Washington State Department of Transportation
Encyclopedia
The Washington State Department of Transportation (WSDOT), was established in 1905. The agency, led by a Secretary and overseen by the Governor, is a Washington governmental agency that constructs, maintains, and regulates the use of the state's transportation infrastructure. WSDOT is responsible for more than 20,000 lane-miles of roadway, nearly 3,000 vehicular bridges and 524 other structures. This infrastructure includes rail lines, state highways, state ferries
(considered part of the highway system) and state airports
to fund new roads that linked the state. The State Highway Board was managed by State Treasurer, State Auditor, and Highway Commissioner Joseph M. Snow and the Board first met on April 17, 1905 to plan the 12 original state roads. The first state highway districts, each managed by a District Engineer, were established in 1918. During this period, the construction of highways began.
In 1921, the State Highway Board was replaced by the Washington Highway Committee and the Washington State Highways Department became a division of the Washington State Department of Public Works. The first gas tax (1¢
per gallon) was levied and Homer Hadley started planning a pontoon bridge
across Lake Washington
, which would later become the Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
, which opened on July 2, 1940. In 1923, the State Highways Department separated from the Public Works Department and organized the first official system of highways, Washington's state road system. In 1926, the U.S. government approved the U.S. route system, which connected the country by road. 11 U.S. Routes entered Washington at the time. Later in 1929, the Highway Committee was merged with the State Highways Department. The Lake Washington Floating Bridge
and the original Tacoma Narrows Bridge opened in 1940. The Tacoma Narrows Bridge collapsed because of winds on November 7, 1940, earning it the name Galloping Gertie. On June 29, 1956, President
Dwight Eisenhower signed the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956
, which started the Interstate Highway System
. Originally, 2 Interstates entered Washington.
Starting in 1961, the Interstate Highways started to be built. There were 2 more Interstates to build and most work was not completed until the 1970s. In 1964, the Highways Department was renamed to WSDOT and the state highways were renumbered
to the current system
. Metro Transit
was created in 1972 and work on highways continued very fast. The North Cascades Highway (SR 20) was completed in 1972 and the first HOV lanes
in Washington were installed on SR 520 in 1972. The Washington State Transportation Commission was established in 1977 and the first meeting was held on September 21, 1977.
On February 13, 1979, the western pontoons of the Hood Canal Bridge
were swept away by a wind storm. In 1980, Mount St. Helens
erupted and caused damage to many state highways, mainly SR 504. The Hood Canal Replacement Bridge
opened on October 3, 1982 and the Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
collapsed on November 25, 1990.
In 1991, a smaller renumbering of state highways occurred. The renumbering produced some new highways and either realigned or removed highways from the system. In 1996, Sound Transit
was formed and in the same year, the Washington State Transportation Commission adopted its first 20-year transportation plan. Throughout the 1990s, WSDOT focused more and more on rail systems and partnered with Amtrak
to make a train route that went from Canada to Oregon, which would later become the Amtrak Cascades
. The 2001 Nisqually earthquake damaged most state highways around the Seattle metropolitan area
and most of the budget was turned over to the Puget Sound
region to help rebuild and repair roads and bridges.
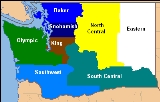
, Northwest
Southwest, North Central, South Central, and Eastern. The Northwest Region is further divided into 3 more regions, which are King County
, Snohomish County
, and Baker (Whatcom
, Skagit
, Island
, and San Juan counties). WSDOT is overseen by the Governor of Washington, who currently is Christine Gregoire
. The Secretary of Transportation, Paula Hammond, also oversees WSDOT.
and third largest in the world. Ferries had been in the Puget Sound
since the 1950s. There are 10 routes and 28 ferries currently operating.
project, which added a southern span to the original bridge, the SR 167 HOT lanes project, which added HOT lanes over SR 167's existing HOV lanes
from the SR 18 area to 180th Street, and the I-5
HOV
extensions project, which extended the HOV lanes in Everett
from the I-5/SR 99
/SR 526/SR 527 interchange to the I-5/US 2
/SR 529 Spur interchange.
Some of the main projects in the future include the Alaskan Way Viaduct
, the SR 520 Floating Bridge
, the ferry terminals
, the I-5
Crash barrier project, SR 704, and more.
Washington State Ferries
Washington State Ferries is a passenger and automobile ferry service owned and operated by the Washington State Department of Transportation that serves communities on Puget Sound and in the San Juan Islands. It is the most used ferry system in the world and the largest passenger and automobile...
(considered part of the highway system) and state airports
History
WSDOT was originally founded as the Washington State Highway Board and the Washington State Highways Department on March 13, 1905, when then-governor Albert Mead signed a bill that gave $110,000 USDUnited States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
to fund new roads that linked the state. The State Highway Board was managed by State Treasurer, State Auditor, and Highway Commissioner Joseph M. Snow and the Board first met on April 17, 1905 to plan the 12 original state roads. The first state highway districts, each managed by a District Engineer, were established in 1918. During this period, the construction of highways began.
In 1921, the State Highway Board was replaced by the Washington Highway Committee and the Washington State Highways Department became a division of the Washington State Department of Public Works. The first gas tax (1¢
Cent (United States coin)
The United States one-cent coin, commonly known as a penny, is a unit of currency equaling one one-hundredth of a United States dollar. The cent's symbol is ¢. Its obverse has featured the profile of President Abraham Lincoln since 1909, the centennial of his birth. From 1959 to 2008, the reverse...
per gallon) was levied and Homer Hadley started planning a pontoon bridge
Pontoon bridge
A pontoon bridge or floating bridge is a bridge that floats on water and in which barge- or boat-like pontoons support the bridge deck and its dynamic loads. While pontoon bridges are usually temporary structures, some are used for long periods of time...
across Lake Washington
Lake Washington
Lake Washington is a large freshwater lake adjacent to the city of Seattle. It is the largest lake in King County and the second largest in the state of Washington, after Lake Chelan. It is bordered by the cities of Seattle on the west, Bellevue and Kirkland on the east, Renton on the south and...
, which would later become the Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
Lake Washington Floating Bridge
The Lake Washington Floating Bridge could refer to one of three floating bridges on Lake Washington:* Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge, opened in 1940 to carry U.S. Route 10 and now carries Interstate 90....
, which opened on July 2, 1940. In 1923, the State Highways Department separated from the Public Works Department and organized the first official system of highways, Washington's state road system. In 1926, the U.S. government approved the U.S. route system, which connected the country by road. 11 U.S. Routes entered Washington at the time. Later in 1929, the Highway Committee was merged with the State Highways Department. The Lake Washington Floating Bridge
Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
The Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge is a floating bridge that carries the eastbound lanes of Interstate 90 across Lake Washington from Seattle to Mercer Island, Washington. It is the second longest floating bridge on Earth at , whereas the longest is the Evergreen Point Floating Bridge just a few...
and the original Tacoma Narrows Bridge opened in 1940. The Tacoma Narrows Bridge collapsed because of winds on November 7, 1940, earning it the name Galloping Gertie. On June 29, 1956, President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Dwight Eisenhower signed the Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956
Federal Aid Highway Act of 1956
The Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, popularly known as the National Interstate and Defense Highways Act , was enacted on June 29, 1956, when Dwight D. Eisenhower signed the bill into law...
, which started the Interstate Highway System
Interstate Highway System
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, , is a network of limited-access roads including freeways, highways, and expressways forming part of the National Highway System of the United States of America...
. Originally, 2 Interstates entered Washington.
Starting in 1961, the Interstate Highways started to be built. There were 2 more Interstates to build and most work was not completed until the 1970s. In 1964, the Highways Department was renamed to WSDOT and the state highways were renumbered
1964 state highway renumbering (Washington)
In 1963, a law was passed authorizing a new numbering for sign routes. In 1970 the legislative definitions were changed to use the sign route numbers but renamed state routes...
to the current system
State highways in Washington
In the U.S. state of Washington, the Washington State Department of Transportation maintains a network of over 7000 miles of state highways, including all Interstate and U.S. Highways that pass through the state. The system comprises 8.5% of the state's public road mileage, but carries over half...
. Metro Transit
Metro Transit
There is more than one public transit system named Metro Transit. Some of the most significant include:* Metro Transit , serving Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia* Metro Transit , serving Kalamazoo, Michigan...
was created in 1972 and work on highways continued very fast. The North Cascades Highway (SR 20) was completed in 1972 and the first HOV lanes
High-occupancy vehicle lane
In transportation engineering and transportation planning, a high-occupancy vehicle lane is a lane reserved for vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers...
in Washington were installed on SR 520 in 1972. The Washington State Transportation Commission was established in 1977 and the first meeting was held on September 21, 1977.
On February 13, 1979, the western pontoons of the Hood Canal Bridge
Hood Canal Bridge
The Hood Canal Bridge is a floating bridge located in the U.S. state of Washington that carries Washington State Route 104 across Hood Canal and connects the Olympic and Kitsap Peninsulas. At long, The Hood Canal Bridge (officially William A. Bugge Bridge) is a floating bridge located in the U.S....
were swept away by a wind storm. In 1980, Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is south of Seattle, Washington and northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a...
erupted and caused damage to many state highways, mainly SR 504. The Hood Canal Replacement Bridge
Hood Canal Bridge
The Hood Canal Bridge is a floating bridge located in the U.S. state of Washington that carries Washington State Route 104 across Hood Canal and connects the Olympic and Kitsap Peninsulas. At long, The Hood Canal Bridge (officially William A. Bugge Bridge) is a floating bridge located in the U.S....
opened on October 3, 1982 and the Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge
The Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge is a floating bridge that carries the eastbound lanes of Interstate 90 across Lake Washington from Seattle to Mercer Island, Washington. It is the second longest floating bridge on Earth at , whereas the longest is the Evergreen Point Floating Bridge just a few...
collapsed on November 25, 1990.
In 1991, a smaller renumbering of state highways occurred. The renumbering produced some new highways and either realigned or removed highways from the system. In 1996, Sound Transit
Sound Transit
Sound Transit has been the popular name of Washington state's Central Puget Sound Regional Transit Authority since September 19, 1999. It was formed in 1996 by the Snohomish, King, and Pierce County Councils...
was formed and in the same year, the Washington State Transportation Commission adopted its first 20-year transportation plan. Throughout the 1990s, WSDOT focused more and more on rail systems and partnered with Amtrak
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak , is a government-owned corporation that was organized on May 1, 1971, to provide intercity passenger train service in the United States. "Amtrak" is a portmanteau of the words "America" and "track". It is headquartered at Union...
to make a train route that went from Canada to Oregon, which would later become the Amtrak Cascades
Amtrak Cascades
The Amtrak Cascades is a passenger train route operated by Amtrak in partnership with the states of Washington and Oregon in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and the province of British Columbia in Canada...
. The 2001 Nisqually earthquake damaged most state highways around the Seattle metropolitan area
Seattle metropolitan area
The Seattle metropolitan area in the US state of Washington includes the city of Seattle, King County, Snohomish County, and Pierce County within the Puget Sound region. The U.S...
and most of the budget was turned over to the Puget Sound
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
region to help rebuild and repair roads and bridges.
Administration
WSDOT divides Washington into 6 regions, the OlympicOlympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is the large arm of land in western Washington state of the USA, that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, and the east by Puget Sound. Cape Alava, the westernmost point in the contiguous...
, Northwest
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
Southwest, North Central, South Central, and Eastern. The Northwest Region is further divided into 3 more regions, which are King County
King County, Washington
King County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. The population in the 2010 census was 1,931,249. King is the most populous county in Washington, and the 14th most populous in the United States....
, Snohomish County
Snohomish County, Washington
Snohomish County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. It is named after the Snohomish tribe. Since 2000, the county's population has grown from 606,024 to 713,335 residents , making it one of the fastest-growing in the state, ranking third in overall population after King and...
, and Baker (Whatcom
Whatcom County, Washington
Whatcom County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. Its name ultimately derives from the Lummi word Xwotʼqom, meaning "noisy water." As of 2010, the population was 201,140. The county seat is at Bellingham, which is also the county's largest city...
, Skagit
Skagit County, Washington
Skagit County is a county in the U.S. state of Washington. It is named after the Skagit Indian tribe. As of 2010, the population was 116,901. It is included in the Mount Vernon-Anacortes, Washington, Metropolitan Statistical Area...
, Island
Island County, Washington
Island County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. In 2010 census, its population was 78,506. Its county seat is Coupeville, while its largest city is Oak Harbor....
, and San Juan counties). WSDOT is overseen by the Governor of Washington, who currently is Christine Gregoire
Christine Gregoire
Christine O'Grady "Chris" Gregoire is the 22nd and current Governor of the state of Washington, and a member of the Democratic Party. Gregoire defeated Republican candidate Dino Rossi in 2004, and again in 2008. She is the second female governor of Washington...
. The Secretary of Transportation, Paula Hammond, also oversees WSDOT.
Ferries
WSDOT manages the official ferry service in Washington. WSDOT's ferry service, called Washington State Ferries, is the largest in the United StatesUnited States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and third largest in the world. Ferries had been in the Puget Sound
Puget Sound
Puget Sound is a sound in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and one minor connection to the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Pacific Ocean — Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and...
since the 1950s. There are 10 routes and 28 ferries currently operating.
Current projects
There are currently about 250 projects that WSDOT is currently planning or constructing. Some of the most notable projects that were recently finished include the Tacoma Narrows BridgeTacoma Narrows Bridge
The Tacoma Narrows Bridge is a pair of twin suspension bridges in the U.S. state of Washington, which carry State Route 16 across the Tacoma Narrows strait of Puget Sound between Tacoma and the Kitsap Peninsula...
project, which added a southern span to the original bridge, the SR 167 HOT lanes project, which added HOT lanes over SR 167's existing HOV lanes
High-occupancy vehicle lane
In transportation engineering and transportation planning, a high-occupancy vehicle lane is a lane reserved for vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers...
from the SR 18 area to 180th Street, and the I-5
Interstate 5 in Washington
Interstate 5 in Washington is a highway in the U.S. state of Washington that extends from its border with Oregon to its border with Canada...
HOV
High-occupancy vehicle lane
In transportation engineering and transportation planning, a high-occupancy vehicle lane is a lane reserved for vehicles with a driver and one or more passengers...
extensions project, which extended the HOV lanes in Everett
Everett, Washington
Everett is the county seat of and the largest city in Snohomish County, Washington, United States. Named for Everett Colby, son of founder Charles L. Colby, it lies north of Seattle. The city had a total population of 103,019 at the 2010 census, making it the 6th largest in the state and...
from the I-5/SR 99
Washington State Route 99
State Route 99, abbreviated SR 99, commonly called Highway 99, is a numbered state highway in the U.S. state of Washington extending just under from Fife in the south to Everett in the north, with a gap in Tukwila.-Southern division:...
/SR 526/SR 527 interchange to the I-5/US 2
U.S. Route 2 in Washington
U.S. Route 2 is a part of the United States Numbered Highway System that has a western segment that runs from Everett, Washington, to the Upper Peninsula of the US state of Michigan. In Washington, it is a state highway that begins at in Downtown Everett. The of US 2 that lie within...
/SR 529 Spur interchange.
Some of the main projects in the future include the Alaskan Way Viaduct
Alaskan Way Viaduct
The Alaskan Way Viaduct, completed on April 4, 1953, is a double-decked elevated section of State Route 99 that runs along the Elliott Bay waterfront in Seattle's Industrial District and downtown Seattle. It is the smaller of the two major north–south traffic corridors through Seattle ,...
, the SR 520 Floating Bridge
Evergreen Point Floating Bridge
The Governor Albert D. Rosellini Bridge—Evergreen Point is the longest floating bridge on Earth at and carries State Route 520 across Lake Washington from Seattle to Medina.The Evergreen Point of the bridge's original name is the westernmost of the three small Eastside...
, the ferry terminals
Washington State Ferries
Washington State Ferries is a passenger and automobile ferry service owned and operated by the Washington State Department of Transportation that serves communities on Puget Sound and in the San Juan Islands. It is the most used ferry system in the world and the largest passenger and automobile...
, the I-5
Interstate 5 in Washington
Interstate 5 in Washington is a highway in the U.S. state of Washington that extends from its border with Oregon to its border with Canada...
Crash barrier project, SR 704, and more.
See also
- U.S. Department of Transportation
- State highways in WashingtonState highways in WashingtonIn the U.S. state of Washington, the Washington State Department of Transportation maintains a network of over 7000 miles of state highways, including all Interstate and U.S. Highways that pass through the state. The system comprises 8.5% of the state's public road mileage, but carries over half...

