Contextual design
Encyclopedia
Contextual Design is a user-centered design
process developed by Hugh Beyer and Karen Holtzblatt. It incorporates ethnographic
methods for gathering data relevant to the product via field studies, rationalizing workflows
, and designing human-computer interfaces. In practice, this means that researchers aggregate data from customers in the field where people are living and applying these findings into a final product. Contextual Design can be seen as an alternative to engineering and feature driven models of creating new systems.
The design ideas and relevant issues that arise during the process should be included in the affinity diagram. The affinity diagram is a Bottom-up method. Consolidated data may also be used to create a set of personas describing typical users of the proposed system.
helps the design team address the problems and design the new workflow. Storyboards work out the details of the vision, guided by the consolidated data, using pictures and text in a series of hand-drawn cells.
or even with more sophisticated interactive prototypes before the implementation phase helps the designers communicate with users about the new system and develop the design further. Prototypes test the structure of a User Environment Design and initial user interface ideas, as well as the understanding of the work, before the implementation phase. Depending on the results of the prototype test, more iterations or alternative designs may be needed.
evaluation method. Contextual design has also been applied to the design of digital libraries and other learning technologies.
Contextual design has also been used as a means of teaching user-centered design
/Human–computer interaction
at the university level.
A more lightweight approach to contextual design has been developed by its originators to address an oft-heard criticism that the method is too labor-intensive or lengthy for some needs. Yet others find the designer/user engagement promoted by contextual design to be too brief.
User-centered design
In broad terms, user-centered design or pervasive usability is a design philosophy and a process in which the needs, wants, and limitations of end users of a product are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process...
process developed by Hugh Beyer and Karen Holtzblatt. It incorporates ethnographic
Ethnography
Ethnography is a qualitative method aimed to learn and understand cultural phenomena which reflect the knowledge and system of meanings guiding the life of a cultural group...
methods for gathering data relevant to the product via field studies, rationalizing workflows
Workflow
A workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
, and designing human-computer interfaces. In practice, this means that researchers aggregate data from customers in the field where people are living and applying these findings into a final product. Contextual Design can be seen as an alternative to engineering and feature driven models of creating new systems.
Process Overview
The Contextual Design process consists of the following top-level steps: Contextual Inquiry, Interpretation, Data Consolidation, Visioning, Storyboarding, User Environment Design, and Prototyping.Collecting data - contextual inquiry
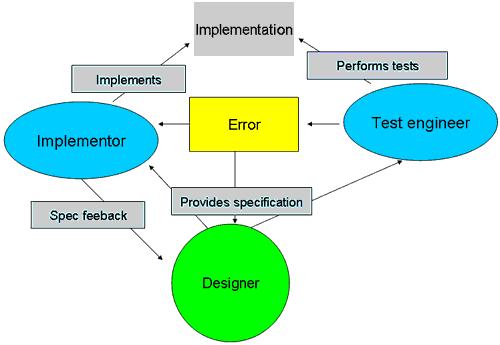
Contextual inquiry is a field data collection technique used to capture detailed information about how users of a product interact with the product in their normal work environment. This information is captured by both observations of user behavior and conversations with the user while she or he works. A key aspect of the technique is to partner with the user, letting their work and the issues they encounter guide the interview. Key takeaways from the technique are to learn what users actually do, why they do it that way, latent needs, and core values.Interpretation
Data from each interview is analyzed and key issues and insights are captured. Detailed work models are also created in order to understand the different aspects of the work that matter for design. Contextual design consists of five work models which are used to model the work tasks and details of the working environment. These work models are :- Flow model - represents the coordination, communication, interaction, roles, and responsibilities of the people in a certain work practice
- Sequence model - represents the steps users go through to accomplish a certain activity, including breakdowns
- Cultural model - represents the norms, influences, and pressures that are present in the work environment
- Artifact model - represents the documents or other physical things that are created while working or are used to support the work. Artifacts often have a structure or styling that could represent the user's way of structuring the work
- Physical model - represents the physical environment where the work tasks are accomplished; often, there are multiple physical models representing, e.g., office layout, network topology, or the layout of tools on a computer display.

Data Consolidation
Data from individual customer interviews are analyzed in order to reveal patterns and the structure across distinct interviews. Models of the same type can be consolidated together (but not generalized—detail must be maintained). Another method of processing the observations is making an affinity diagram ("wall"), as described by Beyer & Holtzblatt :- A single observation is written on each piece of paper
- Individual notes are grouped according to the similarity of their contents
- These groups are labeled with colored Post-it notes, each color representing a distinct level in the hierarchy
- Then the groups are combined with other groups to get the final construct of observations in a hierarchy of up to three levels.
The design ideas and relevant issues that arise during the process should be included in the affinity diagram. The affinity diagram is a Bottom-up method. Consolidated data may also be used to create a set of personas describing typical users of the proposed system.
Visioning
In visioning, a cross-functional team comes together to create stories of how new product concepts, services, and technology can better support the user work practice. The visioning team starts by reviewing the data to identify key issues and opportunities. The data walking session is followed by a group visioning session during which the visioning team generates a variety of new product concepts by telling stories of different usage scenarios based on the data collected. A vision includes the system, its delivery, and support structures to make the new work practice successful, but is told from the user's point of view.Storyboarding
After visioning, the team develops the vision in storyboards, capturing scenarios of how people will work with the new system. Understanding the current way of working, its structure and the complete workflowWorkflow
A workflow consists of a sequence of connected steps. It is a depiction of a sequence of operations, declared as work of a person, a group of persons, an organization of staff, or one or more simple or complex mechanisms. Workflow may be seen as any abstraction of real work...
helps the design team address the problems and design the new workflow. Storyboards work out the details of the vision, guided by the consolidated data, using pictures and text in a series of hand-drawn cells.
User Environment Design
The User Environment Design captures the floor plan of the new system. It shows each part of the system, how it supports the user's work, exactly what function is available in that part, and how the user gets to and from other parts of the system. CD uses the User Environment Design (UED) diagram, which displays the focus areas, i.e., areas which are visible to the user or which are relevant to the user. Focus areas can be defined further as functions in a system that support a certain type or part of the work. The UED also presents how the focus areas relate to each other and shows the links between focus areas.Prototyping
Testing the design ideas with paper prototypesPaper prototypes
In human–computer interaction, paper prototyping is a widely used method in the user-centered design process, a process that helps developers to create software that meets the user's expectations and needs - in this case, especially for designing and testing user interfaces...
or even with more sophisticated interactive prototypes before the implementation phase helps the designers communicate with users about the new system and develop the design further. Prototypes test the structure of a User Environment Design and initial user interface ideas, as well as the understanding of the work, before the implementation phase. Depending on the results of the prototype test, more iterations or alternative designs may be needed.
Uses and Adaptations
Contextual design has primarily been used for the design of computer information systems, including hardware and software. Parts of contextual design have been adapted for use as a usabilityUsability
Usability is the ease of use and learnability of a human-made object. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a usability analyst or as a secondary job...
evaluation method. Contextual design has also been applied to the design of digital libraries and other learning technologies.
Contextual design has also been used as a means of teaching user-centered design
User-centered design
In broad terms, user-centered design or pervasive usability is a design philosophy and a process in which the needs, wants, and limitations of end users of a product are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process...
/Human–computer interaction
Human–computer interaction
Human–computer Interaction is the study, planning, and design of the interaction between people and computers. It is often regarded as the intersection of computer science, behavioral sciences, design and several other fields of study...
at the university level.
A more lightweight approach to contextual design has been developed by its originators to address an oft-heard criticism that the method is too labor-intensive or lengthy for some needs. Yet others find the designer/user engagement promoted by contextual design to be too brief.
External links
- Description of Contextual Design, from InContext Design (founded by Karen Holtzblatt and Hugh Beyer)
- Peer-reviewed introduction to Contextual Design written by Karen Holtzblatt and Hugh Beyer
- "Contextual Design: A Customer-Centered Approach to Systems Designs" book on Amazon.com
- "Rapid Contextual Design: A How-to Guide to Key Techniques for User-Centered Design" book on Amazon.com
- Contextual inquiry in Usability net
- Contextual Design encyclopedia entry at Interaction-Design.org

