series of decimal digits. The leading digit is between0 and 9 (3 or 4 binary bits), and the rest of the significand uses the densely packed decimal
Densely Packed Decimal
Densely packed decimal is a system of binary encoding for decimal digits.The traditional system of binary encoding for decimal digits, known as Binary-coded decimal , uses four bits to encode each digit, resulting in significant wastage of binary data bandwidth...
encoding.
Unlike the binary integer significand version, where the exponent changed position and came before the significand, this encoding combines the leading 2 bits of the exponent and the leading digit (3 or 4 bits)
of the significand into the five bits that follow the sign bit.
This six bits after that are the exponent continuation field, providing the less-significant bits of the exponent.
The last 20 bits are the significand continuation field, consisting of 2 10-bit "declets".
Each declet encodes three decimal digits using the DPD encoding.
If the first two bits after the sign bit are "00", "01", or "10", then those are
the leading bits of the exponent, and the three bits after that are interpreted as
the leading decimal digit (0 to 7):
s 00 TTT (00)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 01 TTT (01)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 10 TTT (10)eeeeee (TTT)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
If the 4 bits after the sign bit are "1100", "1101", or "1110", then the
second two bits are the leading bits of the exponent, and the last bit is
prefixed with "100" to form the leading decimal digit (8 or 9):
s 1100 T (00)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 1101 T (01)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
s 1110 T (10)eeeeee (100T)[tttttttttt][tttttttttt]
The remaining two combinations (11110 and 11111) of the 5-bit field
are used to represent ±infinity and NaNs, respectively.
The DPD/3BCD transcoding for the declets is given by the following table.
b9...b0 are the bits of the DPD, and d2...d0 are the three BCD digits.
The 8 decimal values whose digits are all 8s or 9s have four codings each.
The bits marked x in the table above are ignored on input, but will always be 0 in computed results.
(The 8×3 = 24 non-standard encodings fill in the gap between 103=1000 and 210=1024.)
In the above cases, with the true significand as the sequence of decimal digits decoded, the value represented is
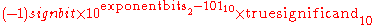
See also
- IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE 754)
- ISO/IEC 10967ISO/IEC 10967ISO/IEC 10967, Language independent arithmetic , is a series ofstandards on computer arithmetic. It is compatible with IEC 60559, and indeed much of thespecifications in parts 2 and 3 are for IEEE 754 special values...
, Language Independent Arithmetic - Primitive data type

