
Berlekamp–Welch algorithm
Encyclopedia
The Berlekamp–Welch algorithm, also known as the Welch–Berlekamp algorithm, is named for Elwyn R. Berlekamp and Lloyd R. Welch
. The algorithm efficiently corrects errors in BCH code
s and Reed–Solomon codes
(which are a subset of BCH codes). Unlike many other decoding algorithms, and in correspondence with the code-domain Berlekamp–Massey algorithm that uses syndrome decoding and the dual of the codes, the Berlekamp–Welch decoding algorithm provides a method for decoding Reed–Solomon codes using just the generator matrix and not syndromes.
 ’s (i = 1, . . ., n) where
’s (i = 1, . . ., n) where  with dimension
with dimension  and distance
and distance
 and a codeword
and a codeword  =
= 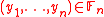 . Our goal is to describe an algorithm that can correct
. Our goal is to describe an algorithm that can correct  many errors in polynomial time. To do so we have to find a polynomial
many errors in polynomial time. To do so we have to find a polynomial 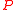 over
over 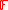 such that
such that 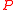 has degree less than
has degree less than  and (the number of
and (the number of 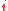 ’s such that
’s such that 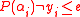 . We can assume that there exists a polynomial
. We can assume that there exists a polynomial 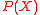 such that
such that 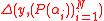 ≤
≤  or
or 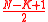 .
.
Note that the coefficients of are the encoded information. To solve this, we use an indicator for those
are the encoded information. To solve this, we use an indicator for those  ’s where an error may have occurred. Thus we define
’s where an error may have occurred. Thus we define 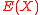 , which is an error locator polynomial over
, which is an error locator polynomial over 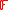 such that
such that 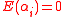 if
if 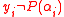 and the degree of
and the degree of  can be given by:
can be given by: 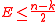 .
.
We can also claim that for every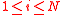 ,
, 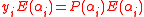 . This fact holds true because in the event of
. This fact holds true because in the event of 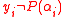 , both sides of the above equation become
, both sides of the above equation become 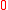 owing to the fact that
owing to the fact that 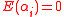 .
.
However since both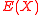 and
and 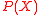 are unknown, the main task of the decoding algorithm would be to find
are unknown, the main task of the decoding algorithm would be to find 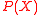 . To do this we use a seemingly useless yet very powerful method and define another polynomial
. To do this we use a seemingly useless yet very powerful method and define another polynomial 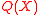 as
as 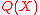 =
= 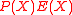 . This is because the
. This is because the  equations with
equations with  we need to solve are quadratic in nature. Thus by defining a product of two variables that gives rise to a quadratic term as one unknown variable, we increase the number of unknowns but make the equations linear in nature. This method is called linearization and is a very powerful tool.
we need to solve are quadratic in nature. Thus by defining a product of two variables that gives rise to a quadratic term as one unknown variable, we increase the number of unknowns but make the equations linear in nature. This method is called linearization and is a very powerful tool.
Thus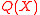 is a polynomial over
is a polynomial over 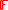 having the properties:
having the properties:
This helps because if we now manage to find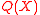 and
and 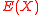 , we can easily find
, we can easily find 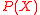 using
using  .
.
The main purpose of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm is to find out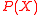 using degree bounded polynomials
using degree bounded polynomials 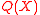 and
and  and the properties of
and the properties of  and
and  .
.
Computing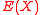 is as hard as finding the end solution, polynomial
is as hard as finding the end solution, polynomial 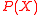 . Once
. Once 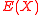 is computed, using erasure decoding for Reed–Solomon codes, we can easily recover
is computed, using erasure decoding for Reed–Solomon codes, we can easily recover 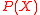 . However in a few cases, even the polynomial
. However in a few cases, even the polynomial 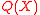 is as hard to find as
is as hard to find as  . As an example, given
. As an example, given 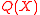 and
and  (such that
(such that  for
for 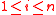 ), by checking positions where
), by checking positions where 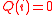 , we can find the error locations. Thus the algorithm works on the principle that while each of the polynomials
, we can find the error locations. Thus the algorithm works on the principle that while each of the polynomials 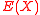 and
and 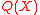 are hard to find individually; computing them together is much easier.
are hard to find individually; computing them together is much easier.
The inputs given to the Berlekamp Welch decoder are the integers denoting Block Length , the number of errors
, the number of errors  such that
such that  <
< 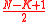 , and the received word
, and the received word 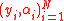 satisfying the condition that there exists at most one
satisfying the condition that there exists at most one 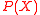 with
with  with
with  .
.
The output of the decoder is either the polynomial , or in some cases, a failure. This decoder functions in two steps as follows:
, or in some cases, a failure. This decoder functions in two steps as follows:
According to the algorithm, in the cases where it does not output a failure, it outputs a that is the correct and desired polynomial. To prove that, the algorithm always outputs the desired polynomial, we need to prove a few claims we have made while describing the algorithm. Let us go ahead and do so now.
that is the correct and desired polynomial. To prove that, the algorithm always outputs the desired polynomial, we need to prove a few claims we have made while describing the algorithm. Let us go ahead and do so now.
Claim 1: There exist a pair of polynomials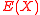 and
and 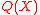 that satisfy Step 1 of the BW algorithm such that
that satisfy Step 1 of the BW algorithm such that 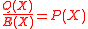 .
.
Let E(x) be the error-locating polynomial for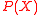 such that
such that 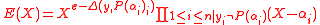 and let
and let 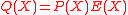 . Note that
. Note that 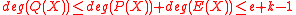 . We also stated that
. We also stated that 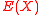 is a polynomial of degree exactly
is a polynomial of degree exactly  . Note that
. Note that 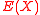 is a polynomial following the property that
is a polynomial following the property that 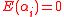 if and only if
if and only if 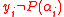 .We can now state that
.We can now state that 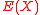 and
and 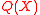 satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation 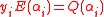 from the first step of the BW algorithm. If
from the first step of the BW algorithm. If  , then
, then 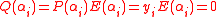 . However whenever
. However whenever 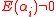 , we can easily state that
, we can easily state that  and therefore also state that
and therefore also state that  just as we claimed.
just as we claimed.
This above claim however just reiterates and proves the fact that there exists a pair of polynomials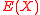 and
and  such that
such that  =
=  . It however does not necessarily guarantee the fact that the algorithm we discussed above would indeed output such a pair of polynomials. We therefore move on to look at another claim that helps establish this fact using the above claim and thereby proving the correctness of the algorithm.
. It however does not necessarily guarantee the fact that the algorithm we discussed above would indeed output such a pair of polynomials. We therefore move on to look at another claim that helps establish this fact using the above claim and thereby proving the correctness of the algorithm.
Claim 2: For any two distinct solutions that satisfy the first step of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm given above, they will also satisfy the equation
that satisfy the first step of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm given above, they will also satisfy the equation 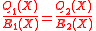
The total degrees of the polynomials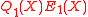 and
and 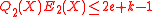 . We define another polynomial
. We define another polynomial  ....................................(i)
....................................(i)
Note that such that
such that  . From step 1 of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm we also know that
. From step 1 of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm we also know that 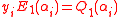 and
and  ) ........…..........(ii)
) ........…..........(ii)
Now, substituting the values of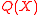 from equation (ii) into equation (i), we get:
from equation (ii) into equation (i), we get:
 for
for 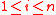 .
.
Thus, the above polynomial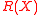 has
has  roots and
roots and  which implies that
which implies that  <
<  because of the upper bound on
because of the upper bound on  .
.
Since <
<  , we can come to the conclusion that the polynomials
, we can come to the conclusion that the polynomials  and
and 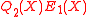 agree on more points than their degree, and hence they are identical. Note that since
agree on more points than their degree, and hence they are identical. Note that since 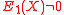 and
and 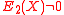 , it can be implied that
, it can be implied that 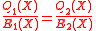 as per our initial claim.
as per our initial claim.
Thus based on the above claims, we can safely state that the output of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm, when outputting the polynomial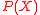 is correct.
is correct.
We can now claim that the algorithm can be implemented such that it has a running time of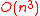 . This can be proved as follows:
. This can be proved as follows:
In Step 1 of the algorithm, the polynomials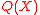 and
and 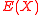 have
have  and
and  unknown values respectively and the constraints
unknown values respectively and the constraints 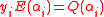 for all
for all 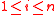 acts as a linear equation with these unknowns. We therefore get a system of
acts as a linear equation with these unknowns. We therefore get a system of  linear equations in
linear equations in 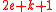 <
< 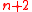 unknowns. Using our first claim, this system of equations has a solution since the degree of polynomial
unknowns. Using our first claim, this system of equations has a solution since the degree of polynomial 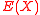 is
is  . This can be solved in
. This can be solved in 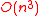 time, by say Gaussian elimination. Finally, we can note that Step 2 of the algorithm can also be implemented in time
time, by say Gaussian elimination. Finally, we can note that Step 2 of the algorithm can also be implemented in time 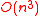 by "long division" method.
by "long division" method.
Hence we can state that the Berlekamp Welch algorithm can be used to uniquely decode any Reed–Solomon code in
Reed–Solomon code in  time for a maximum of
time for a maximum of 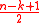 errors.
errors.
Lloyd R. Welch
Lloyd Richard Welch is a noted American information theorist, and co-inventor of the Baum–Welch algorithm.Welch received his B.S. in mathematics from the University of Illinois, 1951, and Ph.D. in mathematics from the California Institute of Technology, 1958, under advisor Frederic Bohnenblust...
. The algorithm efficiently corrects errors in BCH code
BCH code
In coding theory the BCH codes form a class of parameterised error-correcting codes which have been the subject of much academic attention in the last fifty years. BCH codes were invented in 1959 by Hocquenghem, and independently in 1960 by Bose and Ray-Chaudhuri...
s and Reed–Solomon codes
Reed–Solomon error correction
In coding theory, Reed–Solomon codes are non-binary cyclic error-correcting codes invented by Irving S. Reed and Gustave Solomon. They described a systematic way of building codes that could detect and correct multiple random symbol errors...
(which are a subset of BCH codes). Unlike many other decoding algorithms, and in correspondence with the code-domain Berlekamp–Massey algorithm that uses syndrome decoding and the dual of the codes, the Berlekamp–Welch decoding algorithm provides a method for decoding Reed–Solomon codes using just the generator matrix and not syndromes.
History on decoding Reed–Solomon codes
- In 1960, Peterson came up with an algorithm for decoding BCH codes. His algorithm solves the important second stage of the generalized BCH decoding procedure and is used to calculate the error locator polynomial coefficients that in turn provide the error locator polynomial. This is crucial to the decoding of BCH codes.
- In 1963, Gorenstein–Zierler saw that BCH codes and Reed–Solomon codesReed–Solomon error correctionIn coding theory, Reed–Solomon codes are non-binary cyclic error-correcting codes invented by Irving S. Reed and Gustave Solomon. They described a systematic way of building codes that could detect and correct multiple random symbol errors...
have a common generalization and that the decoding algorithm extends to more general situation. - In 1968 / 69, Elwyn BerlekampElwyn BerlekampElwyn Ralph Berlekamp is an American mathematician. He is a professor emeritus of mathematics and EECS at the University of California, Berkeley. Berlekamp is known for his work in information theory and combinatorial game theory....
invented an algorithm for decoding BCH codes. James MasseyJames MasseyJames Lee Massey is an information theorist andcryptographer, Professor Emeritus of Digital Technology at ETH Zurich. His notable work...
recognized its application to linear feedback shift registers and simplified the algorithm. Massey termed the algorithm the LFSR Synthesis Algorithm (Berlekamp Iterative Algorithm) but it is now known as the Berlekamp–Massey algorithm. - In 1986, The Welch–Berlekamp algorithm was developed to solve the decoding equation of Reed–Solomon codesReed–Solomon error correctionIn coding theory, Reed–Solomon codes are non-binary cyclic error-correcting codes invented by Irving S. Reed and Gustave Solomon. They described a systematic way of building codes that could detect and correct multiple random symbol errors...
, using a fast method to solve a certain polynomial equation. The Berlekamp – Welch algorithm has a running time complexity of . We will in the following sections look at the Gemmel and Sudan’s exposition of the Berlekamp Welch Algorithm.
. We will in the following sections look at the Gemmel and Sudan’s exposition of the Berlekamp Welch Algorithm.
Error locator polynomial of Reed–Solomon codes
In the problem of decoding Reed–Solomon codes, the inputs are pair wise distinct evaluation points ’s (i = 1, . . ., n) where
’s (i = 1, . . ., n) where  with dimension
with dimension  and distance
and distanceMinimum distance
The term minimum distance is used in several ways:* In geometry, the minimum distance of a collection of points P in a space is the smallest distance between any two points of the space....
 and a codeword
and a codeword  =
= 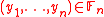 . Our goal is to describe an algorithm that can correct
. Our goal is to describe an algorithm that can correct  many errors in polynomial time. To do so we have to find a polynomial
many errors in polynomial time. To do so we have to find a polynomial 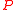 over
over  such that
such that 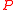 has degree less than
has degree less than  and (the number of
and (the number of  ’s such that
’s such that 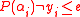 . We can assume that there exists a polynomial
. We can assume that there exists a polynomial 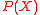 such that
such that 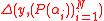 ≤
≤  or
or 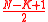 .
.Note that the coefficients of
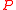 are the encoded information. To solve this, we use an indicator for those
are the encoded information. To solve this, we use an indicator for those  ’s where an error may have occurred. Thus we define
’s where an error may have occurred. Thus we define 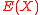 , which is an error locator polynomial over
, which is an error locator polynomial over  such that
such that 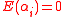 if
if 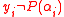 and the degree of
and the degree of  can be given by:
can be given by: 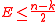 .
.-
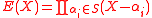 where
where 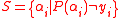
We can also claim that for every
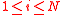 ,
, 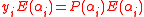 . This fact holds true because in the event of
. This fact holds true because in the event of 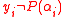 , both sides of the above equation become
, both sides of the above equation become  owing to the fact that
owing to the fact that 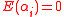 .
.However since both
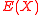 and
and 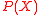 are unknown, the main task of the decoding algorithm would be to find
are unknown, the main task of the decoding algorithm would be to find 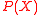 . To do this we use a seemingly useless yet very powerful method and define another polynomial
. To do this we use a seemingly useless yet very powerful method and define another polynomial 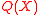 as
as 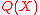 =
= 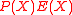 . This is because the
. This is because the  equations with
equations with  we need to solve are quadratic in nature. Thus by defining a product of two variables that gives rise to a quadratic term as one unknown variable, we increase the number of unknowns but make the equations linear in nature. This method is called linearization and is a very powerful tool.
we need to solve are quadratic in nature. Thus by defining a product of two variables that gives rise to a quadratic term as one unknown variable, we increase the number of unknowns but make the equations linear in nature. This method is called linearization and is a very powerful tool.Thus
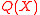 is a polynomial over
is a polynomial over  having the properties:
having the properties:
- \deg
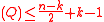
-
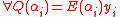
This helps because if we now manage to find
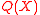 and
and 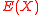 , we can easily find
, we can easily find 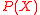 using
using  .
.The main purpose of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm is to find out
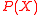 using degree bounded polynomials
using degree bounded polynomials 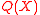 and
and  and the properties of
and the properties of  and
and  .
.Computing
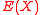 is as hard as finding the end solution, polynomial
is as hard as finding the end solution, polynomial 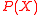 . Once
. Once 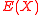 is computed, using erasure decoding for Reed–Solomon codes, we can easily recover
is computed, using erasure decoding for Reed–Solomon codes, we can easily recover 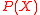 . However in a few cases, even the polynomial
. However in a few cases, even the polynomial 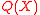 is as hard to find as
is as hard to find as  . As an example, given
. As an example, given 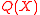 and
and  (such that
(such that  for
for 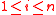 ), by checking positions where
), by checking positions where  , we can find the error locations. Thus the algorithm works on the principle that while each of the polynomials
, we can find the error locations. Thus the algorithm works on the principle that while each of the polynomials 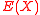 and
and 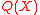 are hard to find individually; computing them together is much easier.
are hard to find individually; computing them together is much easier.The Berlekamp–Welch decoder and algorithm
The Welch–Berlekamp decoder for Reed–Solomon codes consists of the Welch– Berlekamp algorithm augmented by some additional steps that prepare the received word for the algorithm and interpret the result of the algorithm.The inputs given to the Berlekamp Welch decoder are the integers denoting Block Length
 , the number of errors
, the number of errors  such that
such that  <
< 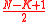 , and the received word
, and the received word 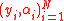 satisfying the condition that there exists at most one
satisfying the condition that there exists at most one 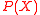 with
with  with
with  .
.The output of the decoder is either the polynomial
 , or in some cases, a failure. This decoder functions in two steps as follows:
, or in some cases, a failure. This decoder functions in two steps as follows:
- This step is called the interpolation step in which the decoder computes a non zero polynomial
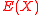 of degree e and another polynomial
of degree e and another polynomial 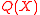 with deg
with deg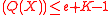 . These polynomials are created such that the condition
. These polynomials are created such that the condition 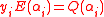 for all
for all 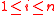 . In the case that polynomials satisfying the above condition cannot be computed, the output of the decoder would be a failure.
. In the case that polynomials satisfying the above condition cannot be computed, the output of the decoder would be a failure. - If
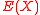 divides
divides  , then a
, then a  ’
’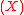 is defined which equals
is defined which equals 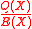 . If
. If 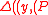 ’
’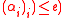 , then the decoder outputs
, then the decoder outputs  ’
’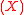 . If the above condition is not satisfied, i.e. if
. If the above condition is not satisfied, i.e. if 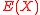 does not divide
does not divide 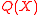 then a failure is returned by the decoder.
then a failure is returned by the decoder.
According to the algorithm, in the cases where it does not output a failure, it outputs a
 that is the correct and desired polynomial. To prove that, the algorithm always outputs the desired polynomial, we need to prove a few claims we have made while describing the algorithm. Let us go ahead and do so now.
that is the correct and desired polynomial. To prove that, the algorithm always outputs the desired polynomial, we need to prove a few claims we have made while describing the algorithm. Let us go ahead and do so now.Claim 1: There exist a pair of polynomials
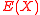 and
and 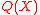 that satisfy Step 1 of the BW algorithm such that
that satisfy Step 1 of the BW algorithm such that 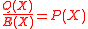 .
.Let E(x) be the error-locating polynomial for
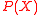 such that
such that 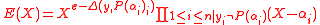 and let
and let 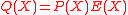 . Note that
. Note that 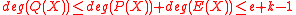 . We also stated that
. We also stated that 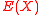 is a polynomial of degree exactly
is a polynomial of degree exactly  . Note that
. Note that 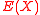 is a polynomial following the property that
is a polynomial following the property that 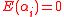 if and only if
if and only if 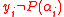 .We can now state that
.We can now state that 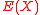 and
and 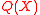 satisfy the equation
satisfy the equation 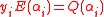 from the first step of the BW algorithm. If
from the first step of the BW algorithm. If  , then
, then 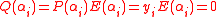 . However whenever
. However whenever  , we can easily state that
, we can easily state that  and therefore also state that
and therefore also state that  just as we claimed.
just as we claimed.This above claim however just reiterates and proves the fact that there exists a pair of polynomials
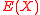 and
and  such that
such that  =
=  . It however does not necessarily guarantee the fact that the algorithm we discussed above would indeed output such a pair of polynomials. We therefore move on to look at another claim that helps establish this fact using the above claim and thereby proving the correctness of the algorithm.
. It however does not necessarily guarantee the fact that the algorithm we discussed above would indeed output such a pair of polynomials. We therefore move on to look at another claim that helps establish this fact using the above claim and thereby proving the correctness of the algorithm.Claim 2: For any two distinct solutions
 that satisfy the first step of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm given above, they will also satisfy the equation
that satisfy the first step of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm given above, they will also satisfy the equation 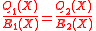
The total degrees of the polynomials
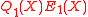 and
and 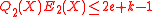 . We define another polynomial
. We define another polynomial  ....................................(i)
....................................(i)Note that
 such that
such that  . From step 1 of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm we also know that
. From step 1 of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm we also know that 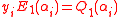 and
and  ) ........…..........(ii)
) ........…..........(ii)Now, substituting the values of
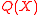 from equation (ii) into equation (i), we get:
from equation (ii) into equation (i), we get: for
for 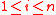 .
.Thus, the above polynomial
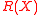 has
has  roots and
roots and  which implies that
which implies that  <
<  because of the upper bound on
because of the upper bound on  .
.Since
 <
<  , we can come to the conclusion that the polynomials
, we can come to the conclusion that the polynomials  and
and 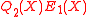 agree on more points than their degree, and hence they are identical. Note that since
agree on more points than their degree, and hence they are identical. Note that since 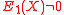 and
and 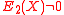 , it can be implied that
, it can be implied that 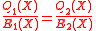 as per our initial claim.
as per our initial claim.Thus based on the above claims, we can safely state that the output of the Berlekamp Welch algorithm, when outputting the polynomial
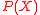 is correct.
is correct.We can now claim that the algorithm can be implemented such that it has a running time of
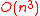 . This can be proved as follows:
. This can be proved as follows:In Step 1 of the algorithm, the polynomials
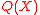 and
and 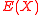 have
have  and
and  unknown values respectively and the constraints
unknown values respectively and the constraints 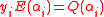 for all
for all 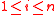 acts as a linear equation with these unknowns. We therefore get a system of
acts as a linear equation with these unknowns. We therefore get a system of  linear equations in
linear equations in  <
<  unknowns. Using our first claim, this system of equations has a solution since the degree of polynomial
unknowns. Using our first claim, this system of equations has a solution since the degree of polynomial 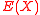 is
is  . This can be solved in
. This can be solved in 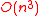 time, by say Gaussian elimination. Finally, we can note that Step 2 of the algorithm can also be implemented in time
time, by say Gaussian elimination. Finally, we can note that Step 2 of the algorithm can also be implemented in time 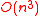 by "long division" method.
by "long division" method.Hence we can state that the Berlekamp Welch algorithm can be used to uniquely decode any
 Reed–Solomon code in
Reed–Solomon code in  time for a maximum of
time for a maximum of 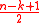 errors.
errors.External links
- MIT Lecture Notes on Essential Coding Theory – Dr. Madhu Sudan
- University at Buffalo Lecture Notes on Coding Theory – Dr. Atri Rudra
- Algebraic Codes on Lines, Planes and Curves, An Engineering Approach – Richard E. Blahut
- Welch Berlekamp Decoding of Reed–Solomon Codes – L. R. Welch – The patent by Lloyd R. Welch and Elewyn R. Berlekamp

