
Bion 6
Encyclopedia
Spaceflight
Spaceflight is the act of travelling into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft which may, or may not, have humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station...
research mission that was launched on December 12, 1983. It was part of the Bion satellite program
Bion (satellite)
The Bion satellites or Bion space program , also named Biocosmos, were a series of Soviet biosatellites. They were part of the Cosmos satellites....
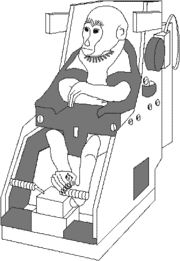
. Two Rhesus monkeys were flown into orbit implanted with sensors to permit monitoring of carotid artery
Carotid artery
Carotid artery can refer to:* Common carotid artery* External carotid artery* Internal carotid artery...
blood flow. Eighteen pregnant white rats were used for studies of the effects of microgravity and radiation. The rats subsequently produced normal litters. The mission ended after five days.
This was the first time the Soviet space agency flew monkeys in space
Monkeys in space
Before humans went into space, several animals were launched into space, including numerous monkeys, so that scientists could investigate the biological effects of space travel. The United States launched flights containing primate cargo primarily between 1948-1961 with one flight in 1969 and one...
, coming 34 years after the U.S. first put a monkey into space (and 22 years after the Soviet Union started putting humans into space).
NSSDC ID: 1983-121A
Other Names
- Biocosmos 6
- Cosmos 1514
- 14549
Launch Date/Time: December 14, 1983 at 07:00:00 UTC
On-orbit Dry Mass: 5700 kg

