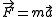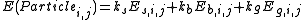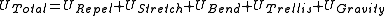Cloth modeling
Encyclopedia
Cloth modeling is the term used for simulating cloth within a computer program; usually in the context of 3D computer graphics
. The main approaches used for this may be classified into three basic types: geometric, physical, and particle/energy.
. This involves using the basic law of motion (Newton's Second Law):
In all of these models, the goal is to find the position and shape of a piece of fabric using this basic equation and several other methods.
Now we apply the basic principle of mechanical equilibrium
in which all bodies seek lowest energy by differentiating this equation to find the minimum energy.
We can also add terms for energy added by any source to this equation, then derive and find minima, which generalizes our model. This allows us to model cloth behavior under any circumstance, and since we are treating the cloth as a collection of particles its behavior can be described with the dynamics provided in our physics engine.
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images...
. The main approaches used for this may be classified into three basic types: geometric, physical, and particle/energy.
Background
Most models of cloth are based on "particles" of mass connected together in some manner of mesh. Newtonian Physics is used to model each particle through the use of a "black box" called a physics enginePhysics engine
A physics engine is computer software that provides an approximate simulation of certain physical systems, such as rigid body dynamics , soft body dynamics, and fluid dynamics, of use in the domains of computer graphics, video games and film. Their main uses are in video games , in which case the...
. This involves using the basic law of motion (Newton's Second Law):
In all of these models, the goal is to find the position and shape of a piece of fabric using this basic equation and several other methods.
Geometric methods
Weil pioneered the first of these, the geometric technique, in 1986. His work was focused on approximating the look of cloth by treating cloth like a collection of cables and using Hyperbolic cosine (catenary) curves. Because of this, it is not suitable for dynamic models but works very well for stationary or single-frame renders . This technique creates an underlying shape out of single points; then, it parses through each set of three of these points and maps a catenary curve to the set. It then takes the lowest out of each overlapping set and uses it for the render.Physical methods
The second technique treats cloth like a grid work of particles connected to each other by springs. Whereas the geometric approach accounted for none of the inherent stretch of a woven material, this physical model accounts for stretch (tension), stiffness, and weight:- s terms are elasticity (by Hooke's LawHooke's lawIn mechanics, and physics, Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load applied to it. Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Materials for which Hooke's law...
) - b terms are bending
- g terms are gravity (see Acceleration due to gravityStandard gravityStandard gravity, or standard acceleration due to free fall, usually denoted by g0 or gn, is the nominal acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined as precisely , or about...
)
Now we apply the basic principle of mechanical equilibrium
Mechanical equilibrium
A standard definition of static equilibrium is:This is a strict definition, and often the term "static equilibrium" is used in a more relaxed manner interchangeably with "mechanical equilibrium", as defined next....
in which all bodies seek lowest energy by differentiating this equation to find the minimum energy.
Particle/energy methods
The last method is more complex than the first two. The particle technique takes the physical technique from (f) a step further and supposes that we have a network of particles interacting directly. That is to say, that rather than springs, we use the energy interactions of the particles to determine the cloth’s shape. For this we use an energy equation that adds on to the following:- The energy of repelling is an artificial element we add to prevent cloth from intersecting itself.
- The energy of stretching is governed by Hooke's lawHooke's lawIn mechanics, and physics, Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load applied to it. Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Materials for which Hooke's law...
as with the Physical Method. - The energy of bending describes the stiffness of the fabric
- The energy of trellising describes the shearing of the fabric (distortion within the plane of the fabric)
- The energy of gravity is based on acceleration due to gravityStandard gravityStandard gravity, or standard acceleration due to free fall, usually denoted by g0 or gn, is the nominal acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined as precisely , or about...
We can also add terms for energy added by any source to this equation, then derive and find minima, which generalizes our model. This allows us to model cloth behavior under any circumstance, and since we are treating the cloth as a collection of particles its behavior can be described with the dynamics provided in our physics engine.
See also
- Soft body dynamicsSoft body dynamicsSoft body dynamics is a field of computer graphics that focuses on visually realistic physical simulations of the motion and properties of deformable objects . The applications are mostly in video games and film. Unlike in simulation of rigid bodies, the shape of soft bodies can change, meaning...
- Classical mechanicsClassical mechanicsIn physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
- Physics enginePhysics engineA physics engine is computer software that provides an approximate simulation of certain physical systems, such as rigid body dynamics , soft body dynamics, and fluid dynamics, of use in the domains of computer graphics, video games and film. Their main uses are in video games , in which case the...
- Rigid body dynamicsRigid body dynamicsIn physics, rigid body dynamics is the study of the motion of rigid bodies. Unlike particles, which move only in three degrees of freedom , rigid bodies occupy space and have geometrical properties, such as a center of mass, moments of inertia, etc., that characterize motion in six degrees of...