
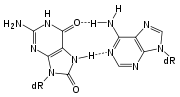
8-oxoguanine
Encyclopedia
8-Oxoguanine is one of the most common DNA lesions resulting from reactive oxygen species
and can result in a mismatched pairing with Adenine
resulting in G to T and C to A substitutions in the genome. In humans, it is primarily repaired by the DNA glycosylase OGG1. It can be caused by ionizing radiation
, in connection with oxidative metabolism.
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
and can result in a mismatched pairing with Adenine
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
resulting in G to T and C to A substitutions in the genome. In humans, it is primarily repaired by the DNA glycosylase OGG1. It can be caused by ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
, in connection with oxidative metabolism.


