
West Branch Susquehanna River
Encyclopedia
The West Branch Susquehanna River is one of the two principal branches, along with the North Branch, of the Susquehanna River
in the northeastern United States
. The North Branch, which rises in upstate New York
, is generally regarded as the extension of the main branch, with the shorter West Branch being its principal tributary
. The West Branch, which is 243 miles (391.1 km) long, is entirely within the state of Pennsylvania
, draining a large mountainous area within the Allegheny Plateau
in the western part of the state. Along most of its course it meander
s along mountain ridges and through water gap
s, forming a large zigzag arc through central Pennsylvania around the north end of the Allegheny Ridge
. In colonial times the river provided an important water route to the Ohio River
valley. In the 18th century, its lower valley became a significant industrial heartland of Pennsylvania.
, just outside the borough of Carrolltown
. It flows generally north, crossing the eastern corner of Indiana County
at Cherry Tree
, then into southern Clearfield County
. Near Mahaffey
it turns generally northeast and flows past Curwensville
and Clearfield
. In northern Clinton County
it turns to the southeast to Lock Haven
. At Lock Haven it turns east, flowing through the West Branch Susquehanna Valley
along the foot of Bald Eagle Mountain
ridge past Williamsport
, the largest city on the river, then turns south at the end of the ridge. From there it winds around the Muncy
, emerging from a water gap between Montour Ridge and Shamokin Mountain and joining the north (main) branch of the Susquehanna from the northwest approximately 2 miles (3 km) north of Sunbury
.

route across the Alleghenies connecting the Susquehanna and Ohio
valleys, with a portage
at Cherry Tree
to Blacklick Creek
, a tributary of the Conemaugh River
. In the late 18th century, Cherry Tree marked the frontier between the Pennsylvania Colony and the Shawnee
and Lenape
lands to the west as specified by treaty.
The lands along the West Branch were vital hunting grounds and agricultural lands for Native Americans
. During Pennsylvania’s great lumbering era, the most significant log drive was conveyed on the West Branch of the Susquehanna River. The Susquehanna’s West Branch Canal Division further shaped the corridor, linking towns and villages and providing vital opportunities for commerce. Finally, railroads
in the corridor fused the links between communities and commerce within the corridor. http://www.dcnr.state.pa.us/brc/rivers/riversconservation/registry/64Sec1.pdf
speaking Susquehannock
s. Their name meant 'people of the muddy river', from the Lenape
name of the Susquehanna River, Siskuwihane (<sisku 'mud', hane 'river'). Decimated by diseases and warfare, they had died out, moved away, or been assimilated
into other tribes by the early 18th century. The lands of the West Branch Susquehanna River Valley were then chiefly occupied by the Munsee phratry
of the Lenape
(or Delaware) and were under the nominal control of the Five (later Six) Nations of the Iroquois
.
on the West Branch Susquehanna River was an important stopping point for the Moravian missionaries who were spreading the gospel throughout the wilderness of Pennsylvania during the 1740s. Count Zinzendorf, a missionary being guided by Conrad Weiser
with the permission of Shikellamy
, came to Ostuagy in 1742.
The British
purchased land from the Iroquois in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix
of 1768, opening what is now Lycoming County to settlement. However, the Line of Property
(or Purchase Line
) border defined by "Tiadaghton Creek" dividing colonial and Native American lands was disputed. The colonists claimed this was Pine Creek
, the Iroquois and other tribes Lycoming Creek
. The area between Pine and Lycoming creeks was disputed territory. The illegal settlers there were part of the "Fair Play Men
" system of self-government, with their own Declaration of Independence from Britain on July 4, 1776.
In the American Revolutionary War
, settlements throughout the Susquehanna valley were attacked by Loyalist
s and Native Americans allied with the British. After the Wyoming Valley battle and massacre in the summer of 1778 (near what is now Wilkes-Barre
) and smaller local attacks, the "Big Runaway
" occurred throughout the West Branch Susquehanna valley. Settlers fled feared and actual attacks by the British and their allies. Homes and fields were abandoned, with livestock driven along and a few possessions floated on rafts on the river east to Muncy
, then further south to Sunbury
. The abandoned property was burnt by the attackers. Some settlers soon returned, only to flee again in the summer of 1779 in the "Little Runaway". Sullivan's Expedition helped stabilize the area and encouraged resettlement, which continued after the war. In 1790, Timothy Matlack
, Samuel Maclay and John Adlum were commissioned by the Supreme Executive Council of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania to survey the headwaters of the Susquehanna and explore a route for a passageway to connect the West Branch with the waters of the Allegheny River
.
The Fair Play Men
were illegal settler
s (squatters) who established their own system of self-rule from 1773 to 1785 in the West Branch Susquehanna River Valley of Pennsylvania. Because they settled in territory claimed by Native Americans
, they had no recourse to the Pennsylvania colonial government. Accordingly, they established what was known as the Fair Play System, with three elected commissioners who ruled on land claims and other issues for the group. In a remarkable coincidence, the Fair Play Men made their own Declaration of Independence
from Britain
on July 4, 1776, beneath the "Tiadaghton Elm" on the banks of Pine Creek
.
Fort Antes
was a stockade
surrounding the home of Colonel John Henry Antes, built circa 1778 in Revolutionary
Pennsylvania in the United States. The fort was built under the direction of Colonel Antes, who was a member of the Pennsylvania militia
. It was on the east side of Antes Creek, overlooking and on the left bank of the West Branch Susquehanna River on a plateau
in Nippenose Township south of modern-day Jersey Shore
in western Lycoming County
. The local militia held the fort for a short period of time until it was ordered by Colonel Samuel Hunter to abandon Fort Antes during the Big Runaway
. Despite being abandoned and attempts by the attacking British forces to burn it down, Fort Antes was one of only two structures in the valley to survive the Big Runaway.
was a system of cribs in the West Branch Susquehanna River designed to hold timber
in the river until it could be processed at one of the nearly 60 sawmill
s along the river between Lycoming
and Loyalsock
creeks in Lycoming County
. The boom was constructed in 1846 under the supervision of James H. Perkins.
A boom
is a chain or line of connected floating timbers extended across a river, lake, or harbor (as to obstruct passage or catch floating objects). The Susquehanna Boom extended 7 miles (11.3 km) upstream from Duboistown
to the village of Linden in Woodward Township
. The boom was constructed by creating a series of man-made islands known as "cribs". These cribs built of local mountain stone and sunken timber were stretched diagonally across the river, beginning on the south side near Duboistown and ending on the north side near Linden. The boom was made of 352 separate cribs that were 22 feet (7 m) high. The boom was opened and closed at the upper end by a device known as a "sheer boom." It was 1000 feet (304.8 m) long and was controlled with a hand-powered windlass
. The sheer boom gathered the logs into the main boom that was capable of holding up to 300 million board feet (700,000 m³) of logs. The lower end of the boom was where the logs were sorted. The mills in Williamsport, South Williamsport
, and Duboistown each had their own distinctive brand burnt into the logs. The men working at the end of the boom would sort the logs according to their corresponding brand and float them into the correct holding pond along the bank of the river.
During the height of the lumber industry in Lycoming County, 1861–1891, the various mills produced 5.5 billion board feet (13 million m³) of lumber. Williamsport became one of the most prosperous cities in Pennsylvania and in the United States. Men like James H. Perkins, Peter Herdic
, and Mahlon Fisher became millionaire
s while many of the men who actually worked in the river struggled to survive on the wages paid to them by the lumber barons.
Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River is a river located in the northeastern United States. At long, it is the longest river on the American east coast that drains into the Atlantic Ocean, and with its watershed it is the 16th largest river in the United States, and the longest river in the continental United...
in the northeastern United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. The North Branch, which rises in upstate New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, is generally regarded as the extension of the main branch, with the shorter West Branch being its principal tributary
Tributary
A tributary or affluent is a stream or river that flows into a main stem river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean...
. The West Branch, which is 243 miles (391.1 km) long, is entirely within the state of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, draining a large mountainous area within the Allegheny Plateau
Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau is a large dissected plateau area in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio...
in the western part of the state. Along most of its course it meander
Meander
A meander in general is a bend in a sinuous watercourse. A meander is formed when the moving water in a stream erodes the outer banks and widens its valley. A stream of any volume may assume a meandering course, alternately eroding sediments from the outside of a bend and depositing them on the...
s along mountain ridges and through water gap
Water gap
A water gap is an opening or notch which flowing water has carved through a mountain range. Water gaps often offer a practical route for road and rail transport to cross mountain ridges.- Geology :...
s, forming a large zigzag arc through central Pennsylvania around the north end of the Allegheny Ridge
Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range , also spelled Alleghany, Allegany and, informally, the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the eastern United States and Canada...
. In colonial times the river provided an important water route to the Ohio River
Ohio River
The Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River. At the confluence, the Ohio is even bigger than the Mississippi and, thus, is hydrologically the main stream of the whole river system, including the Allegheny River further upstream...
valley. In the 18th century, its lower valley became a significant industrial heartland of Pennsylvania.
Hydrography
The West Branch rises on the west side of the Alleghenies in northwestern Cambria CountyCambria County, Pennsylvania
Cambria County is a county located in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. It comprises the Johnstown, Pennsylvania, Metropolitan Statistical Area. As of 2010, the population was 143,679....
, just outside the borough of Carrolltown
Carrolltown, Pennsylvania
Carrolltown is a borough within East Carroll Township in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,049 at the 2000 census...
. It flows generally north, crossing the eastern corner of Indiana County
Indiana County, Pennsylvania
-Government and politics:As of November 2008, there are 58,077 registered voters in Indiana County .* Democratic: 26,653 * Republican: 24,159 * Other Parties: 7,265 -County commissioners:*Rodney Ruddock, Chairman, Republican...
at Cherry Tree
Cherry Tree, Pennsylvania
Cherry Tree is a borough in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 443 at the 2000 census.-History:Cherry Tree is situated mostly in a valley near the headwaters of West Branch of the Susquehanna River where the river is fed by Cush Cushion Creek.Cherry Tree was originally...
, then into southern Clearfield County
Clearfield County, Pennsylvania
Clearfield County is a county located in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. As of 2010, the population was 81,642.Clearfield County was created on March 26, 1804, from parts of Huntingdon and Lycoming Counties but was administered as part of Centre County until 1812...
. Near Mahaffey
Mahaffey, Pennsylvania
Mahaffey is a borough in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 402 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Mahaffey is located at .According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all of it land....
it turns generally northeast and flows past Curwensville
Curwensville, Pennsylvania
Curwensville is a borough located in Clearfield County, Pennsylvaniain the United States of America, northwest of Altoona on the West Branch Susquehanna River. Coal mining, tanning, and the manufacture of fire bricks were the industries at the turn of the 20th century. In 1900, 1,937 people lived...
and Clearfield
Clearfield, Pennsylvania
Clearfield is a borough in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 6,631 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Clearfield County.-Geography:Clearfield is located at ....
. In northern Clinton County
Clinton County, Pennsylvania
As of the census of 2000, there were 37,914 people, 14,773 households, and 9,927 families residing in the county. The population density was 43 people per square mile . There were 18,166 housing units at an average density of 20 per square mile...
it turns to the southeast to Lock Haven
Lock Haven, Pennsylvania
The city of Lock Haven is the county seat of Clinton County, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Located near the confluence of the West Branch Susquehanna River and Bald Eagle Creek, it is the principal city of the Lock Haven, Pennsylvania, micropolitan statistical area, itself part of the...
. At Lock Haven it turns east, flowing through the West Branch Susquehanna Valley
West Branch Susquehanna Valley
The West Branch Susquehanna Valley of central Pennsylvania, United States, in the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians, is the low lying area draining into the West Branch Susquehanna River southeast of the Allegheny Front, northeast of the Bald Eagle Valley, southwest of the Wyoming Valley and nort of...
along the foot of Bald Eagle Mountain
Bald Eagle Mountain
Bald Eagle Mountain, once known locally as Muncy Mountain, is a stratigraphic ridge in central Pennsylvania, United States, running east of the Allegheny Front and northwest of Mount Nittany. It lies along the southeast side of Bald Eagle Creek, and south of the West Branch Susquehanna River, and...
ridge past Williamsport
Williamsport, Pennsylvania
Williamsport is a city in and the county seat of Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the United States. In 2009, the population was estimated at 29,304...
, the largest city on the river, then turns south at the end of the ridge. From there it winds around the Muncy
Muncy, Pennsylvania
For other places named 'Muncy', please see Muncy .Muncy is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The name Muncy comes from the Munsee Indians who once lived in the area. The population was 2,663 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania...
, emerging from a water gap between Montour Ridge and Shamokin Mountain and joining the north (main) branch of the Susquehanna from the northwest approximately 2 miles (3 km) north of Sunbury
Sunbury, Pennsylvania
Sunbury is a city in Northumberland County, Pennsylvania, United States. The city is located on the east bank of the Susquehanna River, just downstream of the confluence of its main and West branches. The population was 9,905 at the 2010 census...
.

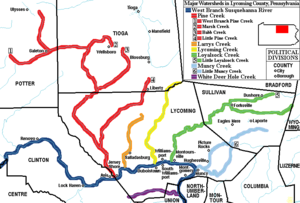
Tributaries
From its upper reaches to its lower reaches, it receives:- Chest CreekChest CreekChest Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Cambria and Clearfield counties, Pennsylvania, in the United States.Chest Creek joins the West Branch Susquehanna River at the borough of Mahaffey.-References:...
from the south at MahaffeyMahaffey, PennsylvaniaMahaffey is a borough in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 402 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Mahaffey is located at .According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all of it land.... - Anderson CreekAnderson CreekAnderson Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania in the United States.-References:*Gertler, Edward. Keystone Canoeing, Seneca Press, 2004. ISBN 0-9749692-0-6...
from the west in CurwensvilleCurwensville, PennsylvaniaCurwensville is a borough located in Clearfield County, Pennsylvaniain the United States of America, northwest of Altoona on the West Branch Susquehanna River. Coal mining, tanning, and the manufacture of fire bricks were the industries at the turn of the 20th century. In 1900, 1,937 people lived... - Clearfield CreekClearfield CreekClearfield Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Cambria and Clearfield counties, Pennsylvania, in the United States.Clearfield Creek joins the West Branch Susquehanna River near the community of Clearfield.-References:...
from the south 2 miles (3 km) east of ClearfieldClearfield, PennsylvaniaClearfield is a borough in Clearfield County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 6,631 at the 2000 census. It is the county seat of Clearfield County.-Geography:Clearfield is located at .... - Sinnemahoning CreekSinnemahoning CreekSinnemahoning Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Cameron and Clinton counties, Pennsylvania, in the United States.Sinnemahoning Creek is formed by the confluence of the Bennett and Driftwood Branches at the borough of Driftwood.The tributary First Fork Sinnemahoning...
from the northwest at KeatingKeating, PennsylvaniaKeating is an unincorporated community in East Keating Township, Clinton County, Pennsylvania. It is located at the confluence of Sinnemahoning Creek and the West Branch Susquehanna River.... - Bald Eagle CreekBald Eagle Creek (West Branch Susquehanna River)Bald Eagle Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River mostly in Centre County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It runs through the Bald Eagle Valley at the foot of the Bald Eagle Mountain ridge to Lock Haven....
from the southwest at Lock HavenLock Haven, PennsylvaniaThe city of Lock Haven is the county seat of Clinton County, in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. Located near the confluence of the West Branch Susquehanna River and Bald Eagle Creek, it is the principal city of the Lock Haven, Pennsylvania, micropolitan statistical area, itself part of the... - Pine CreekPine Creek (Pennsylvania)Pine Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Potter, Tioga, Lycoming, and Clinton counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. The creek is long...
and Larrys CreekLarrys CreekLarrys Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Lycoming County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A part of the Chesapeake Bay drainage basin, its watershed drains in six townships and a borough...
from the north near Jersey ShoreJersey Shore, PennsylvaniaJersey Shore is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is on the West Branch Susquehanna River, west by south of Williamsport. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area. In the past, Jersey Shore held farms, railroad shops, cigar factories, a... - Lycoming CreekLycoming CreekLycoming Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located in Tioga and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States.-Geography:...
from the north at WilliamsportWilliamsport, PennsylvaniaWilliamsport is a city in and the county seat of Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the United States. In 2009, the population was estimated at 29,304... - Loyalsock CreekLoyalsock CreekLoyalsock Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located chiefly in Sullivan and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States...
from the northeast at MontoursvilleMontoursville, PennsylvaniaMontoursville is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. As of the 2000 census, the borough population was 4,777. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area. It was named for Madame Montour, a Native American leader and skilled interpreter... - Muncy CreekMuncy CreekMuncy Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Lycoming and Sullivan counties, Pennsylvania, USA. Little Muncy Creek is its major tributary.-Course:The creek is long. For much of its length, U.S. Route 220 runs parallel to Muncy Creek....
from the northeast at MuncyMuncy, PennsylvaniaFor other places named 'Muncy', please see Muncy .Muncy is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The name Muncy comes from the Munsee Indians who once lived in the area. The population was 2,663 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania... - White Deer Hole CreekWhite Deer Hole CreekWhite Deer Hole Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Clinton, Lycoming and Union counties in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A part of the Chesapeake Bay drainage basin, the White Deer Hole Creek watershed drains parts of ten townships...
from the south at Allenwood.

History
Up through the early 19th century the river provided the principal canoeCanoe
A canoe or Canadian canoe is a small narrow boat, typically human-powered, though it may also be powered by sails or small electric or gas motors. Canoes are usually pointed at both bow and stern and are normally open on top, but can be decked over A canoe (North American English) or Canadian...
route across the Alleghenies connecting the Susquehanna and Ohio
Ohio River
The Ohio River is the largest tributary, by volume, of the Mississippi River. At the confluence, the Ohio is even bigger than the Mississippi and, thus, is hydrologically the main stream of the whole river system, including the Allegheny River further upstream...
valleys, with a portage
Portage
Portage or portaging refers to the practice of carrying watercraft or cargo over land to avoid river obstacles, or between two bodies of water. A place where this carrying occurs is also called a portage; a person doing the carrying is called a porter.The English word portage is derived from the...
at Cherry Tree
Cherry Tree, Pennsylvania
Cherry Tree is a borough in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 443 at the 2000 census.-History:Cherry Tree is situated mostly in a valley near the headwaters of West Branch of the Susquehanna River where the river is fed by Cush Cushion Creek.Cherry Tree was originally...
to Blacklick Creek
Blacklick Creek (Pennsylvania)
Blacklick Creek is a tributary of the Conemaugh River, approximately 30 mi long, in western Pennsylvania in the United States....
, a tributary of the Conemaugh River
Conemaugh River
The Conemaugh River is a long tributary of the Kiskiminetas River in Westmoreland, Indiana, and Cambria counties in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania.- Course :...
. In the late 18th century, Cherry Tree marked the frontier between the Pennsylvania Colony and the Shawnee
Shawnee
The Shawnee, Shaawanwaki, Shaawanooki and Shaawanowi lenaweeki, are an Algonquian-speaking people native to North America. Historically they inhabited the areas of Ohio, Virginia, West Virginia, Western Maryland, Kentucky, Indiana, and Pennsylvania...
and Lenape
Lenape
The Lenape are an Algonquian group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands. They are also called Delaware Indians. As a result of the American Revolutionary War and later Indian removals from the eastern United States, today the main groups live in Canada, where they are enrolled in the...
lands to the west as specified by treaty.
The lands along the West Branch were vital hunting grounds and agricultural lands for Native Americans
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
. During Pennsylvania’s great lumbering era, the most significant log drive was conveyed on the West Branch of the Susquehanna River. The Susquehanna’s West Branch Canal Division further shaped the corridor, linking towns and villages and providing vital opportunities for commerce. Finally, railroads
Rail transport
Rail transport is a means of conveyance of passengers and goods by way of wheeled vehicles running on rail tracks. In contrast to road transport, where vehicles merely run on a prepared surface, rail vehicles are also directionally guided by the tracks they run on...
in the corridor fused the links between communities and commerce within the corridor. http://www.dcnr.state.pa.us/brc/rivers/riversconservation/registry/64Sec1.pdf
Early inhabitants
The first recorded inhabitants of the West Branch Susquehanna River valley were the IroquoianIroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a First Nation and Native American language family.-Family division:*Ruttenber, Edward Manning. 1992 [1872]. History of the Indian tribes of Hudson's River. Hope Farm Press....
speaking Susquehannock
Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people were Iroquoian-speaking Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries from the southern part of what is now New York, through Pennsylvania, to the mouth of the Susquehanna in Maryland at the north end of the Chesapeake Bay...
s. Their name meant 'people of the muddy river', from the Lenape
Lenape language
The Delaware languages, also known as the Lenape languages, are Munsee and Unami, two closely related languages of the Eastern Algonquian subgroup of the Algonquian language family...
name of the Susquehanna River, Siskuwihane (<sisku 'mud', hane 'river'). Decimated by diseases and warfare, they had died out, moved away, or been assimilated
Cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is a socio-political response to demographic multi-ethnicity that supports or promotes the assimilation of ethnic minorities into the dominant culture. The term assimilation is often used with regard to immigrants and various ethnic groups who have settled in a new land. New...
into other tribes by the early 18th century. The lands of the West Branch Susquehanna River Valley were then chiefly occupied by the Munsee phratry
Phratry
In ancient Greece, a phratry ατρία, "brotherhood", "kinfolk", derived from φρατήρ meaning "brother") was a social division of the Greek tribe...
of the Lenape
Lenape
The Lenape are an Algonquian group of Native Americans of the Northeastern Woodlands. They are also called Delaware Indians. As a result of the American Revolutionary War and later Indian removals from the eastern United States, today the main groups live in Canada, where they are enrolled in the...
(or Delaware) and were under the nominal control of the Five (later Six) Nations of the Iroquois
Iroquois
The Iroquois , also known as the Haudenosaunee or the "People of the Longhouse", are an association of several tribes of indigenous people of North America...
.
Colonial settlement
Madame Montour's village of Otstonwakin or Ostuagy was a vitally important location during the settlement of what is now Lycoming County. Her village at the mouth of Loyalsock CreekLoyalsock Creek
Loyalsock Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located chiefly in Sullivan and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States...
on the West Branch Susquehanna River was an important stopping point for the Moravian missionaries who were spreading the gospel throughout the wilderness of Pennsylvania during the 1740s. Count Zinzendorf, a missionary being guided by Conrad Weiser
Conrad Weiser
Weiser's colonial service began in 1731. The Iroquois sent Shikellamy, an Oneida chief, as an emissary to other tribes and the British. Shikellamy lived on the Susquehanna River at Shamokin village, near present-day Sunbury, Pennsylvania. An oral tradition holds that Weiser met Shikellamy while...
with the permission of Shikellamy
Shikellamy
Shikellamy , also known as Swatana, was an Oneida chief and overseer for the Iroquois confederacy. In his position as chief and overseer, Shikellamy served as a supervisor for the Six Nations, overseeing the Shawnee and Lenape tribes in central Pennsylvania along the Susquehanna River and...
, came to Ostuagy in 1742.
The British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
purchased land from the Iroquois in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix
Treaty of Fort Stanwix
The Treaty of Fort Stanwix was an important treaty between North American Indians and the British Empire. It was signed in 1768 at Fort Stanwix, located in present-day Rome, New York...
of 1768, opening what is now Lycoming County to settlement. However, the Line of Property
Line of Property
The Line of Property is the name commonly given to the line dividing Indian from British Colonial lands established in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768...
(or Purchase Line
Purchase line
The Purchase Line is the name commonly given to the line dividing Indian from British Colonial lands established in the Treaty of Fort Stanwix of 1768 in western Pennsylvania...
) border defined by "Tiadaghton Creek" dividing colonial and Native American lands was disputed. The colonists claimed this was Pine Creek
Pine Creek (Pennsylvania)
Pine Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Potter, Tioga, Lycoming, and Clinton counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. The creek is long...
, the Iroquois and other tribes Lycoming Creek
Lycoming Creek
Lycoming Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located in Tioga and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States.-Geography:...
. The area between Pine and Lycoming creeks was disputed territory. The illegal settlers there were part of the "Fair Play Men
Fair Play Men
The Fair Play Men were illegal settlers who established their own system of self-rule from 1773 to 1785 in the West Branch Susquehanna River valley of Pennsylvania in what is now the United States. Because they settled in territory claimed by Native Americans, they had no recourse to the...
" system of self-government, with their own Declaration of Independence from Britain on July 4, 1776.
In the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, settlements throughout the Susquehanna valley were attacked by Loyalist
Loyalist (American Revolution)
Loyalists were American colonists who remained loyal to the Kingdom of Great Britain during the American Revolutionary War. At the time they were often called Tories, Royalists, or King's Men. They were opposed by the Patriots, those who supported the revolution...
s and Native Americans allied with the British. After the Wyoming Valley battle and massacre in the summer of 1778 (near what is now Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania
Wilkes-Barre is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, the county seat of Luzerne County. It is at the center of the Wyoming Valley area and is one of the principal cities in the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area, which had a population of 563,631 as of the 2010 Census...
) and smaller local attacks, the "Big Runaway
Big Runaway
The Big Runaway occurred in 1778, during the American Revolutionary War, when settlements throughout the West Branch Susquehanna Valley in Pennsylvania in what became the United States were attacked by Loyalists and Native Americans allied with the British...
" occurred throughout the West Branch Susquehanna valley. Settlers fled feared and actual attacks by the British and their allies. Homes and fields were abandoned, with livestock driven along and a few possessions floated on rafts on the river east to Muncy
Muncy, Pennsylvania
For other places named 'Muncy', please see Muncy .Muncy is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The name Muncy comes from the Munsee Indians who once lived in the area. The population was 2,663 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania...
, then further south to Sunbury
Sunbury, Pennsylvania
Sunbury is a city in Northumberland County, Pennsylvania, United States. The city is located on the east bank of the Susquehanna River, just downstream of the confluence of its main and West branches. The population was 9,905 at the 2010 census...
. The abandoned property was burnt by the attackers. Some settlers soon returned, only to flee again in the summer of 1779 in the "Little Runaway". Sullivan's Expedition helped stabilize the area and encouraged resettlement, which continued after the war. In 1790, Timothy Matlack
Timothy Matlack
Timothy Matlack was a merchant, surveyor, architect, statesman, and patriot in the American Revolution. A delegate from Pennsylvania to the Second Continental Congress in 1780, he emerged during the Revolutionary period as one of Pennsylvania's most provocative and influential political...
, Samuel Maclay and John Adlum were commissioned by the Supreme Executive Council of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania to survey the headwaters of the Susquehanna and explore a route for a passageway to connect the West Branch with the waters of the Allegheny River
Allegheny River
The Allegheny River is a principal tributary of the Ohio River; it is located in the Eastern United States. The Allegheny River joins with the Monongahela River to form the Ohio River at the "Point" of Point State Park in Downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania...
.
The Fair Play Men
Fair Play Men
The Fair Play Men were illegal settlers who established their own system of self-rule from 1773 to 1785 in the West Branch Susquehanna River valley of Pennsylvania in what is now the United States. Because they settled in territory claimed by Native Americans, they had no recourse to the...
were illegal settler
Settler
A settler is a person who has migrated to an area and established permanent residence there, often to colonize the area. Settlers are generally people who take up residence on land and cultivate it, as opposed to nomads...
s (squatters) who established their own system of self-rule from 1773 to 1785 in the West Branch Susquehanna River Valley of Pennsylvania. Because they settled in territory claimed by Native Americans
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
, they had no recourse to the Pennsylvania colonial government. Accordingly, they established what was known as the Fair Play System, with three elected commissioners who ruled on land claims and other issues for the group. In a remarkable coincidence, the Fair Play Men made their own Declaration of Independence
Declaration of independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion of the independence of an aspiring state or states. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another nation or failed nation, or are breakaway territories from within the larger state...
from Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
on July 4, 1776, beneath the "Tiadaghton Elm" on the banks of Pine Creek
Pine Creek (Pennsylvania)
Pine Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River in Potter, Tioga, Lycoming, and Clinton counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. The creek is long...
.
Fort Antes
Fort Antes
Fort Antes was a stockade surrounding the home of Colonel John Henry Antes, built circa 1778 in Revolutionary Pennsylvania in the United States. The fort was built under the direction of Colonel Antes, who was a member of the Pennsylvania militia...
was a stockade
Stockade
A stockade is an enclosure of palisades and tall walls made of logs placed side by side vertically with the tops sharpened to provide security.-Stockade as a security fence:...
surrounding the home of Colonel John Henry Antes, built circa 1778 in Revolutionary
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
Pennsylvania in the United States. The fort was built under the direction of Colonel Antes, who was a member of the Pennsylvania militia
Militia
The term militia is commonly used today to refer to a military force composed of ordinary citizens to provide defense, emergency law enforcement, or paramilitary service, in times of emergency without being paid a regular salary or committed to a fixed term of service. It is a polyseme with...
. It was on the east side of Antes Creek, overlooking and on the left bank of the West Branch Susquehanna River on a plateau
Plateau
In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau...
in Nippenose Township south of modern-day Jersey Shore
Jersey Shore, Pennsylvania
Jersey Shore is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is on the West Branch Susquehanna River, west by south of Williamsport. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area. In the past, Jersey Shore held farms, railroad shops, cigar factories, a...
in western Lycoming County
Lycoming County, Pennsylvania
-Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Plateau:Lycoming County is divided between the Appalachian Mountains in the south, the dissected Allegheny Plateau in the north and east, and the valley of the West Branch Susquehanna River between these.-West Branch Susquehanna River:The West Branch of the...
. The local militia held the fort for a short period of time until it was ordered by Colonel Samuel Hunter to abandon Fort Antes during the Big Runaway
Big Runaway
The Big Runaway occurred in 1778, during the American Revolutionary War, when settlements throughout the West Branch Susquehanna Valley in Pennsylvania in what became the United States were attacked by Loyalists and Native Americans allied with the British...
. Despite being abandoned and attempts by the attacking British forces to burn it down, Fort Antes was one of only two structures in the valley to survive the Big Runaway.
Log boom
The Susquehanna BoomSusquehanna Boom
The Susquehanna Boom was a system of cribs and chained logs in the West Branch Susquehanna River, designed to catch and hold floating timber until it could be processed at one of the nearly 60 sawmills along the river between Lycoming and Loyalsock Creeks in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the...
was a system of cribs in the West Branch Susquehanna River designed to hold timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
in the river until it could be processed at one of the nearly 60 sawmill
Sawmill
A sawmill is a facility where logs are cut into boards.-Sawmill process:A sawmill's basic operation is much like those of hundreds of years ago; a log enters on one end and dimensional lumber exits on the other end....
s along the river between Lycoming
Lycoming Creek
Lycoming Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located in Tioga and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States.-Geography:...
and Loyalsock
Loyalsock Creek
Loyalsock Creek is a tributary of the West Branch Susquehanna River located chiefly in Sullivan and Lycoming counties in Pennsylvania in the United States...
creeks in Lycoming County
Lycoming County, Pennsylvania
-Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Plateau:Lycoming County is divided between the Appalachian Mountains in the south, the dissected Allegheny Plateau in the north and east, and the valley of the West Branch Susquehanna River between these.-West Branch Susquehanna River:The West Branch of the...
. The boom was constructed in 1846 under the supervision of James H. Perkins.
A boom
Log boom
A log boom is a barrier placed in a river, designed to collect and or contain floating logs timbered from nearby forests sometimes called a fence or bag. The term is also used as a place where logs were collected into booms, as at the mouth of a river...
is a chain or line of connected floating timbers extended across a river, lake, or harbor (as to obstruct passage or catch floating objects). The Susquehanna Boom extended 7 miles (11.3 km) upstream from Duboistown
Duboistown, Pennsylvania
Duboistown is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 1,280 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area.-History:...
to the village of Linden in Woodward Township
Woodward Township, Lycoming County, Pennsylvania
Woodward Township is a township in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, in the United States. The population was 2,397 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area.-History:...
. The boom was constructed by creating a series of man-made islands known as "cribs". These cribs built of local mountain stone and sunken timber were stretched diagonally across the river, beginning on the south side near Duboistown and ending on the north side near Linden. The boom was made of 352 separate cribs that were 22 feet (7 m) high. The boom was opened and closed at the upper end by a device known as a "sheer boom." It was 1000 feet (304.8 m) long and was controlled with a hand-powered windlass
Windlass
The windlass is an apparatus for moving heavy weights. Typically, a windlass consists of a horizontal cylinder , which is rotated by the turn of a crank or belt...
. The sheer boom gathered the logs into the main boom that was capable of holding up to 300 million board feet (700,000 m³) of logs. The lower end of the boom was where the logs were sorted. The mills in Williamsport, South Williamsport
South Williamsport, Pennsylvania
South Williamsport is a borough in Lycoming County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 6,412 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Williamsport, Pennsylvania Metropolitan Statistical Area.-History:...
, and Duboistown each had their own distinctive brand burnt into the logs. The men working at the end of the boom would sort the logs according to their corresponding brand and float them into the correct holding pond along the bank of the river.
During the height of the lumber industry in Lycoming County, 1861–1891, the various mills produced 5.5 billion board feet (13 million m³) of lumber. Williamsport became one of the most prosperous cities in Pennsylvania and in the United States. Men like James H. Perkins, Peter Herdic
Peter Herdic
Peter Herdic was a lumber baron, entrepreneur, inventor, politician, and philanthropist in Victorian era Williamsport, Lycoming County, Pennsylvania in the United States. He was the youngest of seven children born to Henry and Elizabeth Herdic on December 14, 1824 in Fort Plain, New York. Herdic's...
, and Mahlon Fisher became millionaire
Millionaire
A millionaire is an individual whose net worth or wealth is equal to or exceeds one million units of currency. It can also be a person who owns one million units of currency in a bank account or savings account...
s while many of the men who actually worked in the river struggled to survive on the wages paid to them by the lumber barons.
See also
- List of Pennsylvania rivers
- List of dams and reservoirs of the Susquehanna River
- List of crossings of the Susquehanna River

