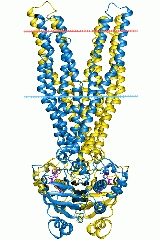
ATP-binding domain of ABC transporters
Encyclopedia
In molecular biology, ATP-binding domain of ABC transporters is a water-soluble domain
of transmembrane ABC transporters.
ABC transporters belong to the ATP-Binding Cassette superfamily, which uses the hydrolysis of ATP
to translocate a variety of compounds across biological membranes. ABC transporters are minimally constituted of two conserved regions: a highly conserved ATP binding cassette (ABC) and a less conserved transmembrane domain (TMD). These regions can be found on the same protein or on two different ones. Most ABC transporters function as a dimer and therefore are constituted of four domains, two ABC modules and two TMDs.
, and a magnesium binding site: Walker B. Besides these two regions, three other conserved motifs are present in the ABC cassette: the switch region which contains a histidine loop, postulated to polarize the attacking water molecule for hydrolysis, the signature conserved motif (LSGGQ) specific to the ABC transporter, and the Q-motif (between Walker A and the signature), which interacts with the gamma phosphate through a water bond. The Walker A, Walker B, Q-loop and switch region form the nucleotide binding site.
; ABCA10; ABCA12
; ABCA13
; ABCA2
; ABCA3
; ABCA4
; ABCA5;
ABCA6; ABCA7
; ABCA8
; ABCA9
; ABCB1; ABCB10; ABCB11
; ABCB4
;
ABCB5
; ABCB6
; ABCB7
; ABCB8
; ABCB9
; ABCC1
; ABCC10
; ABCC11
;
ABCC12
; ABCC2
; ABCC3
; ABCC4
; ABCC5
; ABCC6
; ABCC8
; ABCC9
;
ABCD1
; ABCD2
; ABCD3
; ABCD4
; ABCE1; ABCF1
; ABCF2
; ABCF3;
ABCG1
; ABCG2
; ABCG4
; ABCG5
; ABCG8
; CFTR
; MRP3; TAP1
;
TAP2
; TAPL;
Protein domain
A protein domain is a part of protein sequence and structure that can evolve, function, and exist independently of the rest of the protein chain. Each domain forms a compact three-dimensional structure and often can be independently stable and folded. Many proteins consist of several structural...
of transmembrane ABC transporters.
ABC transporters belong to the ATP-Binding Cassette superfamily, which uses the hydrolysis of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
to translocate a variety of compounds across biological membranes. ABC transporters are minimally constituted of two conserved regions: a highly conserved ATP binding cassette (ABC) and a less conserved transmembrane domain (TMD). These regions can be found on the same protein or on two different ones. Most ABC transporters function as a dimer and therefore are constituted of four domains, two ABC modules and two TMDs.
Biological function
ABC transporters are involved in the export or import of a wide variety of substrates ranging from small ions to macromolecules. The major function of ABC import systems is to provide essential nutrients to bacteria. They are found only in prokaryotes and their four constitutive domains are usually encoded by independent polypeptides (two ABC proteins and two TMD proteins). Prokaryotic importers require additional extracytoplasmic binding proteins (one or more per systems) for function. In contrast, export systems are involved in the extrusion of noxious substances, the export of extracellular toxins and the targeting of membrane components. They are found in all living organisms and in general the TMD is fused to the ABC module in a variety of combinations. Some eukaryotic exporters encode the four domains on the same polypeptide chain.Amino acid sequence
The ABC module (approximately two hundred amino acid residues) is known to bind and hydrolyze ATP, thereby coupling transport to ATP hydrolysis in a large number of biological processes. The cassette is duplicated in several subfamilies. Its primary sequence is highly conserved, displaying a typical phosphate-binding loop: Walker AWalker motifs
The Walker A and Walker B motifs are protein sequence motifs. These were first reported in ATP-binding proteins by Walker and co-workers in 1982.-Walker A motif:...
, and a magnesium binding site: Walker B. Besides these two regions, three other conserved motifs are present in the ABC cassette: the switch region which contains a histidine loop, postulated to polarize the attacking water molecule for hydrolysis, the signature conserved motif (LSGGQ) specific to the ABC transporter, and the Q-motif (between Walker A and the signature), which interacts with the gamma phosphate through a water bond. The Walker A, Walker B, Q-loop and switch region form the nucleotide binding site.
3D structure
The 3D structure of a monomeric ABC module adopts a stubby L-shape with two distinct arms. ArmI (mainly beta-strand) contains Walker A and Walker B. The important residues for ATP hydrolysis and/or binding are located in the P-loop. The ATP-binding pocket is located at the extremity of armI. The perpendicular armII contains mostly the alpha helical subdomain with the signature motif. It only seems to be required for structural integrity of the ABC module. ArmII is in direct contact with the TMD. The hinge between armI and armII contains both the histidine loop and the Q-loop, making contact with the gamma phosphate of the ATP molecule. ATP hydrolysis leads to a conformational change that could facilitate ADP release. In the dimer the two ABC cassettes contact each other through hydrophobic interactions at the antiparallel beta-sheet of armI by a two-fold axis.Human proteins containing this domain
ABCA1ABCA1
ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCA1 , also known as the cholesterol efflux regulatory protein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCA1 gene...
; ABCA10; ABCA12
ABCA12
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA12 gene....
; ABCA13
ABCA13
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 13 also known as ABCA13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA13 gene on chromosome 7. It belongs to the wide ATP-binding cassette family of proteins...
; ABCA2
ABCA2
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA2 gene.- External links :...
; ABCA3
ABCA3
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA3 gene.It is associated with Surfactant metabolism dysfunction type 3.- External links :...
; ABCA4
ABCA4
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family A , member 4, also known as ABCA4 or ABCR, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCA4 gene....
; ABCA5;
ABCA6; ABCA7
ABCA7
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA7 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes...
; ABCA8
ABCA8
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA8 gene.-Further reading:...
; ABCA9
ABCA9
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCA9 gene.-Further reading:...
; ABCB1; ABCB10; ABCB11
ABCB11
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family B member 11 also known as ABCB11 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ABCB11 gene.- Function :...
; ABCB4
ABCB4
Multidrug resistance protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB4 gene. ABCB4 is associated with progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3.-External links:...
;
ABCB5
ABCB5
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 5 also known as P-glycoprotein ABCB5 is a plasma membrane-spanning protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB5 gene...
; ABCB6
ABCB6
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 6, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB6 gene.- External links :...
; ABCB7
ABCB7
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 7, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB7 gene.-Interactions:ABCB7 has been shown to interact with Ferrochelatase.- External Links :*...
; ABCB8
ABCB8
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 8, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB8 gene.-Further reading:...
; ABCB9
ABCB9
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB9 gene.- External links :...
; ABCC1
ABCC1
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC1 gene.ABCC1 clears beta-amyloid from brains of mice and can be activated by thiethylperazine.- External links :...
; ABCC10
ABCC10
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC10 gene.- External links :...
; ABCC11
ABCC11
ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC11 gene.- External links :...
;
ABCC12
ABCC12
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC12 gene.-Further reading:...
; ABCC2
ABCC2
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 also called canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 1 or ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC2 gene....
; ABCC3
ABCC3
Canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC3 gene.- External links :...
; ABCC4
ABCC4
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 4 , also known as the multidrug resistance-associated protein 4 or multi-specific organic anion transporter B , is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC4 gene....
; ABCC5
ABCC5
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC5 gene.- External links :...
; ABCC6
ABCC6
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6 also known as ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 and multi-specific organic anion transporter E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC6 gene...
; ABCC8
ABCC8
ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC8 gene. ABCC8 orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.-External links:* *...
; ABCC9
ABCC9
ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C member 9 also known as sulfonylurea receptor 2 is a ATP-binding cassette transporter that in humans is encoded by the ABCC9 gene.- Function :...
;
ABCD1
ABCD1
ABCD1 is a protein that transfers fatty acids into peroxisomes.The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct...
; ABCD2
ABCD2
ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD2 gene.- External links :...
; ABCD3
ABCD3
ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD3 gene.- External links :*...
; ABCD4
ABCD4
ATP-binding cassette sub-family D member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCD4 gene.- External links :...
; ABCE1; ABCF1
ABCF1
ATP-binding cassette sub-family F member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCF1 gene.- External links :...
; ABCF2
ABCF2
ATP-binding cassette sub-family F member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCF2 gene.- External links :...
; ABCF3;
ABCG1
ABCG1
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG1 gene. It is a homolog of the well-known Drosophila gene white.- External links :...
; ABCG2
ABCG2
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG2 gene. ABCG2 has also been designated as CDw338 . - External links :...
; ABCG4
ABCG4
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG4 gene.- External links :...
; ABCG5
ABCG5
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG5 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes...
; ABCG8
ABCG8
ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCG8 gene.- External links :...
; CFTR
CFTR
CFTR is:*Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, a protein involved in the transport of chloride ions across cell membranes or the gene that encodes this protein*CFTR inhibitory factor, a protein virulence factor...
; MRP3; TAP1
TAP1
Antigen peptide transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAP1 gene.-Interactions:TAP1 has been shown to interact with Tapasin and HLA-A.-Further reading:...
;
TAP2
TAP2
TAP2 is a gene in humans that encodes the protein Antigen peptide transporter 2....
; TAPL;

