
Whitening transformation
Encyclopedia
The whitening transformation is a decorrelation
method that converts the covariance matrix
S of a set of samples into the identity matrix I. This effectively creates new random variables that are uncorrelated and have the same variances as the original random variables. The method is called the whitening transform because it transforms the input matrix closer towards white noise
.
This can be expressed as

where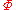 is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and
is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and 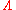 is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.
is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.
Decorrelation
Decorrelation is a general term for any process that is used to reduce autocorrelation within a signal, or cross-correlation within a set of signals, while preserving other aspects of the signal. A frequently used method of decorrelation is the use of a matched linear filter to reduce the...
method that converts the covariance matrix
Covariance matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix is a matrix whose element in the i, j position is the covariance between the i th and j th elements of a random vector...
S of a set of samples into the identity matrix I. This effectively creates new random variables that are uncorrelated and have the same variances as the original random variables. The method is called the whitening transform because it transforms the input matrix closer towards white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
.
This can be expressed as

where
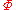 is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and
is the matrix with the eigenvectors of "S" as its columns and 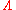 is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.
is the diagonal matrix of corresponding eigenvalues.See also
- DecorrelationDecorrelationDecorrelation is a general term for any process that is used to reduce autocorrelation within a signal, or cross-correlation within a set of signals, while preserving other aspects of the signal. A frequently used method of decorrelation is the use of a matched linear filter to reduce the...
- Randomness extractorRandomness extractorA randomness extractor, often simply called "an extractor," is a function which, when applied to a high-entropy source , generates a random output that is shorter, but uniformly distributed...
- Hardware random number generatorHardware random number generatorIn computing, a hardware random number generator is an apparatus that generates random numbers from a physical process. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate a low-level, statistically random "noise" signal, such as thermal noise or the photoelectric effect or other...
- Principal component analysis

