
ABNT NBR 15606
Encyclopedia
ABNT NBR 15606 refers to a collection of technical standards that govern the transmission of digital terrestrial television in Brazil.
The data coding aspects of the Brazilian Digital Terrestrial Television Standards are described in the following documents published by ABNT, the Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas): ABNT NBR 15606-1:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 1: Data coding; ABNT NBR 15606-2:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 2: Ginga-NCL for fixed and mobile receivers: XML application language for application coding; ABNT NBR 15606-3:2007- Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 3: Data transmission specifications for digital broadcasting; and ABNT NBR 15606-5:2008 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification – Part 5: Ginga
-NCL
for portable receivers: XML
application language for application coding.
The standard was written by telecommunications and television experts from many countries with their works coordinated by the SBTVD Forum and cover in detail all the aspects of video and audio coding that applies to SBTVD
. The complete document can be found and downloaded freely in English, Spanish and Portuguese at ABNT's website.
The standard addresses one of the main advances regarding the middleware specification, one of the Brazilian digital television system. The middleware specification comprises a procedural portion, performed by Java, and a declarative portion, performed by NCL
and Lua, with a bridge that allow for mutual access between them. The combined Brazilian middleware specification is called Ginga
.
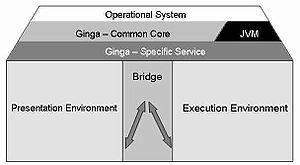 Brazil will have a unique joint implementation of declarative and procedural middleware and the bridge between them. The Brazilian data coding system is called Ginga
Brazil will have a unique joint implementation of declarative and procedural middleware and the bridge between them. The Brazilian data coding system is called Ginga
and comprises the language specification used by the presentation engine Ginga-NCL, the monomidia coding and GEM
compliant Java presentation engine.
The lower level protocol is the data carrousel for transmission of a data block without any kind of semantics. On the upper level the object carrousel allows the transmission of file, archives, applications, folders and event synchronization. Object carrousel is not part of the Japanese ARIB
standards, but rather defined on DVB and ATSC standards.
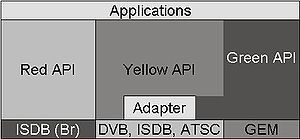 NCL
NCL
, Nested Context Language, is a XML
application language recommendation that allows authors to write interactive multimedia presentations in a very simple and efficient manner. Using NCL, an author can describe the temporal behavior of a multimedia presentation, associate hyperlinks (user interaction) with media objects, define alternatives for presentation (adaptation), and describe the layout of the presentation on multiple devices. Unlike HTML
or XHTML
, NCL has a stricter separation between content and structure and provides non-invasive control of presentation linking and layout. Therefore NCL does not define any media itself. Instead, it defines the glue that holds media together in multimedia presentations.
The procedural part defines a generic interface between interactive digital applications and the terminals on which those applications are executed. It enables digital content providers to address all types of terminals ranging from low-end to high-end receivers with flexibility and portability. The specification also includes a special profile for portable reception.
These documents are also officially available at ABNT website.
The documents describing the reference specification of Ginga are ABNT NBR 15606-1:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 1: Data coding; ABNT NBR 15606-2:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 2: Ginga-NCL for fixed and mobile receivers: XML application language for application coding; ABNT NBR 15606-3:2007- Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 3: Data transmission specifications for digital broadcasting; and ABNT NBR 15606-5:2008 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification – Part 5: Ginga-NCL for portable receivers: XML application language for application coding.
The data coding aspects of the Brazilian Digital Terrestrial Television Standards are described in the following documents published by ABNT, the Brazilian Association of Technical Standards (Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas): ABNT NBR 15606-1:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 1: Data coding; ABNT NBR 15606-2:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 2: Ginga-NCL for fixed and mobile receivers: XML application language for application coding; ABNT NBR 15606-3:2007- Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 3: Data transmission specifications for digital broadcasting; and ABNT NBR 15606-5:2008 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification – Part 5: Ginga
Ginga (SBTVD Middleware)
Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers...
-NCL
Nested Context Language
Nested Context Language is a declarative authoring language for hypermedia documents.NCL is an XML application language, which provides several facilities for authoring a complete hypermedia document with synchronization relationships among its components...
for portable receivers: XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
application language for application coding.
The standard was written by telecommunications and television experts from many countries with their works coordinated by the SBTVD Forum and cover in detail all the aspects of video and audio coding that applies to SBTVD
SBTVD
ISDB-T International or SBTVD, short for Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital is a technical standard for digital television broadcast used in Brazil, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Venezuela, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Philippines, Bolivia, Nicaragua and Uruguay, based on the Japanese ISDB-T...
. The complete document can be found and downloaded freely in English, Spanish and Portuguese at ABNT's website.
The standard addresses one of the main advances regarding the middleware specification, one of the Brazilian digital television system. The middleware specification comprises a procedural portion, performed by Java, and a declarative portion, performed by NCL
Nested Context Language
Nested Context Language is a declarative authoring language for hypermedia documents.NCL is an XML application language, which provides several facilities for authoring a complete hypermedia document with synchronization relationships among its components...
and Lua, with a bridge that allow for mutual access between them. The combined Brazilian middleware specification is called Ginga
Ginga (SBTVD Middleware)
Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers...
.
Document technical overview

Ginga (SBTVD Middleware)
Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers...
and comprises the language specification used by the presentation engine Ginga-NCL, the monomidia coding and GEM
Globally Executable MHP
Globally Executable MHP is a DVB specification of a Java based middleware for TV broadcast receivers, IPTV terminals and Blu-ray players. GEM is an ETSI standard and an ITU "Recommendation...
compliant Java presentation engine.
The lower level protocol is the data carrousel for transmission of a data block without any kind of semantics. On the upper level the object carrousel allows the transmission of file, archives, applications, folders and event synchronization. Object carrousel is not part of the Japanese ARIB
Arib
Arib is a town in northern Algeria....
standards, but rather defined on DVB and ATSC standards.

Nested Context Language
Nested Context Language is a declarative authoring language for hypermedia documents.NCL is an XML application language, which provides several facilities for authoring a complete hypermedia document with synchronization relationships among its components...
, Nested Context Language, is a XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
application language recommendation that allows authors to write interactive multimedia presentations in a very simple and efficient manner. Using NCL, an author can describe the temporal behavior of a multimedia presentation, associate hyperlinks (user interaction) with media objects, define alternatives for presentation (adaptation), and describe the layout of the presentation on multiple devices. Unlike HTML
HTML
HyperText Markup Language is the predominant markup language for web pages. HTML elements are the basic building-blocks of webpages....
or XHTML
XHTML
XHTML is a family of XML markup languages that mirror or extend versions of the widely-used Hypertext Markup Language , the language in which web pages are written....
, NCL has a stricter separation between content and structure and provides non-invasive control of presentation linking and layout. Therefore NCL does not define any media itself. Instead, it defines the glue that holds media together in multimedia presentations.
The procedural part defines a generic interface between interactive digital applications and the terminals on which those applications are executed. It enables digital content providers to address all types of terminals ranging from low-end to high-end receivers with flexibility and portability. The specification also includes a special profile for portable reception.
These documents are also officially available at ABNT website.
Summary
The performance levels for the Ginga middleware exceeds the current levels achieved by similar systems by using smaller and more efficient script languages, like Lua. Also, the combination of a procedural and declarative programming languages in one single system allow for the creating of a greater set of applications with minimum effort to the programmer. The transmission of interactive application within free-to-air programming will improve broadcasters relashionship with its audience.The documents describing the reference specification of Ginga are ABNT NBR 15606-1:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 1: Data coding; ABNT NBR 15606-2:2007 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 2: Ginga-NCL for fixed and mobile receivers: XML application language for application coding; ABNT NBR 15606-3:2007- Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification - Part 3: Data transmission specifications for digital broadcasting; and ABNT NBR 15606-5:2008 - Digital terrestrial television - Data coding and transmission specification – Part 5: Ginga-NCL for portable receivers: XML application language for application coding.
External links
- ABNT website http://www.abnt.org.br/tvdigital
 Brazil
Brazil - SBTVD Forum SBTVD Forum website http://www.forumsbtvd.org.br/
 Brazil
Brazil - ARIBAribArib is a town in northern Algeria....
Association of Radio Industries and Businesses website http://www.arib.or.jp/english/ Japan
Japan - DiBEGDiBEGDiBEG was founded in September 1997 to promote ISDB-T International, the Digital Broadcasting System, in the world....
Digital Broadcasting Experts Group website http://www.dibeg.org/ Japan
Japan

