
Wideband Global SATCOM system
Encyclopedia
The Wideband Global SATCOM system (sometimes called the Wideband Gapfiller Satellite system) is a satellite communications system planned for use in partnership by the United States Department of Defense
(DoD) and the Australian Department of Defence. The system is composed of the Space Segment satellites, the Terminal Segment users and the Control Segment operators. DoD wideband satellite communication services are currently provided by a combination of the existing Defense Satellite Communications System
(DSCS) and Global Broadcast Service
(GBS) satellites. According to United Launch Alliance
, quoted on Spaceflight Now, "A single WGS spacecraft has as much bandwidth as the entire existing DSCS constellation."
, surveillance
, and reconnaissance
(C4ISR); battle management; and combat support information. WGS also augments the current Ka-band Global Broadcast Service (on UHF F/O satellites) by providing additional information broadcast capabilities. The combination of the Wideband Global Satellites, DSCS satellites, GBS payloads, wideband payload and platform control assets, and earth terminals operating with them has been referred to as the Interim Wideband System (IWS). It provides services to the US and Aus. Department of Defence. The IWS System supports continuous 24 hour per day wideband satellite services to tactical users and some fixed infrastructure users. Limited protected services will be provided under conditions of stress to selected users employing terrestrial modems capable of providing protection against jamming
. The combined wideband
satellite communications system consists of space vehicles of multiple types, control terminals and facilities, and user terminals.
satellite platform. Originally five satellites were planned. On 3 October 2007 the Australian Defence Ministry announced Australia would join in partnership and fund a sixth satellite in the constellation. Once in their orbits at an altitude of 22300 mi (35,888.3 km), each will weigh approximately 7600 lb (3,447.3 kg). The program intends to use both the Delta IV
and the Atlas V
as launch vehicle
s. The Air Force Space Command
estimates each satellite will cost approximately US$300 million.
The first three WGS satellites form Block I of the space segment. WGS satellites 4, 5, and 6 make up Block II.
(ULA) on 10 October 2007. The satellite was carried by an Atlas V
(421) lifting off from LC-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
(CCAFS). After launch, the WGS-1 satellite was given the US military designation USA-195. Its coverage area stretches from the U.S. western coast to Southeast Asia.
will also use the WGS in a similar manner as the DSCS III constellation is used to route ATM packets through the DISA
"cloud" to establish command and control streams with various satellite constellations. One of the emerging applications is SATCOM-ON-The-Move which is now being extensively used on the military tactical vehicles for Blue Force Tracking and C3 missions.
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
(DoD) and the Australian Department of Defence. The system is composed of the Space Segment satellites, the Terminal Segment users and the Control Segment operators. DoD wideband satellite communication services are currently provided by a combination of the existing Defense Satellite Communications System
Defense Satellite Communications System
The Defense Satellite Communications System provides the United States with military communications to support globally distributed military users. DSCS will be replaced by the Wideband Global SATCOM system. A total of 14 DSCS III satellites were launched between the early 1980s and 2003. Two...
(DSCS) and Global Broadcast Service
Global Broadcast Service
The Global Broadcast Service is a combined United States space and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence system, that provides a one-way Wideband/high-Throughput of information to forces garrisoned, deployed, or on the move....
(GBS) satellites. According to United Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance is a joint venture of Lockheed Martin and Boeing. ULA was formed in December 2006 by combining the teams at these companies which provide spacecraft launch services to the government of the United States. U.S...
, quoted on Spaceflight Now, "A single WGS spacecraft has as much bandwidth as the entire existing DSCS constellation."
Mission
The Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) satellites are key elements of a system that increases the communications capabilities of the U.S. and Australia. WGS supports the U.S. and Aus Department of Defense's warfighting information exchange requirements, enabling execution of tactical command and control, communications, and computers; intelligenceIntelligence
Intelligence has been defined in different ways, including the abilities for abstract thought, understanding, communication, reasoning, learning, planning, emotional intelligence and problem solving....
, surveillance
Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of the behavior, activities, or other changing information, usually of people. It is sometimes done in a surreptitious manner...
, and reconnaissance
Reconnaissance
Reconnaissance is the military term for exploring beyond the area occupied by friendly forces to gain information about enemy forces or features of the environment....
(C4ISR); battle management; and combat support information. WGS also augments the current Ka-band Global Broadcast Service (on UHF F/O satellites) by providing additional information broadcast capabilities. The combination of the Wideband Global Satellites, DSCS satellites, GBS payloads, wideband payload and platform control assets, and earth terminals operating with them has been referred to as the Interim Wideband System (IWS). It provides services to the US and Aus. Department of Defence. The IWS System supports continuous 24 hour per day wideband satellite services to tactical users and some fixed infrastructure users. Limited protected services will be provided under conditions of stress to selected users employing terrestrial modems capable of providing protection against jamming
Radio jamming
Radio jamming is the transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal to noise ratio. Unintentional jamming occurs when an operator transmits on a busy frequency without first checking whether it is in use, or without being able to hear stations using the frequency...
. The combined wideband
Wideband
In communications, wideband is a relative term used to describe a wide range of frequencies in a spectrum. A system is typically described as wideband if the message bandwidth significantly exceeds the channel's coherence bandwidth....
satellite communications system consists of space vehicles of multiple types, control terminals and facilities, and user terminals.
Capabilities
The new Wideband Global SATCOM (WGS) satellites will complement the DSCS III Service Life Enhancement Program (SLEP) and GBS payloads, and offset the eventual decline in DSCS III capability. WGS will offer 4.875 GHz of instantaneous switchable bandwidth, thus each WGS can supply more than 10 times the capacity of a DSCS III Service Life Enhancement Program (SLEP) satellite. Together these assets will provide wideband services during the transition period between today's systems and the advent of the Objective X/Ka wideband system or Advanced Wideband System (AWS), which has merged with Transformational Communications System (TCS), in 2008-2009. The DSCS system will be replaced by six fully operational WGS satellites, each of which will be able to downlink 2.4 Gbit/s of data to tactical users. The very first WGS satellite in orbit will provide greater capability and bandwidth than all the DSCS satellites combined.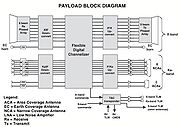 |
Space segment
The primary contractor for the satellites is Boeing Satellite Systems, which will build them around the Boeing 702Boeing 702
Boeing 702 is a communications satellite design. The Boeing Satellite Development Center tailors the payload of each Boeing 702 to meet customer specifications based on a modular design but with usually more than seventy transponders....
satellite platform. Originally five satellites were planned. On 3 October 2007 the Australian Defence Ministry announced Australia would join in partnership and fund a sixth satellite in the constellation. Once in their orbits at an altitude of 22300 mi (35,888.3 km), each will weigh approximately 7600 lb (3,447.3 kg). The program intends to use both the Delta IV
Delta IV rocket
Delta IV is an active expendable launch system in the Delta rocket family. Delta IV uses rockets designed by Boeing's Integrated Defense Systems division and built in the United Launch Alliance facility in Decatur, Alabama. Final assembly is completed at the launch site by ULA...
and the Atlas V
Atlas V
Atlas V is an active expendable launch system in the Atlas rocket family. Atlas V was formerly operated by Lockheed Martin, and is now operated by the Lockheed Martin-Boeing joint venture United Launch Alliance...
as launch vehicle
Launch vehicle
In spaceflight, a launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket used to carry a payload from the Earth's surface into outer space. A launch system includes the launch vehicle, the launch pad and other infrastructure....
s. The Air Force Space Command
Air Force Space Command
Air Force Space Command is a major command of the United States Department of the Air Force, with its headquarters at Peterson Air Force Base, Colorado. AFSPC supports U.S. military operations worldwide through the use of many different types of satellite, launch and cyber operations....
estimates each satellite will cost approximately US$300 million.
The first three WGS satellites form Block I of the space segment. WGS satellites 4, 5, and 6 make up Block II.
WGS-1
The first launch (WGS-1) was conducted by United Launch AllianceUnited Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance is a joint venture of Lockheed Martin and Boeing. ULA was formed in December 2006 by combining the teams at these companies which provide spacecraft launch services to the government of the United States. U.S...
(ULA) on 10 October 2007. The satellite was carried by an Atlas V
Atlas V
Atlas V is an active expendable launch system in the Atlas rocket family. Atlas V was formerly operated by Lockheed Martin, and is now operated by the Lockheed Martin-Boeing joint venture United Launch Alliance...
(421) lifting off from LC-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is an installation of the United States Air Force Space Command's 45th Space Wing, headquartered at nearby Patrick Air Force Base. Located on Cape Canaveral in the state of Florida, CCAFS is the primary launch head of America's Eastern Range with four launch pads...
(CCAFS). After launch, the WGS-1 satellite was given the US military designation USA-195. Its coverage area stretches from the U.S. western coast to Southeast Asia.
WGS-2
Launch of the second satellite (WGS-2) was also conducted by ULA, at 01:31 GMT on 4 April 2009, using an Atlas V 421. A ULA Delta IV flying from LC-37B at CCAFS launched the third spacecraft on 6 December 2009. The WGS-2 satellite was positioned over the equator around 60° East longitude (over the Indian Ocean) for use by U.S. Central Command in Afghanistan, Iraq and other parts of Southwest Asia. Originally, the second spacecraft was to fly on the Delta, and the third on the Atlas, but they were switched for an undisclosed reason.WGS-3
SATCOM3, launched on 6 December 2009, covers the eastern Atlantic Ocean. The satellite was launched by a Delta IV "Medium+ (5,4)" rocket (originally Atlas V but switched with WGS-2; see above).WGS-4, 5, and 6
WGS 4, 5 and 6 are under construction by Boeing for deployment in the coming years. These satellites represent the Block II WGS satellites. Like WGS-3, launch of WGS-4 is planned for a Delta IV Medium+ (5,4). The target date for the launch is between December 2011 and February 2012.WGS-7
On Aug. 23, 2010, Boeing was awarded an Air Force contract worth $182 million to begin work on the seventh WGS satellite. The new spacecraft is being procured under the WGS Block II follow-on contract. The contract will ultimately include options for production of up to six WGS satellites.Terminal segment
The Terminal segment describes the "users" or "customers" of the communication services provided by the WGS. Users include the Australian Defence Force and U.S. Army ground mobile terminals, U.S. Navy ships and submarines, national command authorities for the nuclear forces, and various national security/allied national forces. Additionally the Air Force Satellite Control NetworkAir Force Satellite Control Network
The Air Force Satellite Control Network provides support for the operation, control, and maintenance of a variety of United States Department of Defense and some non-DoD satellites. This involves continual execution of the tasks involved in Tracking, Telemetry, and Command...
will also use the WGS in a similar manner as the DSCS III constellation is used to route ATM packets through the DISA
Disa
Disa is the heroine of a Swedish legendary saga, which was documented by Olaus Magnus, in 1555. It is believed to be from the Middle Ages, but includes Old Norse themes....
"cloud" to establish command and control streams with various satellite constellations. One of the emerging applications is SATCOM-ON-The-Move which is now being extensively used on the military tactical vehicles for Blue Force Tracking and C3 missions.

