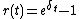Accumulation function
Encyclopedia
The accumulation function a(t) is a function defined in terms of time t expressing the ratio of the value at time t (future value
) and the initial investment (present value
). It is used in interest theory.
Thus a(0)=1 and the value at time t is given by:
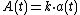 .
.
where the initial investment is k.
Examples:
In the case of a positive rate of return
, as in the case of interest, the accumulation function is an increasing function.
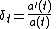
which is the rate of change with time of the natural logarithm of the accumulation function.
Conversely:
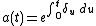
reducing to
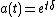
for constant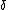 .
.
The effective annual percentage rate
at any time is: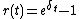
Future value
Future value is the value of an asset at a specific date. It measures the nominal future sum of money that a given sum of money is "worth" at a specified time in the future assuming a certain interest rate, or more generally, rate of return; it is the present value multiplied by the accumulation...
) and the initial investment (present value
Present value
Present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a future payment or series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money and other factors such as investment risk...
). It is used in interest theory.
Thus a(0)=1 and the value at time t is given by:
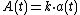 .
.where the initial investment is k.
Examples:
- simple interest:
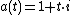
- compound interestCompound interestCompound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
: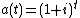
- simple discount:
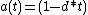
- compound discount:
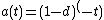
In the case of a positive rate of return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
, as in the case of interest, the accumulation function is an increasing function.
Variable rate of return
The logarithmic or continuously compounded return, sometimes called force of interest, is a function of time defined as follows: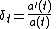
which is the rate of change with time of the natural logarithm of the accumulation function.
Conversely:
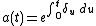
reducing to
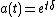
for constant
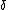 .
.The effective annual percentage rate
Annual percentage rate
The term annual percentage rate , also called nominal APR, and the term effective APR, also called EAR, describe the interest rate for a whole year , rather than just a monthly fee/rate, as applied on a loan, mortgage loan, credit card, etc. It is a finance charge expressed as an annual rate...
at any time is: