
Cribbing (rescue)
Encyclopedia

Vehicle extrication
Vehicle extrication is the process of removing the vehicle from around a person that has been involved in a motor vehicle accident, when conventional means of exit are impossible or unadvisable. A delicate approach is needed to minimize injury to the victim during the extrication...
and urban search and rescue
Urban search and rescue
Urban search and rescue involves the location, extrication, and initial medical stabilization of victims trapped in confined spaces due to natural disasters, structural collapse, transportation accidents, mines and collapsed trenches.USAR teams in different countries may be organised in a...
. It is commonly used to secure overturned motor vehicles, and debris within collapsed building
Building
In architecture, construction, engineering, real estate development and technology the word building may refer to one of the following:...
s. Cribbing is often used in conjunction with other stabilization equipment, such as pneumatic or hydraulic shoring. Cribbing is also used in sub-surface mining
Sub-surface mining
Underground mining refers to a group of underground mining techniques used to extract coal, oil shale and other minerals or geological materials from sedimentary rocks...
as a roof support. Cribbing has largely been replaced by hydraulic shoring in modern mining applications.
Some forms of cribbing can also be used on movie sets and production sites for stabilizing dolly tracks, platforms, and various temporary structures when quick setup times are needed.
Stability
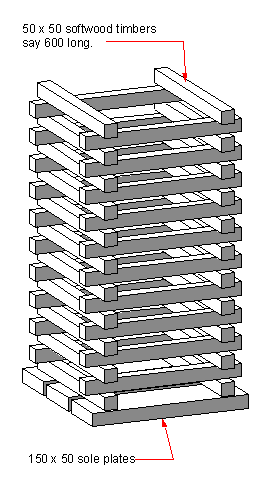
The stability of a crib is effected by a variety of factors: the material used (often a soft wood which gives audible warnings before failure), the number of contact points between the crib and the supported surface, the ratio of the footprint of the crib to its height, and the area of contact made between the crib and the ground and supported surface.Materials
Cribbing is usually accomplished with blocks of wood, often 4"x4" or 6"x6" and 18"-24" long. Soft woods, like spruce and pine are often preferred because they crack slowly and make loud noises before completely failing, whereas stiffer woods may fail explosively and without warning.Cribbing may also be made out of plastic, which unlike wood is not susceptible to rot or corrosion from fluids the cribbing may come in contact with (e.g. oil, gasoline, hydraulic fluid).
Cribbing equipment is normally of three varieties: rectangular blocks, wedges (also called shims), and "step chocks" (large wooden chocks constructed of wood of different lengths). Blocks are the bread and butter of cribbing and will be used in most cribbing evolutions. Shims are used to snug up contact between the crib and supported object or change the direction of the crib (tilt). Step chocks are often used as a quick solution for stabilizing vehicles on all fours or to quickly increase the height of a crib.
Methods
Cribbing structures are often categorized by shape. Different shapes of cribbing structures are chosen depending on the area available and the point being cribbed to.A box crib is the simplest, most stable and most common method of cribbing. It is constructed by arranging sets (2 or more) of matched blocks in a regular log-cabin style to form a rising square or rectangular frame. The more blocks on each level, the greater the number of support points and therefore the greater the strength of the crib tower.
A triangle or A' crib is similar to the box crib, except it resembles a triangular prism instead of rectangular.
A parallelogram crib resembles a diamond prism.
A tilted tower crib is a box crib in which pairs of shims are used to change the direction of the rising structure, resulting in a curve. Curving a crib must be done in moderation and is only advisable for structures at sharp angles to the ground.
Uses
Cribbing is often performed as part of lifting/lowering operations. Expressions such as "lift an inch, crib and inch" and "pack as you jack" are used to remind operators of the importance of cribbing to secure and protect the load. The use of cribbing also allows for the use of a lifting device with a limited working range (such as a jack, lifting air bags or hydraulic rescue toolsHydraulic Rescue Tools
Hydraulic rescue tools are used by emergency rescue personnel to assist vehicle extrication of crash victims, as well as other rescues from small spaces. These tools include cutters, spreaders, door busters and rams...
) as the load can be raised to the maximum range of the device, then lowered a short distance onto the cribbing, allowing another platform of cribbing to be built to raise the device and repeat the process.
Cribbing can be used to secure a load following a building collapse, vehicular accident or other event where the regular stability of a structure or vehicle has been reduced.
Cribbing is used when moving buildings in whole, or in part. Cribbing is used to raise the structure and allow the carrying vehicle to be positioned underneath, at which point the structure is then lowered onto the vehicle and the cribbing towers are removed. At the other end of the operation, the process is reversed, and the structure is lowered into its new position.
External links
- Using box cribs A description of two men lifting a demountable building off a truck and placing it on prepared foundations by hand.
- Moving the U-505 Time-lapse video showing box cribs used in relocation of the German submarine U-505 at the Museum of Science and IndustryMuseum of Science and Industry (Chicago)The Museum of Science and Industry is located in Chicago, Illinois, USA in Jackson Park, in the Hyde Park neighborhood adjacent to Lake Michigan. It is housed in the former Palace of Fine Arts from the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition...
in Chicago.

