
Cutback technique
Encyclopedia
In telecommunications, a cutback technique is a destructive technique for determining certain optical fiber
transmission characteristics, such as attenuation and bandwidth
.
The cut should be made to retain 1 meter or more of the fiber, in order to establish equilibrium mode distribution
conditions for the second measurement. In a multimode fiber, the lack of an equilibrium mode distribution could introduce errors in the measurement due to output coupling effects. In a single-mode fiber, measuring a shorter cutback fiber could result in significant transmission of cladding modes (light carried in the cladding rather than the core of the optical fiber), distorting the measurement. The errors introduced will result in conservative results (i.e., higher transmission losses and lower bandwidths) than would be realized under equilibrium conditions.
of the light source is kept consistent between the initial and the cutback measurements.
Several characteristics may be determined using the same test fiber.
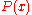 and
and 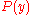 , where
, where 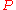 is the power at point
is the power at point  and
and 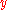 respectively. Using the cutback technique, the power transmitted through a fiber of known length is measured and compared with the same measurement for the same fiber cut to a length of
respectively. Using the cutback technique, the power transmitted through a fiber of known length is measured and compared with the same measurement for the same fiber cut to a length of  approximately.
approximately.
, in which measurements are made on a full length of fiber, and then on a short length of fiber having the same characteristics (core size, numerical aperture
), with the results from the short length being subtracted to give the results for the full length.
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
transmission characteristics, such as attenuation and bandwidth
Bandwidth (computing)
In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
.
Procedure
The measurement technique consists of:- performing the desired measurements on a long length of the fiber under test,
- cutting the fiber under test at a point near the launching end,
- repeating the measurements on the short length of fiber, and
- subtracting the results obtained on the short length to determine the results for the residual long length.
The cut should be made to retain 1 meter or more of the fiber, in order to establish equilibrium mode distribution
Equilibrium mode distribution
The equilibrium mode [power] distribution of light travelling in an optical waveguide or fiber, is the distribution of light that is no longer changing with fibre length or with input modal excitation. This phenomenon requires both mode filtering and mode mixing to occur in the fibre to produce a...
conditions for the second measurement. In a multimode fiber, the lack of an equilibrium mode distribution could introduce errors in the measurement due to output coupling effects. In a single-mode fiber, measuring a shorter cutback fiber could result in significant transmission of cladding modes (light carried in the cladding rather than the core of the optical fiber), distorting the measurement. The errors introduced will result in conservative results (i.e., higher transmission losses and lower bandwidths) than would be realized under equilibrium conditions.
Benefits
The benefit of this technique is that it allows measurement of the fiber characteristics without introducing errors due to variation in the launch conditions. For example, the coupling efficiencyCoupling loss
Coupling loss also known as connection loss is the loss that occurs when energy is transferred from one circuit, circuit element, or medium to another...
of the light source is kept consistent between the initial and the cutback measurements.
Several characteristics may be determined using the same test fiber.
Attenuation measurement
Since the attenuation is defined as proportional to the logarithm of the ratio between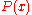 and
and 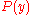 , where
, where 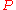 is the power at point
is the power at point  and
and 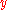 respectively. Using the cutback technique, the power transmitted through a fiber of known length is measured and compared with the same measurement for the same fiber cut to a length of
respectively. Using the cutback technique, the power transmitted through a fiber of known length is measured and compared with the same measurement for the same fiber cut to a length of  approximately.
approximately.Related techniques
A variation of the cutback technique is the substitution methodSubstitution method
In optical fiber technology, the substitution method is a method of measuring the transmission loss of a fiber. It consists of:#using a stable optical source, at the wavelength of interest, to drive a mode scrambler, the output of which overfills a 1 to 2 meter long reference fiber having...
, in which measurements are made on a full length of fiber, and then on a short length of fiber having the same characteristics (core size, numerical aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
), with the results from the short length being subtracted to give the results for the full length.

