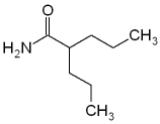
Valpromide
Encyclopedia
Valpromide is a carboxamide
derivative of valproic acid
used in the treatment of epilepsy
and some affective disorders. It is rapidly metabolised (80%) to valproic acid
(another anticonvulsant
) but has anticonvulsant properties itself. It may produce more stable plasma levels than valproic acid
or sodium valproate
and may be more effectively at preventing febrile seizures. However it is over one hundred times more potent inhibitor of liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase
. This makes it incompatible with carbamazepine
and can affect the ability of the body to remove other toxins. Valpromide is no safer during pregnancy than valproic acid.
Valpromide is formed through the reaction of valproic acid and ammonia
via an intermediate acid
chloride
.
In pure form, valpromide is a white crystalline powder and has melting point 125-126°C
. It is practically insoluble in water but soluble in hot water. It is available on the market in some European countries.
Carboxamide
In organic chemistry carboxamides are functional groups with the general structure R-CO-NH2 with R as an organic substituent.Two amino acids, asparagine and glutamine, have a carboxamide group in them....
derivative of valproic acid
Valproic acid
Valproic acid is a chemical compound that has found clinical use as an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug, primarily in the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and, less commonly, major depression. It is also used to treat migraine headaches and schizophrenia...
used in the treatment of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
and some affective disorders. It is rapidly metabolised (80%) to valproic acid
Valproic acid
Valproic acid is a chemical compound that has found clinical use as an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug, primarily in the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and, less commonly, major depression. It is also used to treat migraine headaches and schizophrenia...
(another anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsant
The anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and in the treatment of neuropathic pain. The goal of an...
) but has anticonvulsant properties itself. It may produce more stable plasma levels than valproic acid
Valproic acid
Valproic acid is a chemical compound that has found clinical use as an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug, primarily in the treatment of epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and, less commonly, major depression. It is also used to treat migraine headaches and schizophrenia...
or sodium valproate
Sodium valproate
Sodium valproate or valproate sodium is the sodium salt of valproic acid and is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy, anorexia nervosa, panic attack, anxiety disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, migraine and bipolar disorder, as well as other psychiatric conditions requiring...
and may be more effectively at preventing febrile seizures. However it is over one hundred times more potent inhibitor of liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase
Epoxide hydrolase
Epoxide hydrolase functions in detoxication during drug metabolism. It converts epoxides to trans-dihydrodiols, which can be conjugated and excreted from the body. Epoxides result from the degradation of aromatic compounds...
. This makes it incompatible with carbamazepine
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant and mood-stabilizing drug used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder, as well as trigeminal neuralgia...
and can affect the ability of the body to remove other toxins. Valpromide is no safer during pregnancy than valproic acid.
Valpromide is formed through the reaction of valproic acid and ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
via an intermediate acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
.
In pure form, valpromide is a white crystalline powder and has melting point 125-126°C
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
. It is practically insoluble in water but soluble in hot water. It is available on the market in some European countries.

