
Boolean grammar
Encyclopedia
Boolean grammars are a class of formal grammars studied in formal language
theory. They extend the basic type of grammars, the context-free grammars, with conjunction
and negation
operations. Besides these explicit operations, Boolean grammars allow implicit disjunction
represented by multiple rules for a single nonterminal symbol, which is the only logical connective expressible in context-free grammars. Conjunction and negation can be used, in particular, to specify intersection and complement of languages. An intermediate class of grammars known as conjunctive grammar
s allows conjunction and disjunction, but not negation.
The rules of a Boolean grammar are of the form
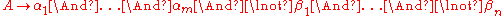
where is a nonterminal,
is a nonterminal, 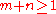 and
and 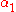 , ...,
, ..., 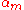 ,
, 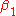 , ...,
, ...,  are strings formed of symbols in
are strings formed of symbols in  and
and  . Informally, such a rule asserts that every string
. Informally, such a rule asserts that every string 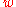 over
over 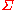 that satisfies each of the syntactical conditions represented by
that satisfies each of the syntactical conditions represented by 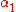 , ...,
, ..., 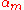 and none of the syntactical conditions represented by
and none of the syntactical conditions represented by 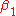 , ...,
, ..., 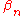 therefore satisfies the condition defined by
therefore satisfies the condition defined by 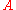 .
.
There exist several formal definitions of the language generated by a Boolean grammar. They have one thing in common: if the grammar is represented as a system of language equation
s with union, intersection, complementation and concatenation, the languages generated by the grammar must be the solution of this system. The semantics differ in details, some define the languages using language equations, some draw upon ideas from the field of logic programming
. However, these nontrivial issues of formal definition are mostly irrelevant for practical considerations, and one can construct grammars according to the given informal semantics. The practical properties of the model are similar to those of conjunctive grammar
s, while the descriptional capabilities are further improved. In particular, some practically useful properties inherited from context-free grammars, such as efficient parsing algorithms, are retained, see .
Formal language
A formal language is a set of words—that is, finite strings of letters, symbols, or tokens that are defined in the language. The set from which these letters are taken is the alphabet over which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar...
theory. They extend the basic type of grammars, the context-free grammars, with conjunction
Logical conjunction
In logic and mathematics, a two-place logical operator and, also known as logical conjunction, results in true if both of its operands are true, otherwise the value of false....
and negation
Negation
In logic and mathematics, negation, also called logical complement, is an operation on propositions, truth values, or semantic values more generally. Intuitively, the negation of a proposition is true when that proposition is false, and vice versa. In classical logic negation is normally identified...
operations. Besides these explicit operations, Boolean grammars allow implicit disjunction
Logical disjunction
In logic and mathematics, a two-place logical connective or, is a logical disjunction, also known as inclusive disjunction or alternation, that results in true whenever one or more of its operands are true. E.g. in this context, "A or B" is true if A is true, or if B is true, or if both A and B are...
represented by multiple rules for a single nonterminal symbol, which is the only logical connective expressible in context-free grammars. Conjunction and negation can be used, in particular, to specify intersection and complement of languages. An intermediate class of grammars known as conjunctive grammar
Conjunctive grammar
Conjunctive grammars are a class of formal grammarsstudied in formal language theory.They extend the basic type of grammars,the context-free grammars,with a conjunction operation.Besides explicit conjunction,conjunctive grammars allow implicit disjunction...
s allows conjunction and disjunction, but not negation.
The rules of a Boolean grammar are of the form
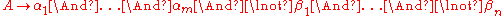
where
 is a nonterminal,
is a nonterminal,  and
and 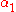 , ...,
, ..., 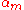 ,
, 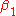 , ...,
, ...,  are strings formed of symbols in
are strings formed of symbols in  and
and  . Informally, such a rule asserts that every string
. Informally, such a rule asserts that every string  over
over  that satisfies each of the syntactical conditions represented by
that satisfies each of the syntactical conditions represented by 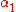 , ...,
, ..., 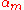 and none of the syntactical conditions represented by
and none of the syntactical conditions represented by 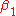 , ...,
, ..., 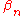 therefore satisfies the condition defined by
therefore satisfies the condition defined by  .
.There exist several formal definitions of the language generated by a Boolean grammar. They have one thing in common: if the grammar is represented as a system of language equation
Language equation
Language equations are mathematical statements that resemble numerical equations, but the variables assume values of formal languages rather than numbers. Instead of arithmetic operations in numerical equations, the variables are joined by language operations...
s with union, intersection, complementation and concatenation, the languages generated by the grammar must be the solution of this system. The semantics differ in details, some define the languages using language equations, some draw upon ideas from the field of logic programming
Logic programming
Logic programming is, in its broadest sense, the use of mathematical logic for computer programming. In this view of logic programming, which can be traced at least as far back as John McCarthy's [1958] advice-taker proposal, logic is used as a purely declarative representation language, and a...
. However, these nontrivial issues of formal definition are mostly irrelevant for practical considerations, and one can construct grammars according to the given informal semantics. The practical properties of the model are similar to those of conjunctive grammar
Conjunctive grammar
Conjunctive grammars are a class of formal grammarsstudied in formal language theory.They extend the basic type of grammars,the context-free grammars,with a conjunction operation.Besides explicit conjunction,conjunctive grammars allow implicit disjunction...
s, while the descriptional capabilities are further improved. In particular, some practically useful properties inherited from context-free grammars, such as efficient parsing algorithms, are retained, see .

