Allochthon
Encyclopedia
- In structural geologyStructural geologyStructural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation in the rocks, and...
, an allochthon (or allochthonous block) is a large block of rock which has been moved from its original site of formation, usually by low angle thrust faultingThrust faultA thrust fault is a type of fault, or break in the Earth's crust across which there has been relative movement, in which rocks of lower stratigraphic position are pushed up and over higher strata. They are often recognized because they place older rocks above younger...
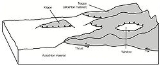
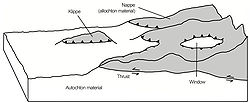
. An allochthon which is isolated from the rock that pushed it into position is called a klippeKlippethumb|right|350px|Schematic overview of a thrust system. The shaded material is called a [[nappe]]. The erosional hole is called a [[window |window or fenster]]. The klippe is the isolated block of the nappe overlying autochthonous material....
. If an allochthon has a "hole" in it so that one can view the autochthon beneath the allochthon, the hole is called a "windowWindow (geology)thumb|right|350px|Schematic overview of a thrust system. The [[fault |hanging wall block]] is called a [[nappe]]. If an [[erosion]]al hole is created in the nappe that is called a window. A [[klippe]] is a solitary outcrop of the nappe in the middle of autochthonous material.A tectonic window...
" (or Fenster). Etymology: Greek; 'allo' = other, and 'chthon' = earth.
- In limnologyLimnologyLimnology , also called freshwater science, is the study of inland waters. It is often regarded as a division of ecology or environmental science. It covers the biological, chemical, physical, geological, and other attributes of all inland waters...
, allochthonous sources of carbon or nutrients come from outside the aquatic system (such as plant and soil material). Carbon sources from within the system, such as algae and the microbial breakdown of particulate organic carbon, are autochthonous. In streams and small lakes, allochthonous sources of carbon are dominant while in large lakes and the ocean, autochthonous sources dominate. (Eby, 2004)
NB: The term "allochtonous" is also used in the social sciences, as the opposite to autochthonous.

