
Chvorinov's rule
Encyclopedia
Chvorinov's Rule is a mathematical relationship first expressed by Nicolas Chvorinov in 1940, that relates the solidification time for a simple casting
to the volume
and surface area
of the casting. In simple terms the rule establishes that under otherwise identical conditions, the casting with large surface area and small volume will cool more rapidly than a casting with small surface area and a large volume. The relationship can be written as:
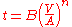
Where t is the solidification time, V is the volume of the casting, A is the surface area of the casting that contacts the mold
, n is a constant, and B is the mold constant. The mold constant B depends on the properties of the metal, such as density, heat capacity
, heat of fusion and superheat, and the mold, such as initial temperature, density, thermal conductivity
, heat capacity and wall thickness. The metric units of the mold constant B are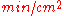 . According to Askeland, the constant n is usually 2, however Degarmo claims it is between 1.5 and 2. The mold constant of Chvorinov's rule, B, can be calculated using the following formula:
. According to Askeland, the constant n is usually 2, however Degarmo claims it is between 1.5 and 2. The mold constant of Chvorinov's rule, B, can be calculated using the following formula:
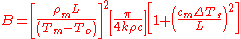
Where
It is most useful in determining if a riser
will solidify before the casting, because if the riser solidifies first then it is worthless.
Casting
In metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
to the volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
and surface area
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
of the casting. In simple terms the rule establishes that under otherwise identical conditions, the casting with large surface area and small volume will cool more rapidly than a casting with small surface area and a large volume. The relationship can be written as:
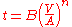
Where t is the solidification time, V is the volume of the casting, A is the surface area of the casting that contacts the mold
Molding (process)
Molding or moulding is the process of manufacturing by shaping pliable raw material using a rigid frame or model called a pattern....
, n is a constant, and B is the mold constant. The mold constant B depends on the properties of the metal, such as density, heat capacity
Heat capacity
Heat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
, heat of fusion and superheat, and the mold, such as initial temperature, density, thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
, heat capacity and wall thickness. The metric units of the mold constant B are
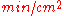 . According to Askeland, the constant n is usually 2, however Degarmo claims it is between 1.5 and 2. The mold constant of Chvorinov's rule, B, can be calculated using the following formula:
. According to Askeland, the constant n is usually 2, however Degarmo claims it is between 1.5 and 2. The mold constant of Chvorinov's rule, B, can be calculated using the following formula: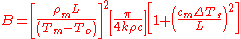
Where
- Tm = melting or freezing temperature of the liquid
- To = initial temperature of the mold
- ΔTs = Tpour − Tm = superheat
- L = latent heat of fusion
- k = thermal conductivity of the mold
- ρ = density of the mold
- c = specific heat of the mold
- ρm = density of the metal
- cm = specific heat of the metal
It is most useful in determining if a riser
Riser (casting)
A riser, also known as a feeder, is a reservoir built into a metal casting mold to prevent cavities due to shrinkage. Most metals are less dense as a liquid than as a solid so castings shrink upon cooling, which can leave a void at the last point to solidify...
will solidify before the casting, because if the riser solidifies first then it is worthless.

