
Bogomol'nyi-Prasad-Sommerfield bound
Encyclopedia
The Bogomol'nyi–Prasad–Sommerfeld bound (named after Eugène Bogomolny, Manoj Prasad, and Charles Sommerfield) is a series of inequalities for solutions of partial differential equation
s depending on the homotopy class of the solution at infinity. This set of inequalities is very useful for solving soliton equations. Often, by insisting that the bound be satisfied (called "saturated"), one can come up with a simpler set of partial differential equations to solve, the Bogomol'nyi equations. Solutions saturating the bound are called BPS states and play an important role in field theory and string theory
.
Examples:
The energy at a given time t is given by

where D is the covariant derivative
and V is the potential. If we assume that V is nonnegative and is zero only for the Higgs vacuum and that the Higgs field is in the adjoint representation
, then

Therefore,
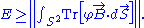
Saturation happens when and
and
This quantity is the absolute value of the magnetic flux
.
A slight generalization applying to dyons also exists. For that, the Higgs field needs to be a complex adjoint, not a real adjoint.
In fact, most bosonic BPS bounds actually come from the bosonic sector of a supersymmetric theory and this explains their origin.
Partial differential equation
In mathematics, partial differential equations are a type of differential equation, i.e., a relation involving an unknown function of several independent variables and their partial derivatives with respect to those variables...
s depending on the homotopy class of the solution at infinity. This set of inequalities is very useful for solving soliton equations. Often, by insisting that the bound be satisfied (called "saturated"), one can come up with a simpler set of partial differential equations to solve, the Bogomol'nyi equations. Solutions saturating the bound are called BPS states and play an important role in field theory and string theory
String theory
String theory is an active research framework in particle physics that attempts to reconcile quantum mechanics and general relativity. It is a contender for a theory of everything , a manner of describing the known fundamental forces and matter in a mathematically complete system...
.
Examples:
- InstantonInstantonAn instanton is a notion appearing in theoretical and mathematical physics. Mathematically, a Yang–Mills instanton is a self-dual or anti-self-dual connection in a principal bundle over a four-dimensional Riemannian manifold that plays the role of physical space-time in non-abelian gauge theory...
. - Incomplete: Yang-Mills-Higgs partial differential equations.
The energy at a given time t is given by

where D is the covariant derivative
Covariant derivative
In mathematics, the covariant derivative is a way of specifying a derivative along tangent vectors of a manifold. Alternatively, the covariant derivative is a way of introducing and working with a connection on a manifold by means of a differential operator, to be contrasted with the approach given...
and V is the potential. If we assume that V is nonnegative and is zero only for the Higgs vacuum and that the Higgs field is in the adjoint representation
Adjoint representation
In mathematics, the adjoint representation of a Lie group G is the natural representation of G on its own Lie algebra...
, then

Therefore,
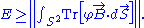
Saturation happens when
 and
and
- <Áequation. The other condition for saturation is the Higgs mass and self-interaction are zero, which is the case in N=2 supersymmetric theories.
This quantity is the absolute value of the magnetic flux
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux , is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a given surface . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber...
.
A slight generalization applying to dyons also exists. For that, the Higgs field needs to be a complex adjoint, not a real adjoint.
Supersymmetry
In supersymmetry, the BPS bound is saturated when half (or a quarter or an eighth) of the SUSY generators are unbroken. This happens when the mass is equal to the central extension, which is typically a topological charge.In fact, most bosonic BPS bounds actually come from the bosonic sector of a supersymmetric theory and this explains their origin.

