
Concurrent estimation
Encyclopedia
In discrete event simulation
concurrent estimation is a technique used to estimate the effect of alternate parameter settings on a discrete event system. For example from observation of a (computer simulated) telecommunications system with a specified buffer size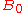 , one estimates what the performance would be if the buffer size had been set to the alternate values
, one estimates what the performance would be if the buffer size had been set to the alternate values 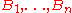 . Effectively the technique generates (during a single simulation run)
. Effectively the technique generates (during a single simulation run)  alternative histories for the system state variables, which have the same probability of occurring as the main simulated state path; this results in a computational saving as compared to running
alternative histories for the system state variables, which have the same probability of occurring as the main simulated state path; this results in a computational saving as compared to running  additional simulations, one for each alternative parameter value.
additional simulations, one for each alternative parameter value.
The technique was developed by Cassandras, Strickland and Panayiotou.
Discrete Event Simulation
In discrete-event simulation, the operation of a system is represented as a chronological sequence of events. Each event occurs at an instant in time and marks a change of state in the system...
concurrent estimation is a technique used to estimate the effect of alternate parameter settings on a discrete event system. For example from observation of a (computer simulated) telecommunications system with a specified buffer size
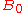 , one estimates what the performance would be if the buffer size had been set to the alternate values
, one estimates what the performance would be if the buffer size had been set to the alternate values  . Effectively the technique generates (during a single simulation run)
. Effectively the technique generates (during a single simulation run)  alternative histories for the system state variables, which have the same probability of occurring as the main simulated state path; this results in a computational saving as compared to running
alternative histories for the system state variables, which have the same probability of occurring as the main simulated state path; this results in a computational saving as compared to running  additional simulations, one for each alternative parameter value.
additional simulations, one for each alternative parameter value.The technique was developed by Cassandras, Strickland and Panayiotou.

