
Brocard's problem
Encyclopedia
Brocard's problem asks to find integer
values of n for which
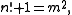
where n! is the factorial
. It was posed by Henri Brocard
in a pair of articles in 1876 and 1885, and independently in 1913 by Ramanujan.
Paul Erdős
conjectured that no other solutions exist. showed that there are only finitely many solutions provided that the abc conjecture
is true. Most recently performed calculations for n up to 109 and found no further solutions.
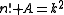
has only finitely many solutions, for any given integer A. This result was further generalized by , who showed (again assuming the abc conjecture) that the equation
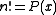
has only finitely many integer solutions for a given polynomial
P(x) of degree at least 2 with integer coefficients.
Integer
The integers are formed by the natural numbers together with the negatives of the non-zero natural numbers .They are known as Positive and Negative Integers respectively...
values of n for which
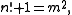
where n! is the factorial
Factorial
In mathematics, the factorial of a non-negative integer n, denoted by n!, is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n...
. It was posed by Henri Brocard
Henri Brocard
Pierre René Jean Baptiste Henri Brocard was a French meteorologist and mathematician, in particular a geometer...
in a pair of articles in 1876 and 1885, and independently in 1913 by Ramanujan.
Brown numbers
Pairs of the numbers (n, m) that solve Brocard's problem are called Brown numbers. There are only three known pairs of Brown numbers:, (5,11), and (7,71).Paul Erdős
Paul Erdos
Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. Erdős published more papers than any other mathematician in history, working with hundreds of collaborators. He worked on problems in combinatorics, graph theory, number theory, classical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory...
conjectured that no other solutions exist. showed that there are only finitely many solutions provided that the abc conjecture
Abc conjecture
The abc conjecture is a conjecture in number theory, first proposed by Joseph Oesterlé and David Masser in 1985. The conjecture is stated in terms of three positive integers, a, b and c , which have no common factor and satisfy a + b = c...
is true. Most recently performed calculations for n up to 109 and found no further solutions.
Variants of the problem
generalized Overholt's result by showing that it would follow from the abc conjecture that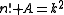
has only finitely many solutions, for any given integer A. This result was further generalized by , who showed (again assuming the abc conjecture) that the equation
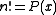
has only finitely many integer solutions for a given polynomial
Polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
P(x) of degree at least 2 with integer coefficients.

