
Bray Curtis dissimilarity
Encyclopedia
In ecology
and biology
, the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, named after J. Roger Bray and John T. Curtis, is a statistic used to quantify the compositional dissimilarity between two different sites. It is equivalent to the total number of species that are unique to any one of the two sites divided by the total number of species over the two sites. In other words, it is the ratio between the turnover of species between the two sites and the total species richness
over the two sites.
The short hand formula for the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is:
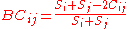
Where is the sum of minimum abundances of the various species (abundance at the site where the species is the rarest).
is the sum of minimum abundances of the various species (abundance at the site where the species is the rarest). 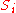 and
and  are the total number of specimens captured at both sites.
are the total number of specimens captured at both sites.
The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is directly related to the Sørensen similarity index
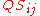 between the same sites:
between the same sites:
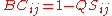 .
.
The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is bound between 0 and 1, where 0 means the two sites have the same composition (that is they share all the species), and 1 means the two sites do not share any species.
The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is often erroneously called a distance. The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is not a distance since it does not satisfy triangle inequality
, and should always be called a dissimilarity to avoid confusion.
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
and biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, named after J. Roger Bray and John T. Curtis, is a statistic used to quantify the compositional dissimilarity between two different sites. It is equivalent to the total number of species that are unique to any one of the two sites divided by the total number of species over the two sites. In other words, it is the ratio between the turnover of species between the two sites and the total species richness
Species richness
Species richness is the number of different species in a given area. It is represented in equation form as S.Species richness is the fundamental unit in which to assess the homogeneity of an environment. Typically, species richness is used in conservation studies to determine the sensitivity of...
over the two sites.
The short hand formula for the Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is:
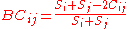
Where
 is the sum of minimum abundances of the various species (abundance at the site where the species is the rarest).
is the sum of minimum abundances of the various species (abundance at the site where the species is the rarest). 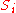 and
and  are the total number of specimens captured at both sites.
are the total number of specimens captured at both sites.The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is directly related to the Sørensen similarity index
Sørensen similarity index
The Sørensen index, also known as Sørensen’s similarity coefficient, is a statistic used for comparing the similarity of two samples. It was developed by the botanist Thorvald Sørensen and published in 1948....
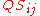 between the same sites:
between the same sites: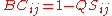 .
.The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is bound between 0 and 1, where 0 means the two sites have the same composition (that is they share all the species), and 1 means the two sites do not share any species.
The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is often erroneously called a distance. The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity is not a distance since it does not satisfy triangle inequality
Triangle inequality
In mathematics, the triangle inequality states that for any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remaining side ....
, and should always be called a dissimilarity to avoid confusion.

