
Akbulut cork
Encyclopedia
In topology
an Akbulut cork is a structure is frequently used to show that in four dimensions, the smooth h-cobordism
theorem fails. It was named after Selman Akbulut
.
The basic idea of the Akbulut cork is that when attempting to use the h-corbodism theorem in four dimensions, the cork is the sub-cobordism that contains all the exotic properties of the spaces connected with the cobordism, and when removed the two spaces become trivially h-cobordant and smooth. This shows that in four dimensions, although the theorem does not tell us that two manifold
s are diffeomorphic (only homeomorphic), they are "not far" from being diffeomorphic.
To illustrate this (without proof), consider a smooth h-cobordism W5 between two 4-manifolds M and N. Then within W there is a sub-cobordism K5 between A4 ⊂ M and B4 ⊂ N and there is a diffeomorphism
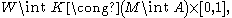
which is the content of the h-cobordism theorem for n ≥ 5 (here int X refers to the interior of a manifold X). In addition, A and B are diffeomorphic with a diffeomorphism that is an involution
on the boundary ∂A = ∂B. Therefore it can be seen that the h-corbordism K connects A with its "inverted" image B. This submanifold A is the Akbulut cork.
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
an Akbulut cork is a structure is frequently used to show that in four dimensions, the smooth h-cobordism
H-cobordism
A cobordism W between M and N is an h-cobordism if the inclusion mapsare homotopy equivalences...
theorem fails. It was named after Selman Akbulut
Selman Akbulut
Selman Akbulut is a Turkish mathematician and a Professor at Michigan State University. He got his Ph.D. at the University of California, Berkeley in 1975 as a student of Robion Kirby...
.
The basic idea of the Akbulut cork is that when attempting to use the h-corbodism theorem in four dimensions, the cork is the sub-cobordism that contains all the exotic properties of the spaces connected with the cobordism, and when removed the two spaces become trivially h-cobordant and smooth. This shows that in four dimensions, although the theorem does not tell us that two manifold
Manifold
In mathematics , a manifold is a topological space that on a small enough scale resembles the Euclidean space of a specific dimension, called the dimension of the manifold....
s are diffeomorphic (only homeomorphic), they are "not far" from being diffeomorphic.
To illustrate this (without proof), consider a smooth h-cobordism W5 between two 4-manifolds M and N. Then within W there is a sub-cobordism K5 between A4 ⊂ M and B4 ⊂ N and there is a diffeomorphism
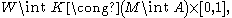
which is the content of the h-cobordism theorem for n ≥ 5 (here int X refers to the interior of a manifold X). In addition, A and B are diffeomorphic with a diffeomorphism that is an involution
Involute
In the differential geometry of curves, an involute is a curve obtained from another given curve by attaching an imaginary taut string to the given curve and tracing its free end as it is wound onto that given curve; or in reverse, unwound. It is a roulette wherein the rolling curve is a straight...
on the boundary ∂A = ∂B. Therefore it can be seen that the h-corbordism K connects A with its "inverted" image B. This submanifold A is the Akbulut cork.

