
WiMAX MIMO
Encyclopedia

WiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
, which is the technology brand name for the implementation of the standard IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16 is a series of Wireless Broadband standards authored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . The IEEE Standards Board in established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks...
.
WiMAX
WiMAXWiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
is the technology brand name for the implementation of the standard IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16
IEEE 802.16 is a series of Wireless Broadband standards authored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . The IEEE Standards Board in established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks...
, which specifies the air interface
Air interface
In mobile or wireless communication, the air interface is the radio-based communication link between the mobile station and the active base station...
at the PHY (Physical layer)
PHY
PHY is an abbreviation for the physical layer of the OSI model.An instantiation of PHY connects a link layer device to a physical medium such as an optical fiber or copper cable. A PHY device typically includes a Physical Coding Sublayer and a Physical Medium Dependent layer. The PCS encodes and...
and at the MAC (Medium Access Control layer) . Aside from specifying the support of various channel bandwidths and adaptive modulation and coding, it also specifies the support for MIMO antennas to provide good Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) characteristics.
See Also: WiMax Forum
MIMO
MIMO stands for Multiple Input and Multiple Output, and refers to the technology where there are multiple antennas at the base stationBase station
The term base station can be used in the context of land surveying and wireless communications.- Land surveying :In the context of external land surveying, a base station is a GPS receiver at an accurately-known fixed location which is used to derive correction information for nearby portable GPS...
and multiple antennas at the mobile device. Typical usage of multiple antenna technology includes cellular phones with two antennas, laptops with two antennas (e.g. built in the left and right side of the screen), as well as CPE
Customer-premises equipment
Customer-premises equipment or customer-provided equipment is any terminal and associated equipment located at a subscriber's premises and connected with a carrier's telecommunication channel at the demarcation point...
devices with multiple sprouting antennas.
The predominant cellular network
Cellular network
A cellular network is a radio network distributed over land areas called cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver known as a cell site or base station. When joined together these cells provide radio coverage over a wide geographic area...
implementation is to have multiple antennas at the base station and a single antenna on the mobile device
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
. This minimizes the cost of the mobile radio. As the costs for radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
(RF) components in mobile devices go down, second antennas in mobile device may become more common. Multiple mobile device antennas are currently used in Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
technology (e.g. IEEE 802.11n), where WiFi-enabled cellular phones, laptops and other devices often have two or more antennas.
MIMO Technology in WiMAX
WiMAX implementations that use MIMO technology have become important. The use of MIMO technology improves the reception and allows for a better reach and rate of transmission. The implementation of MIMO also gives WiMAX a significant increase in spectral efficiencySpectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
.
MIMO auto-negotiation
The 802.16 defined MIMO configuration is negotiated dynamically between each individual base station and mobile station. The 802.16 specification supports the ability to support a mix of mobile stations with different MIMO capabilities. This helps to maximize the sector throughput by leveraging the different capabilities of a diverse set of vendor mobile stations.Space Time Code
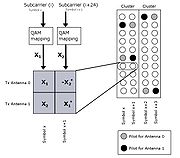
Transmit diversity
Transmit diversity is radio communication using signals that originate from two or more independent sources that have been modulated with identical information-bearing signals and that may vary in their transmission characteristics at any given instant....
, which is commonly referred to Space Time Code (STC). With this method, two or more antennas are employed at the transmitter and one antenna at the receiver. The use of multiple receive antennas (thus MIMO) can further improve the reception of STC transmitted signals.
With a Transmit Diversity rate = 1 (aka "Matrix A" in the 802.16 standard), different data bit constellations are transferred on two different antennas during the same symbol. The conjugate and/or inverse of the same two constellations are transferred again on the same antennas during the next symbol. The data transfer rate with STC remains the same as the baseline case. The received signal is more robust with this method due to the transmission redundancy. This configuration delivers similar performance to the case of two receive antennas and one transmitter antenna.
Spatial Multiplexing
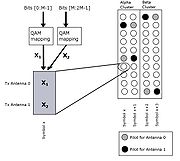
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
, also known as Transmit Diversity rate = 2 (aka "Matrix B" in the 802.16 standard). Instead of transmitting the same bit over two antennas, this method transmits one data bit from the first antenna, and another bit from the second antenna simultaneously, per symbol. As long as the receiver has more than one antenna and the signal is of sufficient quality, the receiver can separate the signals. This method involves added complexity and expense at both the transmitter and receiver. However, with two transmit antennas and two receive antennas, data can be transmitted twice as fast as compared systems using Space Time Codes with only one receive antenna.

WiMAX Network use of Spatial Multiplexing
One specific use of Spatial Multiplexing is to apply it to users who have the best signal quality, so that less time is spent transmitting to them. Users whose signal quality is too low to allow the spatially multiplexed signals to be resolved stay with conventional transmission. This allows an operator to offer higher data rates to some users and/or to serve more users. The WiMAX specification's dynamic negotiation mechanism helps enable this use.WiMAX MISO/MIMO with four antennas
The 802.16 specification also supports the use of four antennas. Three configurations are supported.WiMAX four antenna mode 1
With rate = 1 using four antennas, data is transmitted four times per symbol, where each time the data is conjugated and/or inverted. This does not change the data rate, but does give the signal more robustness and avoids sudden increases in error rates.WiMAX four antenna mode 2
With rate = 2 using four antennas, the data rate is only doubled, but increases in robustness since the same data is transmitted twice as compared to only once with using two antennas.WiMAX four antenna Matrix C mode
The third configuration that is only available using four antennas is Matrix C, where a different data bit is transmitted from the four antennas per symbol, which gives it four times the baseline data rate.| Data Rate | |||||
| 1x | 2x | 4x | |||
| 4 | STC (Matrix A) |
STC & SMX (Matrix B) |
SMX only (Matrix C) |
||
| Number of Transmit Antennas |
2 | STC (Matrix A) |
SMX (Matrix B) |
not possible | |
| 1 | Baseline Case | not possible | not possible | ||
| Rx | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| 4 | STC (Matrix A) |
2xSMX (Matrix B) STC + 2xMRC (Matrix A) |
2xSMX (Matrix B) STC + 3xMRC (Matrix A) |
4xSMX (Matrix C) |
|
| Tx | 2 | STC (Matrix A) |
2xSMX (Matrix B) STC + 2xMRC (Matrix A) |
2xSMX (Matrix B) STC + 3xMRC (Matrix A) |
STC + 4xMRC (Matrix A) |
| 1 | Baseline Case | Uplink: Uplink Collaborative MIMO Downlink: MRC |
MRC | MRC | |
Note: MRC (Maximum Ratio Combining)
Maximal-ratio combining
In telecommunications, maximal-ratio combining is a method of diversity combining in which: the signals from each channel are added together, the gain of each channel is made proportional to the rms signal level and inversely proportional to the mean square noise level in that channel. different...
is vendor discretionary and improves rate and range. In WiMAX, MRC at the Base Station is sometimes also referred to as Receive Beamforming.
See also: Space Time Coding and Spatial Multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing
Spatial multiplexing is a transmission technique in MIMO wireless communication to transmit independent and separately encoded data signals, so-called streams, from each of the multiple transmit antennas...
Uplink Collaborative MIMO
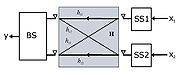

WiMAX Uplink Collaborative MIMO
In the case of WiMAXWiMAX
WiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
, Uplink Collaborative MIMO is spatial multiplexing with two different devices, each with one antenna. These transmitting devices are collaborating in the sense that both devices must be synchronized in time and frequency so that the intentional overlapping occurs under controlled circumstances. The two streams of data will then interfere with each other. As long as the signal quality is sufficiently good and the receiver at the base station has at least two antennas, the two data streams can be separated again. This technique is sometimes also termed Virtual Spatial Multiplexing.
Adaptive Antenna Steering (AAS), a.k.a. Beamforming

Beamforming
Beamforming is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in the array in a way where signals at particular angles experience constructive interference and while others experience destructive...
. Multiple antennas and multiple signals are employed, which then shape the beam with the intent of improving transmission to the desired station. The result is reduced interference because the signal going to the desired user is increased and the signal going to other users is reduced.
Cyclic Delay Diversity
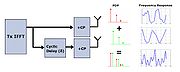
Cyclic delay diversity
Cyclic Delay Diversity is a diversity scheme used in OFDM-based telecommunication systems, transforming spatial diversity into frequency diversity avoiding intersymbol interference....
. In this technique, one or more of the signals are delayed before transmission. Because the signals are coming out of two antennas, their receive spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
s differ as each spectrum is characterized by humps and notches due to multi-path fading. At the receiver the signals combine, which improves reception because the joint reception results in shallower spectral humps and fewer spectral notches. The closer the signal can get towards a flat channel at a certain power level, the higher the throughput that can be obtained.
Radio Conformance Test of WiMAX MIMO
The WiMax Forum has a set of standardized conformance test proceduresConformance testing
Conformance testing or type testing is testing to determine whether a product or system meets some specified standard that has been developed for efficiency or interoperability....
for PHY
PHY
PHY is an abbreviation for the physical layer of the OSI model.An instantiation of PHY connects a link layer device to a physical medium such as an optical fiber or copper cable. A PHY device typically includes a Physical Coding Sublayer and a Physical Medium Dependent layer. The PCS encodes and...
and MAC
Media Access Control
The media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
specification compliance called the Radio Conformance Test (RCT). Any technology aspect of a particular implementation of a radio interface must first undergo the RCT. Generally, any aspect of the IEEE 802.16 standard that does not have a test procedure in the RCT may be assumed to not yet be widely implemented.
Silicon implementations of WiMAX MIMO
Companies that make RFICs that support WiMAX MIMO include Intel, Beceem http://www.beceem.com/, NXP Semiconductors and PMC-SierraPMC-Sierra
PMC-Sierra is a fabless semiconductor company which develops and sells devices into the communications, storage, printing, and embedded computing marketplaces.-Corporate history:...
.
See also
- Advanced MIMO communications
- IEEE 802.16IEEE 802.16IEEE 802.16 is a series of Wireless Broadband standards authored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . The IEEE Standards Board in established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks...
- Integrated Circuit DesignIntegrated circuit designIntegrated circuit design, or IC design, is a subset of electrical engineering and computer engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs...
- MIMOMIMOIn radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
- OFDM
- WiMAXWiMAXWiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
- Wi-FiWi-FiWi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
External links
- The WiMAX Forum
- IEEE website for 802.16
- PMC-Sierra WiMAX Products
- WiMAX Evolution: Emerging Technologies and Applications, edited by M. Katz and F. Fitzek, 2009. Chapter 16, MIMO Technologies for WiMAX Systems: Present and Future, by C.-B. Chae, K. Huang, and T. Inoue
- GEDOMIS (GEneric hardware DemOnstrator for MIMO Systems): PHY-layer implementation of MIMO mobile WiMAX

