
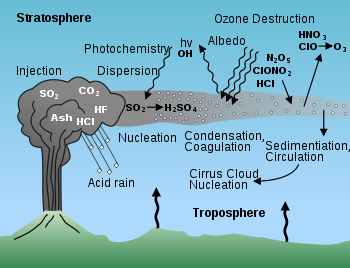
Volcanic gas
Encyclopedia


Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es. These include gases trapped in cavities (vesicles
Vesicular texture
Vesicular texture is a volcanic rock texture characterised by a rock being pitted with many cavities at its surface and inside. The texture is often found in extrusive aphanitic, or glassy, igneous rock...
) in volcanic rock
Volcanic rock
Volcanic rock is a rock formed from magma erupted from a volcano. In other words, it is an igneous rock of volcanic origin...
s, dissolved or dissociated gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es in magma
Magma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
and lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
, or gases emanating directly from lava or indirectly through ground water heated by volcanic action.
The sources of volcanic gases on Earth include:
- primordial and recycled constituents from the Earth's mantleMantle (geology)The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
, - assimilated constituents from the Earth's crust,
- groundwaterGroundwaterGroundwater is water located beneath the ground surface in soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. A unit of rock or an unconsolidated deposit is called an aquifer when it can yield a usable quantity of water. The depth at which soil pore spaces or fractures and voids in rock...
and the Earth's atmosphereEarth's atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
.
Substances that may become gaseous or give off gases when heated are termed volatile substances.
Magmatic gases and high-temperature volcanic gases
Gases are released from magmaMagma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
through volatile constituents reaching such high concentrations in the base magma that they evaporate. (Technically, this would be described as the exsolution and accumulation of the gases upon reaching excess supersaturation of these constituents in the host solution (magmatic melt), and their subsequent loss from the host by diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
and phase separation into bubbles). Molten rock (either magma
Magma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
or lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
) near the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
releases high-temperature volcanic gas (>400 °C).
In explosive volcanic eruptions, sudden release of gases from magma may cause rapid movements of the molten rock. When the magma encounters water, seawater, lake water or groundwater, it can be rapidly fragmented. The rapid expansion of gases is the driving mechanism of most explosive volcanic eruptions. However, a significant portion of volcanic gas release occurs during quasi-continuous quiescent phases of active volcanism.
Low-temperature volcanic gases and hydrothermal systems
If the magmatic gas traveling upward encounters meteoric water in an aquiferAquifer
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water-bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology...
, steam is produced. Latent magmatic heat can also cause meteoric waters to ascent as a vapour phase. Extended fluid-rock interaction of this hot mixture can leach constituents out of the cooling magmatic rock and also the country rock
Country rock (geology)
Country rock is a geological term meaning the rock native to an area. It is similar and in many cases interchangeable with the terms basement and wall rocks....
, causing volume changes and phase transitions, reactions and thus an increase in ionic strength
Ionic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts...
of the upward percolating fluid. This process also decreases the fluid's pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
. Cooling can cause phase separation and mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
deposition, accompanied by a shift toward more reducing conditions. At the surface expression of such hydrothermal systems, low-temperature volcanic gases (<400 °C) are either emanating as steam-gas mixtures or in dissolved form in hot springs
Hot Springs
Hot Springs may refer to:* Hot Springs, Arkansas** Hot Springs National Park, Arkansas*Hot Springs, California**Hot Springs, Lassen County, California**Hot Springs, Modoc County, California**Hot Springs, Placer County, California...
. At the ocean floor, such hot supersaturated hydrothermal fluids form gigantic chimney structures called black smokers, at the point of emission into the cold seawater
Seawater
Seawater is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% . This means that every kilogram of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts . The average density of seawater at the ocean surface is 1.025 g/ml...
.
Non-explosive volcanic gas release
The gas release can occur by advection through fractures, or via diffuse degassing through large areas of permeable ground as Diffuse Degassing Structures (DDS). At sites of advective gas loss, precipitation of sulfur and rare salts forms sulfur deposits and small sulfur chimneys, called fumaroleFumarole
A fumarole is an opening in a planet's crust, often in the neighborhood of volcanoes, which emits steam and gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrochloric acid, and hydrogen sulfide. The steam is created when superheated water turns to steam as its pressure drops when it emerges from...
s. Very low-temperature <100 °C) fumarolic structures are also known as solfataras. Sites of cold degassing of predominantly carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
are called mofettes. Hot springs
Hot Springs
Hot Springs may refer to:* Hot Springs, Arkansas** Hot Springs National Park, Arkansas*Hot Springs, California**Hot Springs, Lassen County, California**Hot Springs, Modoc County, California**Hot Springs, Placer County, California...
on volcanoes often show a measurable amount of magmatic gas in dissolved form.
Composition
Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
(H2O), carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2), sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
either as sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is released by volcanoes and in various industrial processes. Since coal and petroleum often contain sulfur compounds, their combustion generates sulfur dioxide unless the sulfur compounds are removed before burning the fuel...
(SO2) (high-temperature volcanic gases) or hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
(H2S) (low-temperature volcanic gases), nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, argon
Argon
Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide...
, helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
, neon
Neon
Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or...
, methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
. Other compounds detected in volcanic gases are oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(meteoric), hydrogen chloride
Hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the formula HCl. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric humidity. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry...
, hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula HF. This colorless gas is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the aqueous form as hydrofluoric acid, and thus is the precursor to many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers . HF is widely used in the...
, hydrogen bromide
Hydrogen bromide
Hydrogen bromide is the diatomic molecule HBr. HBr is a gas at standard conditions. Hydrobromic acid forms upon dissolving HBr in water. Conversely, HBr can be liberated from hydrobromic acid solutions with the addition of a dehydration agent, but not by distillation. Hydrogen bromide and...
, nitrogen oxide
Nitrogen oxide
Nitrogen oxide can refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:* Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, , nitrogen oxide* Nitrogen dioxide , nitrogen oxide...
(NOx), sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride is an inorganic, colorless, odorless, and non-flammable greenhouse gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule. Typical for a nonpolar gas, it is poorly soluble in water but soluble in...
, carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide
Carbonyl sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula OCS. Commonly written as COS, it is a colourless flammable gas with an unpleasant odor. It is a linear molecule consisting of a carbonyl group double bonded to a sulfur atom...
, and organic compounds. Exotic trace compounds include methylmercury
Methylmercury
Methylmercury is an organometallic cation with the formula . It is a bioaccumulative environmental toxicant.-Structure:...
, halocarbons (including CFCs), and halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
radicals
Radical (chemistry)
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons on an open shell configuration. Free radicals may have positive, negative, or zero charge...
.
The abundance of gases varies considerably from volcano to volcano. Water vapor is consistently the most common volcanic gas, normally comprising more than 60% of total emissions. Carbon dioxide typically accounts for 10 to 40% of emissions.
Volcanoes located at convergent plate boundaries emit more water vapor and chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
than volcanoes at hot spot
Hotspot (geology)
The places known as hotspots or hot spots in geology are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the mantle elsewhere. They may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses to explain them...
s or divergent plate boundaries. This is caused by the addition of seawater into magmas formed at subduction zones. Convergent plate boundary volcanoes also have higher H2O/H2, H2O/CO2, CO2/He and N2/He ratios than hot spot
Hotspot (geology)
The places known as hotspots or hot spots in geology are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the mantle elsewhere. They may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses to explain them...
or divergent plate boundary volcanoes.
Sensing, collection and measurement
Volcanic gases were collected and analysed as long ago as 1790 by Scipione BreislakScipione Breislak
Scipione Breislak , Italian geologist of German parentage, was born in Rome in 1748. He distinguished himself as professor of mathematical and mechanical philosophy in the college of Ragusa; but after residing there for several years he returned to his native city, where he became a professor in...
in Italy.
Volcanic gases can be sensed (measured in-situ) or sampled for further analysis. Volcanic gas sensing can be:
- within the gas by means of electrochemical sensors and flow-through infrared-spectroscopicInfrared spectroscopyInfrared spectroscopy is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic...
gas cells - outside the gas by ground-based or airborne remote spectroscopySpectroscopySpectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
(e.g., COSPEC, FLYSPEC, DOAS, FTIR)
Volcanic gas sampling is often done by a method involving an evacuated flask with caustic solution, first used by Robert W. Bunsen
Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium and rubidium with Gustav Kirchhoff. Bunsen developed several gas-analytical methods, was a pioneer in photochemistry, and did early work in the field of organoarsenic...
(1811-1899) and later refined by the German chemist Werner F. Giggenbach (1937-1997), dubbed Giggenbach-bottle. Other methods include collection in evacuated empty containers, in flow-through glass tubes, in gas wash bottles (cryogenic scrubbers), on impregnated filter packs and on solid adsorbent tubes.
Analytical techniques for gas samples comprise gas chromatography
Chromatography
Chromatography is the collective term for a set of laboratory techniques for the separation of mixtures....
with thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
detection (TCD), flame ionization detection
Flame ionization detector
A flame ionization detector is a type of gas detector used in gas chromatography. The first flame ionization detector was developed in 1957 by scientists working for the CSIRO in Melbourne, Australia....
(FID) and mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
(GC-MS) for gases, and various wet chemical techniques for dissolved species (e.g., acidimetric titration
Titration
Titration, also known as titrimetry, is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis that is used to determine the unknown concentration of an identified analyte. Because volume measurements play a key role in titration, it is also known as volumetric analysis. A reagent, called the...
for dissolved CO2, and ion chromatography for sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
, chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
, fluoride
Fluoride
Fluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
). The trace metal, trace organic and isotopic
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
composition is usually determined by different mass spectrometric methods.
Volcanic gases and volcano monitoring
Main article: Prediction of volcanic activityCertain constituents of volcanic gases may show very early signs of changing conditions at depth, making them a powerful tool to predict imminent unrest. Used in conjunction with monitoring data on seismicity and deformation, correlative monitoring gains great efficiency. Volcanic gas monitoring is a standard tool of any volcano observatory
Volcano observatory
A volcano observatory is an institution that conducts research and monitoring of a volcano.Each observatory provides continuous and periodic monitoring of the seismicity, other geophysical changes, ground movements, volcanic gas chemistry, and hydrologic conditions and activity between and during...
. Unfortunately, the most precise compositional data still require dangerous field sampling campaigns. However, remote sensing
Remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon, without making physical contact with the object. In modern usage, the term generally refers to the use of aerial sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth by means of propagated signals Remote sensing...
techniques have advanced tremendously through the 1990s.
Hazards
Volcanic gases were directly responsible for approximately 3% of all volcano-related deaths of humans between 1900 and 1986. Some volcanic gases kill by acidic corrosionCorrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
; others kill by asphyxiation. The greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
, carbon dioxide, is emitted from volcanoes, accounting for nearly 1% of the annual global total. Some volcanic gases including sulfur dioxide, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen sulfide and hydrogen fluoride react with other atmospheric particles to form aerosol
Aerosol
Technically, an aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas. Examples are clouds, and air pollution such as smog and smoke. In general conversation, aerosol usually refers to an aerosol spray can or the output of such a can...
s.

