1-Methylimidazole
Encyclopedia
1-Methylimidazole or N-Methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. Its N-methylation removes the possibility of tautomerization, which occurs in imidazole
and many imidazole derivatives. 1-Methylimidazole maintains the pyridine-like nitrogen of imidazole, only with a slightly higher pKa. The methylation also provides a significantly lower melting point, which makes 1-methylimidazole a useful solvent.
1-Methylimidazole has found use as a solvent, a base, a catalyst, a mimic for purine nucleoside bases and histidine and histamine, and as an ionic liquid precursor.
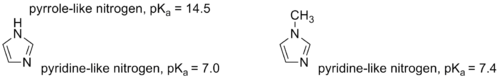
from glyoxal
, formaldehyde
, and a mixture of ammonia
and methylamine
.
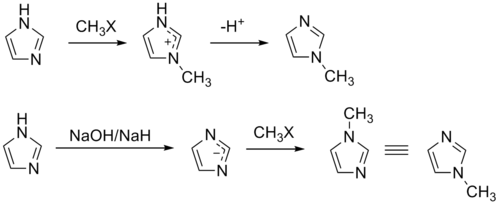
The compound can also be synthesized on a laboratory scale by methylation
of imidazole at the pyridine
-like nitrogen and subsequent deprotonation. Similarly, 1-methylimidazole may be synthesized by first deprotonating imidazole to form a sodium salt followed by methylation.
1-Methylimidazole and its derivatives have been used to mimic aspects of these biomolecules. These mimics can be useful in studies to elucidate biological mechanisms and as portions of synthetic bioactive molecules.
1-Methylimidazole is also the precursor for the synthesis of the methylimidazole monomer of pyrrole-imidazole polyamides. These polymers can selectively bind specific sequences of double-stranded DNA by intercalating in a sequence dependent manner.
s result, e.g. 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
("BMIMPF6"):
BASF has used 1-methylimidazole as a means to remove acid during their industrial-scale production of diethoxyphenylphosphine. In this biphasic acid scavenging using ionic liquids (BASIL) process, 1-methylimidazole reacts with HCl to produce 1-methylimidazolium chloride, a salt that is easily separated and deprotonated to regenerate 1-methylimidazole.
Imidazole
Imidazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H4N2. This aromatic heterocyclic is a diazole and is classified as an alkaloid. Imidazole refers to the parent compound, whereas imidazoles are a class of heterocycles with similar ring structure, but varying substituents...
and many imidazole derivatives. 1-Methylimidazole maintains the pyridine-like nitrogen of imidazole, only with a slightly higher pKa. The methylation also provides a significantly lower melting point, which makes 1-methylimidazole a useful solvent.
1-Methylimidazole has found use as a solvent, a base, a catalyst, a mimic for purine nucleoside bases and histidine and histamine, and as an ionic liquid precursor.
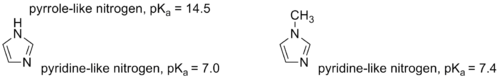
Synthesis
1-Methylimidazole is synthesized on an industrial scale by the Radziszewski reactionDebus-Radziszewski imidazole synthesis
The Debus-Radziszewski imidazole synthesis is an organic reaction describing the synthesis of an imidazole from a diketone, an aldehyde and ammonia...
from glyoxal
Glyoxal
Glyoxal is an organic compound with the formula OCHCHO. This yellow colored liquid is the smallest dialdehyde . Its tautomer acetylenediol is unstable.-Production:...
, formaldehyde
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde is an organic compound with the formula CH2O. It is the simplest aldehyde, hence its systematic name methanal.Formaldehyde is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent odor. It is an important precursor to many other chemical compounds, especially for polymers...
, and a mixture of ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
and methylamine
Methylamine
Methylamine is the organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colourless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one H atom replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine. It is sold as a solution in methanol, ethanol, THF, and water, or as the anhydrous gas in pressurized...
.
The compound can also be synthesized on a laboratory scale by methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
of imidazole at the pyridine
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one C-H group replaced by a nitrogen atom...
-like nitrogen and subsequent deprotonation. Similarly, 1-methylimidazole may be synthesized by first deprotonating imidazole to form a sodium salt followed by methylation.
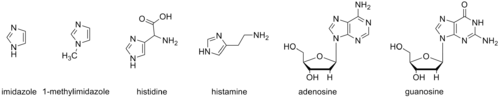
Biomolecule analog
The imidazole backbone is an essential functional unit in biology. The amino acid histidine, the signaling molecule histamine, and the purine nucleobases all contain an imidazole ring.
1-Methylimidazole and its derivatives have been used to mimic aspects of these biomolecules. These mimics can be useful in studies to elucidate biological mechanisms and as portions of synthetic bioactive molecules.
1-Methylimidazole is also the precursor for the synthesis of the methylimidazole monomer of pyrrole-imidazole polyamides. These polymers can selectively bind specific sequences of double-stranded DNA by intercalating in a sequence dependent manner.
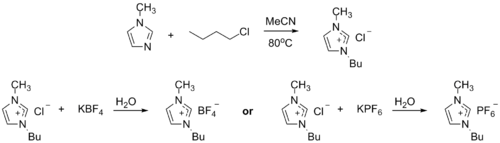
Ionic liquid precursor
1-Methylimidazole alkylates to form dialkyl imidazolium salts. Depending on the alkylating agent and the counteranion, various ionic liquidIonic liquid
An ionic liquid is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below some arbitrary temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ILs are largely made...
s result, e.g. 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water soluble ionic liquid. Together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIM-BF4, it is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids and is commercially available...
("BMIMPF6"):
BASF has used 1-methylimidazole as a means to remove acid during their industrial-scale production of diethoxyphenylphosphine. In this biphasic acid scavenging using ionic liquids (BASIL) process, 1-methylimidazole reacts with HCl to produce 1-methylimidazolium chloride, a salt that is easily separated and deprotonated to regenerate 1-methylimidazole.
- 2 MeC3N2H3 + C6H5PCl2 + 2 C2H5OH → 2 [MeC3N2H4]Cl + C6H5P(OC2H5)2