
Worldwide Governance Indicators
Encyclopedia
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
, the Worldwide Governance Indicators capture six key dimensions of governance
Governance
Governance is the act of governing. It relates to decisions that define expectations, grant power, or verify performance. It consists of either a separate process or part of management or leadership processes...
(Voice & Accountability, Political Stability and Lack of Violence, Government
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
Effectiveness, Regulatory Quality, Rule of Law
Rule of law
The rule of law, sometimes called supremacy of law, is a legal maxim that says that governmental decisions should be made by applying known principles or laws with minimal discretion in their application...
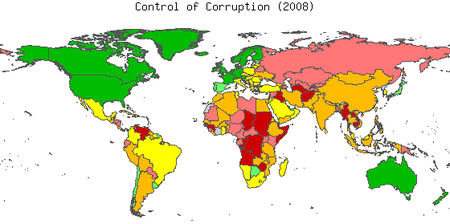
, and Control of Corruption
Political corruption
Political corruption is the use of legislated powers by government officials for illegitimate private gain. Misuse of government power for other purposes, such as repression of political opponents and general police brutality, is not considered political corruption. Neither are illegal acts by...
) between 1996 and present. They measure the quality of governance in over 200 countries
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
, based on close to 40 data sources produced by over 30 different organizations worldwide and are updated on an annual basis since 2002.
The governance indicators contribute to the growing empirical research of governance which have provided activists
Activism
Activism consists of intentional efforts to bring about social, political, economic, or environmental change. Activism can take a wide range of forms from writing letters to newspapers or politicians, political campaigning, economic activism such as boycotts or preferentially patronizing...
and reformers
Reform movement
A reform movement is a kind of social movement that aims to make gradual change, or change in certain aspects of society, rather than rapid or fundamental changes...
worldwide with advocacy
Advocacy
Advocacy is a political process by an individual or a large group which normally aims to influence public-policy and resource allocation decisions within political, economic, and social systems and institutions; it may be motivated from moral, ethical or faith principles or simply to protect an...
tools for policy reform and monitoring. The indicators, and the underlying data behind them, are part of the current research and opinions that have reinforced the experiences and observations of reform-minded individuals in government, civil society
Civil society
Civil society is composed of the totality of many voluntary social relationships, civic and social organizations, and institutions that form the basis of a functioning society, as distinct from the force-backed structures of a state , the commercial institutions of the market, and private criminal...
, and the private sector, that good governance
Good governance
Good governance is an indeterminate term used in development literature to describe how public institutions conduct public affairs and manage public resources in order to guarantee the realization of human rights. Governance describes "the process of decision-making and the process by which...
is key for development
International development
International development or global development is a concept that lacks a universally accepted definition, but it is most used in a holistic and multi-disciplinary context of human development — the development of greater quality of life for humans...
. Their growing recognition of the link between good governance and successful development, as empirical evidence suggests, has stimulated demand for monitoring the quality of governance across countries and within individual countries over time. Virtually all of the individual data sources underlying the aggregate indicators are, along with the aggregate indicators themselves, publicly available.
The Worldwide Governance Indicators are a compilation of the perceptions of a very diverse group of respondents, collected in large number of surveys
Statistical survey
Survey methodology is the field that studies surveys, that is, the sample of individuals from a population with a view towards making statistical inferences about the population using the sample. Polls about public opinion, such as political beliefs, are reported in the news media in democracies....
and other cross-country assessments
Evaluation
Evaluation is systematic determination of merit, worth, and significance of something or someone using criteria against a set of standards.Evaluation often is used to characterize and appraise subjects of interest in a wide range of human enterprises, including the arts, criminal justice,...
of governance. Some of these instruments capture the views of firms, individuals, and public officials in the countries being assessed. Others reflect the views of NGOs and aid donors with considerable experience in the countries being assessed, while others are based on the assessments of commercial risk-rating agencies.
A complementary vision of the macro-level Worldwide Governance Indicators are the World Bank Governance Surveys
World Bank Governance Surveys
The World Bank Governance Surveys are diagnostic tools used to assist World Bank partner governments in measuring and mapping governance challenges within the public sector structure. Survey questionnaires are applied to households, private enterprises and public officials within the country to...
, which are country level governance assessment tools developed by the World Bank Institute
World Bank Institute
The World Bank Institute is the capacity development branch of the World Bank. It provides learning programs, policy advice and technical assistance to policy makers, government and non-government agencies and development practitioners of developing countries...
.
Criticisms
The Worldwide Governance Indicators offer a useful snapshot of some perceptions of a country’s quality of governance but various researchers have pointed out significant problems in their construction. These critiques have been extensively rebutted by the WGI authors in several publications.These critics have claimed that users often fail to take into account their limitations /often not aware of:
i) lack of transparency: sheer number and diversity of indicators, produced by others, in a single WGI make it very difficult to understand
ii) Not reproducible: Many of the indicators underlying each source’s ratings, are not published
iii) Over-Complexity: the WGI “Control of Corruption” uses 23 different combinations of sources just for East Europe and Central Asia
iv) Arbitrary: e.g. WGI use the indicator “Environmental regulations hurt competitiveness” from the World Economic Forum’s Executive Opinion Survey, but ignore that Survey’s several questions that give high ratings to countries with a high standard of environmental protection.
v) absence of an underlying theory of 'good' governance: no normative concept or unifying single theory to distinguish between good or bad governance – so when are taxes, labour or environmental regulatory protection necessary/desirable and when are they excessive?
vi) hidden biases: Low weight given to household surveys relative to the weights of expert assessments and firm surveys: e.g. Gallup’s World Poll that asks citizens about their exposure to crime gets zero weight for “Rule of Law”, BUT Global Insight Business Risk and Conditions, a US commercial business information provider that measures the crime risk to businesses, gets the third highest weight.
vii) lack of comparability over time/space: e.g. the WGI “Control of Corruption” for the E. Europe and Central Asia has 23 different combinations of sources, but only four pair of countries ratings are based on common set of sources;
viii) lack of actionability: WGI offers little guidance to concrete actions to improve the quality of governance: e.g. an indicator for Rule of Law “how secure business people feel about their property” not WHY they feel that way.
ix) Over-selling: the World Bank Institute advertises its WGIs as “reliable measurements of governance” BUT e.g. gives misleading impression that the views of ordinary citizens are well-represented, making the indicators particularly attractive to donor agencies concerned about the poor: e.g. WBI heavily stressed inclusion of the source “Gallup World Poll “, a cross-country household survey available for a large number of countries BUT Gallup’s World Poll gets zero weight on two WGIs, marginal weight on two other WGIs and provides no data for the remaining two.
x) No concept Validity: “the six governance indicators measure a broad underlying concept of ‘effective governance’ … they appear to say the same thing, with different words … the six indexes do not discriminate usefully among different aspects of governance. Rather, each of the indexes – whatever its label – merely reflects perceptions of the quality of governance more broadly. An implication is that they may have limited use as guides for policymakers, and for academic studies of the causes and consequences of ‘good governance’ as well… their availability may well have crowded out efforts at measuring the impact of institutions as they really exist in a particular place on real outcomes.
Countries with governance indicators
The countries presented in the table have a Country Data Report with the summary of the six aggregate governance indicators trends over the last decade, together with all of the publicly-available disaggregated data on which the aggregate indicators are based. Additional information is available at Worldwide Governance Indicators.External links
- Global Integrity Report provides transparent source data and references used in the Worldwide Governance Indicators
- Worldwide Governance Indicators :Worldwide ratings of country performances on six governance dimensions from 1996 to present
- Press Release 2009
- Relevant Documentation
- Governance Matters VIII: Aggregate and Individual Governance Indicators for 1996-2008
- Governance Indicators: Where Are We, Where Should We Be Going?.

