
Borderline tree
Encyclopedia
Borderline tree is a term used in forestry
.
It is a concept that comes from variable radius plots, or point sampling. It happens when a tree cannot be easily determined as in or out when using a prism
or angle gauge
. Borderline trees occur only when the distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree is equal to the DBH
times plot radius factor (PRF). The PRF is determined based on the type of prism or angle gauge being used. Basal Area
Factor (BAF) 5, 10, and 20 angle gauges result in PRFs of 3.89, 2.75, and 1.94 (feet inch-1) respectively. The metric equivalents of these PRFs are 0.467, 0.33, and 0.233 (m cm-1).
When a tree is borderline, a series of measurements and calculations must be made to determine if the tree is in or out. The horizontal distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree must be measured along with the DBH of the tree. The DBH should then be multiplied by the PRF, which will give a limiting distance. If the measured distance is less than or equal to this limiting distance, the tree is counted as in. If it is greater than the limiting distance, it is out.
PRF =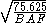 , metric:
, metric:
The horizontal distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree is 34 feet (10.4 m).
DBH x PRF = Limiting Distance
12.4in. x 2.75ft./in. = 34.1ft.
34.1 inches (limiting distance) is greater than 34 inches (measured distance), tree is in.
Forestry
Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands...
.
It is a concept that comes from variable radius plots, or point sampling. It happens when a tree cannot be easily determined as in or out when using a prism
Wedge prism
The wedge prism is a prism with a shallow angle between its input and output surfaces. Refraction at the surfaces causes the prism to deflect light by a fixed angle...
or angle gauge
Angle gauge
An angle gauge is a tool used by foresters to determine which trees to measure when using a variable radius plot design in forest inventory. Using this tool a forester can quickly measure the trees that are in or out of the plot. An angle gauge is a very similar tool to a wedge prism though it...
. Borderline trees occur only when the distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree is equal to the DBH
Diameter at breast height
Diameter at breast height, or DBH, is a standard method of expressing the diameter of the trunk or bole of a standing tree. DBH is one of the most common dendrometric measurements....
times plot radius factor (PRF). The PRF is determined based on the type of prism or angle gauge being used. Basal Area
Basal area
Basal area is the term used in forest management that defines the cross-sectional area of a tree at DBH, inside the bark.In most countries, this is usually a measurement taken at a specimen's breast height above the ground and includes the entire diameter of every tree, including the bark...
Factor (BAF) 5, 10, and 20 angle gauges result in PRFs of 3.89, 2.75, and 1.94 (feet inch-1) respectively. The metric equivalents of these PRFs are 0.467, 0.33, and 0.233 (m cm-1).
When a tree is borderline, a series of measurements and calculations must be made to determine if the tree is in or out. The horizontal distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree must be measured along with the DBH of the tree. The DBH should then be multiplied by the PRF, which will give a limiting distance. If the measured distance is less than or equal to this limiting distance, the tree is counted as in. If it is greater than the limiting distance, it is out.
Formulas
Limiting Distance = DBH x PRFPRF =
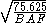 , metric:
, metric:
Example
A tree that appears borderline using a BAF 10 instrument was measured as 12.4 inches (315 mm) DBH.The horizontal distance from the sampling point to the center of the tree is 34 feet (10.4 m).
DBH x PRF = Limiting Distance
12.4in. x 2.75ft./in. = 34.1ft.
34.1 inches (limiting distance) is greater than 34 inches (measured distance), tree is in.

