
Weighting
Encyclopedia
While weighting may be applied to a set of data, for example epidemiological data, it is more commonly applied to measurements of light, heat, sound, gamma radiation, in fact any stimulus that is spread over a spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of frequencies.
Weighting and loudness
In the measurement of loudnessLoudness
Loudness is the quality of a sound that is primarily a psychological correlate of physical strength . More formally, it is defined as "that attribute of auditory sensation in terms of which sounds can be ordered on a scale extending from quiet to loud."Loudness, a subjective measure, is often...
, for example, a weighting filter
Weighting filter
A weighting filter is used to emphasise or suppress some aspects of a phenomenon compared to others, for measurement or other purposes.- Audio applications :...
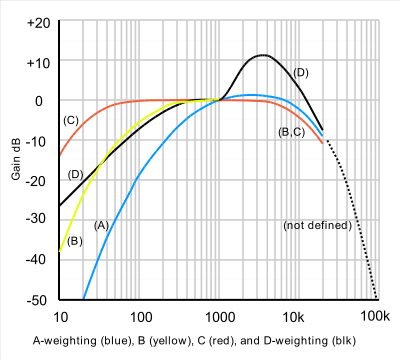
is commonly used to emphasise frequencies around 3 to 6 kHz where the human ear is most sensitive, while attenuating very high and very low frequencies to which the ear is insensitive. A commonly used weighting is the A-weighting
A-weighting
A Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
curve, which results in units of dBA sound pressure level. Because the frequency response of human hearing varies with loudness, the A-weighting curve is only correct at a level of 40-phon
Phon
The phon was proposed in DIN 45631 and ISO 532 B as a unit of perceived loudness level LN for pure tones by S. S. Stevens.-Definition:The purpose of the phon scale is to compensate for the effect of frequency on the perceived loudness of tones...
and other curves known as B, C and D weighting are also used, the latter being particularly intended for the measurement of aircraft noise.
Weighting in audio measurement
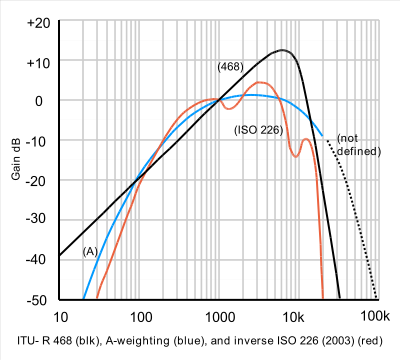
In broadcasting and audio equipment measurements 468-weighting is the preferred weighting to use because it was specifically devised to allow subjectively valid measurements on noise, rather than pure tones. It is often not realised that equal loudness curves, and hence A-weighting, only really apply to tones, as tests with noise bands show increased sensitivity in the 5 to 7 kHz region on noise compared to tones.Other weighting curves are used in rumble measurement and flutter measurement to properly assess subjective effect.
Weighting and gamma rays
In the measurement of gamma rays or other ionising radiation, a radiation monitor or dosimeter will commonly use a filter to attenuate those energy levels or wavelengths that cause the least damage to the human body, while letting through those that do the most damage, so that any source of radiation may be measured in terms of its true danger rather than just its 'strength'. The resulting unit is the sievertSievert
The sievert is the International System of Units SI derived unit of dose equivalent radiation. It attempts to quantitatively evaluate the biological effects of ionizing radiation as opposed to just the absorbed dose of radiation energy, which is measured in gray...
or microsievert.
Weighting and television colour components
Another use of weighting is in television, where the red, green and blue components of the signal are weighted according to their perceived brightness. This ensures compatibility with black and white receivers, and also benefits noise performance and allows separation into meaningful luminance and chrominanceChrominance
Chrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
signals for transmission.
Weighting and UV factor derivation for sun-exposure
Skin damage due to sun exposure is very wavelength dependent over the UV range 295 to 325 nm, with power at the shorter wavelength causing around 30 times as much damage as the longer one. In the calculation of UV IndexUV index
The ultraviolet index or UV Index is an international standard measurement of the strength of the ultraviolet radiation from the sun at a particular place on a particular day...
, a weighting curve is used which is known as the McKinlay-Diffey Erythema action spectrum http://serc.si.edu/labs/photobiology/UVIndex_calculation.aspx
In each field of measurement, special units are used to indicate a weighted measurement as opposed to a basic physical measurement of energy level. For sound, the unit is the phon
Phon
The phon was proposed in DIN 45631 and ISO 532 B as a unit of perceived loudness level LN for pure tones by S. S. Stevens.-Definition:The purpose of the phon scale is to compensate for the effect of frequency on the perceived loudness of tones...
(1 kHz equivalent level).
In the field of acoustics, and audio engineering, it is common to use a standard curve referred to as A-weighting
A-weighting
A Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
, one of a set that are said to be derived from equal-loudness contours.
Weighting in 3D Modeling and Animation
Weighting in the context of 3D modeling and animation refers to how closely the components of a soft body follow their "target," "guide," "goal," or "controller." Components (usually vertices) with higher weights follow (or "conform" to) their guide quite closely, while those with lower weights do not. Take the following instances for example:Skeleton Structure
Often, when an object is rigged with a skeleton, weights are applied to the vertices near the joints. The vertices closer to the joint will usually have a lower weight assigned; the reason for this is so that during deformation, the geometry of the skin does not fold in on itself. Weighting in this situation will most of the time be done automatically using skinning techniques, but is often done by hand in order to fine-tune the skeleton's deformation effects.
Another example of using weights with a skeleton structure would be to actually apply weights to vertices that are not part of a character's skin. An appropriate situation for this method would be the case when an elephant's trunk dangles freely as it walks. The elephant's trunk is rigged with a skeleton and inverse-kinematic (IK) curve. Then a goal curve is created so that the IK curve has something to "aim for" and thus the trunk has a certain shape to which it conforms. Closer to the end of the trunk, the vertices of the IK curve are given lower weights. This way, say if the goal curve was parented to the elephant and a gravity field was in effect, if the elephant stopped walking, the end of the IK curve and thus the end of the trunk would continue to move, dangle back and forth, and ultimately come to a rest in the position determined by the goal curve.
Cloth
Weights are used with cloth as well. Say for instance a character was being outfitted with a dress. Around the waist, the cloth should stay attached to the character, but farther down, its movements should be governed more by effects directly induced by the neighboring cloth vertices rather than the hip movements of the character. In this situation, higher weights are applied to the cloth vertices close to the hip so that they hug the character quite closely compared to the cloth farther down the dress. In order to make the dress more realistic, it is even possible to assign cloth weights of 0 to much of the dress because springs hold the cloth together; one must keep in mind though that doing this for the entire dress would effectively cancel the attachment of the dress to the character.
See also
- Weighting filterWeighting filterA weighting filter is used to emphasise or suppress some aspects of a phenomenon compared to others, for measurement or other purposes.- Audio applications :...
- Equal-loudness contourEqual-loudness contourAn equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure , over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon, and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours...
- A-weightingA-weightingA Weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. The most commonly known example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A,...
- ITU-R 468 noise weightingITU-R 468 noise weightingITU-R 468 is a standard relating to noise measurement, widely used when measuring noise in audio systems. The standard defines a weighting filter curve, together with a quasi-peak rectifier having special characteristics as defined by specified tone-burst tests...
- Psophometric weightingPsophometric weightingPsophometric weighting refers to any weighting curve used in the measurement of noise. In the field of audio engineering it has a more specific meaning, referring to noise weightings used especially in measuring noise on telecommunications circuits...
- Audio quality measurementAudio quality measurementAudio quality measurement seeks to quantify the various forms of corruption present in an audio system or device. The results of such measurement are used to maintain standards in broadcasting, to compile specifications, and to compare pieces of equipment....
- UV indexUV indexThe ultraviolet index or UV Index is an international standard measurement of the strength of the ultraviolet radiation from the sun at a particular place on a particular day...
External links
- Noise measurement briefing
- Calculator for A,C,U, and AU weighting values
- A-weighting filter circuit for audio measurements
- Rane pro audio reference definition of "weighting filters"
- What is a decibel?
- Weighting filter according DIN EN 61672-1 2003-10 (DIN-IEC 651) Calculation: frequency f to dBA and dBC

