Usability testing
Encyclopedia
Usability testing is a technique used in user-centered
interaction design
to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can be seen as an irreplaceable usability
practice, since it gives direct input on how real users use the system. This is in contrast with usability inspection
methods where experts use different methods to evaluate a user interface without involving users.
Usability testing focuses on measuring a human-made product's capacity to meet its intended purpose. Examples of products that commonly benefit from usability testing are food
s, consumer products, web sites
or web applications, computer interfaces
, documents, and devices. Usability testing measures the usability, or ease of use, of a specific object or set of objects, whereas general human-computer interaction studies attempt to formulate universal principles.
in the late 1940s contracted to design the state rooms for the twin ocean liners "Independence" and "Constitution." He built eight prototype staterooms and installed them in a warehouse. He then brought in a series of travelers to "live" in the rooms for a short time, bringing with them all items they would normally take when cruising. His people were able to discover over time, for example, if there was space for large steamer trunks, if light switches needed to be added beside the beds to prevent injury, etc., before hundreds of state rooms had been built into the ship.
A Xerox
Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) employee wrote that PARC
used extensive usability testing in creating the Xerox Star, introduced in 1981. Only about 25,000 units were sold, leading many to consider the Xerox Star
a commercial failure.
The Inside Intuit book, says (page 22, 1984), "... in the first instance of the Usability Testing that later became standard industry practice, LeFevre recruited people off the streets... and timed their Kwik-Chek (Quicken
) usage with a stopwatch. After every test... programmers worked to improve the program."http://books.google.com/books?id=lRs_4U43UcEC&printsec=frontcover&sig=ACfU3U1xvA7-f80TP9Zqt9wkB9adVAqZ4g#PPA22,M1) Scott Cook
, Intuit co-founder, said, "... we did usability testing in 1984, five years before anyone else... there's a very big difference between doing it and having marketing people doing it as part of their... design... a very big difference between doing it and having it be the core of what engineers focus on.
or qualitative research
rather than usability testing. Usability testing usually involves systematic observation under controlled conditions to determine how well people can use the product. However, often both qualitative and usability testing are used in combination, to better understand users' motivations/perceptions, in addition to their actions.
Rather than showing users a rough draft and asking, "Do you understand this?", usability testing involves watching people trying to use something for its intended purpose. For example, when testing instructions for assembling a toy, the test subjects should be given the instructions and a box of parts and, rather than being asked to comment on the parts and materials, they are asked to put the toy together. Instruction phrasing, illustration quality, and the toy's design all affect the assembly process.
, or realistic situation, wherein the person performs a list of tasks using the product being tested while observers watch and take notes. Several other test instruments such as scripted instructions, paper prototypes
, and pre- and post-test questionnaires are also used to gather feedback on the product being tested. For example, to test the attachment function of an e-mail
program, a scenario would describe a situation where a person needs to send an e-mail attachment, and ask him or her to undertake this task. The aim is to observe how people function in a realistic manner, so that developers can see problem areas, and what people like. Techniques popularly used to gather data during a usability test include think aloud protocol
, Co-discovery Learning and eye tracking
.
of usability testing. Rather than using an in-house, trained group of testers, just five to six random people, indicative of a cross-section
of end users, are brought in to test the product, or service. The name of the technique refers to the fact that the testers should be random people who pass by in the hallway.
Hallway testing is particularly effective in the early stages of a new design when the designers are looking for "brick walls," problems so serious that users simply cannot advance. Anyone of normal intelligence other than designers and engineers can be used at this point. (Both designers and engineers immediately turn from being test subjects into being "expert reviewers." They are often too close to the project, so they already know how to accomplish the task, thereby missing ambiguities and false paths.)
Asynchronous methodologies include automatic collection of user’s click streams, user logs of critical incidents that occur while interacting with the application and subjective feedback on the interface by users. Similar to an in-lab study, an asynchronous remote usability test is task-based and the platforms allow you to capture clicks and task times. Hence, for many large companies this allows you to understand the WHY behind the visitors' intents when visiting a website or mobile site. Additionally, this style of user testing also provides an opportunity to segment feedback by demographic, attitudinal and behavioural type. The tests are carried out in the user’s own environment (rather than labs) helping further simulate real-life scenario testing. This approach also provides a vehicle to easily solicit feedback from users in remote areas.
Numerous tools are available to address the needs of both these approaches. WebEx and Go-to-meeting are the most commonly used technologies to conduct a synchronous remote usability test. However, synchronous remote testing may lack the immediacy and sense of “presence” desired to support a collaborative testing process. Moreover, managing inter-personal dynamics across cultural and linguistic barriers may require approaches sensitive to the cultures involved. Other disadvantages include having reduced control over the testing environment and the distractions and interruptions experienced by the participants’ in their native environment. One of the newer methods developed for conducting a synchronous remote usability test is by using virtual worlds.
, at that time a researcher at Sun Microsystems
, popularized the concept of using numerous small usability tests—typically with only five test subjects each—at various stages of the development process. His argument is that, once it is found that two or three people are totally confused by the home page, little is gained by watching more people suffer through the same flawed design. "Elaborate usability tests are a waste of resources. The best results come from testing no more than five users and running as many small tests as you can afford.". Nielsen subsequently published his research and coined the term heuristic evaluation
.
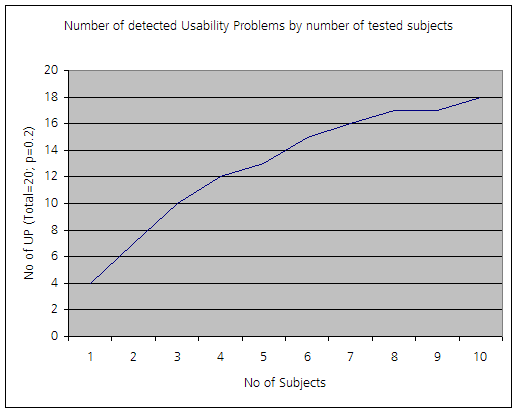
The claim of "Five users is enough" was later described by a mathematical model which states for the proportion of uncovered problems U

where p is the probability of one subject identifying a specific problem and n the number of subjects (or test sessions). This model shows up as an asymptotic graph towards the number of real existing problems (see figure below).
In later research Nielsen's claim has eagerly been questioned with both empirical
evidence and more advanced mathematical model
s. Two key challenges to this assertion are:
It is worth noting that Nielsen does not advocate stopping after a single test with five users; his point is that testing with five users, fixing the problems they uncover, and then testing the revised site with five different users is a better use of limited resources than running a single usability test with 10 users. In practice, the tests are run once or twice per week during the entire development cycle, using three to five test subjects per round, and with the results delivered within 24 hours to the designers. The number of users actually tested over the course of the project can thus easily reach 50 to 100 people.
In the early stage, when users are most likely to immediately encounter problems that stop them in their tracks, almost anyone of normal intelligence can be used as a test subject. In stage two, testers will recruit test subjects across a broad spectrum of abilities. For example, in one study, experienced users showed no problem using any design, from the first to the last, while naive user and self-identified power users both failed repeatedly. Later on, as the design smooths out, users should be recruited from the target population.
When the method is applied to a sufficient number of people over the course of a project, the objections raised above become addressed: The sample size ceases to be small and usability problems that arise with only occasional users are found. The value of the method lies in the fact that specific design problems, once encountered, are never seen again because they are immediately eliminated, while the parts that appear successful are tested over and over. While it's true that the initial problems in the design may be tested by only five users, when the method is properly applied, the parts of the design that worked in that initial test will go on to be tested by 50 to 100 people.
User-centered design
In broad terms, user-centered design or pervasive usability is a design philosophy and a process in which the needs, wants, and limitations of end users of a product are given extensive attention at each stage of the design process...
interaction design
Interaction design
In design, human–computer interaction, and software development, interaction design, often abbreviated IxD, is "the practice of designing interactive digital products, environments, systems, and services." Like many other design fields interaction design also has an interest in form but its main...
to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can be seen as an irreplaceable usability
Usability
Usability is the ease of use and learnability of a human-made object. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a usability analyst or as a secondary job...
practice, since it gives direct input on how real users use the system. This is in contrast with usability inspection
Usability inspection
Usability inspection is the name for a set of methods where an evaluator inspects a user interface. This is in contrast to usability testing where the usability of the interface is evaluated by testing it on real users. Usability inspections can generally be used early in the development process by...
methods where experts use different methods to evaluate a user interface without involving users.
Usability testing focuses on measuring a human-made product's capacity to meet its intended purpose. Examples of products that commonly benefit from usability testing are food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
s, consumer products, web sites
Web design
Web design is the process of planning and creating a website. Text, images, digital media and interactive elements are used by web designers to produce the page seen on the web browser...
or web applications, computer interfaces
User interface
The user interface, in the industrial design field of human–machine interaction, is the space where interaction between humans and machines occurs. The goal of interaction between a human and a machine at the user interface is effective operation and control of the machine, and feedback from the...
, documents, and devices. Usability testing measures the usability, or ease of use, of a specific object or set of objects, whereas general human-computer interaction studies attempt to formulate universal principles.
History of usability testing
Henry DreyfussHenry Dreyfuss
Henry Dreyfuss was an American industrial designer.-Career:Dreyfuss was a native of Brooklyn, New York. As one of the celebrity industrial designers of the 1930s and 1940s, Dreyfuss dramatically improved the look, feel, and usability of dozens of consumer products...
in the late 1940s contracted to design the state rooms for the twin ocean liners "Independence" and "Constitution." He built eight prototype staterooms and installed them in a warehouse. He then brought in a series of travelers to "live" in the rooms for a short time, bringing with them all items they would normally take when cruising. His people were able to discover over time, for example, if there was space for large steamer trunks, if light switches needed to be added beside the beds to prevent injury, etc., before hundreds of state rooms had been built into the ship.
A Xerox
Xerox
Xerox Corporation is an American multinational document management corporation that produced and sells a range of color and black-and-white printers, multifunction systems, photo copiers, digital production printing presses, and related consulting services and supplies...
Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) employee wrote that PARC
PARC
PARC or Parc may refer to:* PARC , the Palo Alto Research Center * PARC Management, a theme park and entertainment venue operator...
used extensive usability testing in creating the Xerox Star, introduced in 1981. Only about 25,000 units were sold, leading many to consider the Xerox Star
Xerox Star
The Star workstation, officially known as the Xerox 8010 Information System, was introduced by Xerox Corporation in 1981. It was the first commercial system to incorporate various technologies that today have become commonplace in personal computers, including a bitmapped display, a window-based...
a commercial failure.
The Inside Intuit book, says (page 22, 1984), "... in the first instance of the Usability Testing that later became standard industry practice, LeFevre recruited people off the streets... and timed their Kwik-Chek (Quicken
Quicken
Quicken is a personal finance management tool developed by Intuit, Inc.Quicken runs on Windows and Macintosh systems. Previous versions ran on DOS. An online version is also available. The last version of Quicken for Macintosh computers was Quicken Essentials for Mac released in February 2010...
) usage with a stopwatch. After every test... programmers worked to improve the program."http://books.google.com/books?id=lRs_4U43UcEC&printsec=frontcover&sig=ACfU3U1xvA7-f80TP9Zqt9wkB9adVAqZ4g#PPA22,M1) Scott Cook
Scott Cook
Scott David Cook is a founder of Intuit, has been a director of Intuit since March 1983 and is currently Chairman of the Executive Committee of the Board. Cook also serves on the boards of directors of eBay Inc., and The Procter & Gamble Company....
, Intuit co-founder, said, "... we did usability testing in 1984, five years before anyone else... there's a very big difference between doing it and having marketing people doing it as part of their... design... a very big difference between doing it and having it be the core of what engineers focus on.
Goals of usability testing
Usability testing is a black-box testing technique. The aim is to observe people using the product to discover errors and areas of improvement. Usability testing generally involves measuring how well test subjects respond in four areas: efficiency, accuracy, recall, and emotional response. The results of the first test can be treated as a baseline or control measurement; all subsequent tests can then be compared to the baseline to indicate improvement.- Performance -- How much time, and how many steps, are required for people to complete basic tasks? (For example, find something to buy, create a new account, and order the item.)
- Accuracy -- How many mistakes did people make? (And were they fatal or recoverable with the right information?)
- Recall -- How much does the person remember afterwards or after periods of non-use?
- Emotional response -- How does the person feel about the tasks completed? Is the person confident, stressed? Would the user recommend this system to a friend?
What usability testing is not
Simply gathering opinions on an object or document is market researchMarket research
Market research is any organized effort to gather information about markets or customers. It is a very important component of business strategy...
or qualitative research
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry employed in many different academic disciplines, traditionally in the social sciences, but also in market research and further contexts. Qualitative researchers aim to gather an in-depth understanding of human behavior and the reasons that govern such...
rather than usability testing. Usability testing usually involves systematic observation under controlled conditions to determine how well people can use the product. However, often both qualitative and usability testing are used in combination, to better understand users' motivations/perceptions, in addition to their actions.
Rather than showing users a rough draft and asking, "Do you understand this?", usability testing involves watching people trying to use something for its intended purpose. For example, when testing instructions for assembling a toy, the test subjects should be given the instructions and a box of parts and, rather than being asked to comment on the parts and materials, they are asked to put the toy together. Instruction phrasing, illustration quality, and the toy's design all affect the assembly process.
Methods
Setting up a usability test involves carefully creating a scenarioScenario
A scenario is a synoptical collage of an event or series of actions and events. In the Commedia dell'arte it was an outline of entrances, exits, and action describing the plot of a play that was literally pinned to the back of the scenery...
, or realistic situation, wherein the person performs a list of tasks using the product being tested while observers watch and take notes. Several other test instruments such as scripted instructions, paper prototypes
Paper prototypes
In human–computer interaction, paper prototyping is a widely used method in the user-centered design process, a process that helps developers to create software that meets the user's expectations and needs - in this case, especially for designing and testing user interfaces...
, and pre- and post-test questionnaires are also used to gather feedback on the product being tested. For example, to test the attachment function of an e-mail
E-mail
Electronic mail, commonly known as email or e-mail, is a method of exchanging digital messages from an author to one or more recipients. Modern email operates across the Internet or other computer networks. Some early email systems required that the author and the recipient both be online at the...
program, a scenario would describe a situation where a person needs to send an e-mail attachment, and ask him or her to undertake this task. The aim is to observe how people function in a realistic manner, so that developers can see problem areas, and what people like. Techniques popularly used to gather data during a usability test include think aloud protocol
Think aloud protocol
Think-aloud protocol is a method used to gather data in usability testing in product design and development, in psychology and a range of social sciences...
, Co-discovery Learning and eye tracking
Eye tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research on the visual system, in psychology, in cognitive linguistics and in product...
.
Hallway testing
Hallway testing (or Hall Intercept Testing) is a general methodologyMethodology
Methodology is generally a guideline for solving a problem, with specificcomponents such as phases, tasks, methods, techniques and tools . It can be defined also as follows:...
of usability testing. Rather than using an in-house, trained group of testers, just five to six random people, indicative of a cross-section
Cross-sectional data
Cross-sectional data or cross section in statistics and econometrics is a type of one-dimensional data set. Cross-sectional data refers to data collected by observing many subjects at the same point of time, or without regard to differences in time...
of end users, are brought in to test the product, or service. The name of the technique refers to the fact that the testers should be random people who pass by in the hallway.
Hallway testing is particularly effective in the early stages of a new design when the designers are looking for "brick walls," problems so serious that users simply cannot advance. Anyone of normal intelligence other than designers and engineers can be used at this point. (Both designers and engineers immediately turn from being test subjects into being "expert reviewers." They are often too close to the project, so they already know how to accomplish the task, thereby missing ambiguities and false paths.)
Remote Usability Testing
In a scenario where usability evaluators, developers and prospective users are located in different countries and time zones, conducting a traditional lab usability evaluation creates challenges both from the cost and logistical perspectives. These concerns led to research on remote usability evaluation, with the user and the evaluators separated over space and time. Remote testing, which facilitates evaluations being done in the context of the user’s other tasks and technology can be either synchronous or asynchronous. Synchronous usability testing methodologies involve video conferencing or employ remote application sharing tools such as WebEx. The former involves real time one-on-one communication between the evaluator and the user, while the latter involves the evaluator and user working separately.Asynchronous methodologies include automatic collection of user’s click streams, user logs of critical incidents that occur while interacting with the application and subjective feedback on the interface by users. Similar to an in-lab study, an asynchronous remote usability test is task-based and the platforms allow you to capture clicks and task times. Hence, for many large companies this allows you to understand the WHY behind the visitors' intents when visiting a website or mobile site. Additionally, this style of user testing also provides an opportunity to segment feedback by demographic, attitudinal and behavioural type. The tests are carried out in the user’s own environment (rather than labs) helping further simulate real-life scenario testing. This approach also provides a vehicle to easily solicit feedback from users in remote areas.
Numerous tools are available to address the needs of both these approaches. WebEx and Go-to-meeting are the most commonly used technologies to conduct a synchronous remote usability test. However, synchronous remote testing may lack the immediacy and sense of “presence” desired to support a collaborative testing process. Moreover, managing inter-personal dynamics across cultural and linguistic barriers may require approaches sensitive to the cultures involved. Other disadvantages include having reduced control over the testing environment and the distractions and interruptions experienced by the participants’ in their native environment. One of the newer methods developed for conducting a synchronous remote usability test is by using virtual worlds.
Expert review
Expert review is another general method of usability testing. As the name suggests, this method relies on bringing in experts with experience in the field (possibly from companies that specialize in usability testing) to evaluate the usability of a product.Automated expert review
Similar to expert reviews, automated expert reviews provide usability testing but through the use of programs given rules for good design and heuristics. Though an automated review might not provide as much detail and insight as reviews from people, they can be finished more quickly and consistently. The idea of creating surrogate users for usability testing is an ambitious direction for the Artificial Intelligence community.How many users to test?
In the early 1990s, Jakob NielsenJakob Nielsen (usability consultant)
Jakob Nielsen is a leading web usability consultant. He holds a Ph.D. in human–computer interaction from the Technical University of Denmark in Copenhagen.-Early life and background:...
, at that time a researcher at Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
, popularized the concept of using numerous small usability tests—typically with only five test subjects each—at various stages of the development process. His argument is that, once it is found that two or three people are totally confused by the home page, little is gained by watching more people suffer through the same flawed design. "Elaborate usability tests are a waste of resources. The best results come from testing no more than five users and running as many small tests as you can afford.". Nielsen subsequently published his research and coined the term heuristic evaluation
Heuristic evaluation
A heuristic evaluation is a discount usability inspection method for computer software that helps to identify usability problems in the user interface design. It specifically involves evaluators examining the interface and judging its compliance with recognized usability principles...
.
The claim of "Five users is enough" was later described by a mathematical model which states for the proportion of uncovered problems U

where p is the probability of one subject identifying a specific problem and n the number of subjects (or test sessions). This model shows up as an asymptotic graph towards the number of real existing problems (see figure below).

In later research Nielsen's claim has eagerly been questioned with both empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
evidence and more advanced mathematical model
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
s. Two key challenges to this assertion are:
- since usability is related to the specific set of users, such a small sample size is unlikely to be representative of the total population so the data from such a small sample is more likely to reflect the sample group than the population they may represent
- Not every usability problem is equally easy-to-detect. Intractable problems happen to decelerate the overall process. Under these circumstances the progress of the process is much shallower than predicted by the Nielsen/Landauer formula.
It is worth noting that Nielsen does not advocate stopping after a single test with five users; his point is that testing with five users, fixing the problems they uncover, and then testing the revised site with five different users is a better use of limited resources than running a single usability test with 10 users. In practice, the tests are run once or twice per week during the entire development cycle, using three to five test subjects per round, and with the results delivered within 24 hours to the designers. The number of users actually tested over the course of the project can thus easily reach 50 to 100 people.
In the early stage, when users are most likely to immediately encounter problems that stop them in their tracks, almost anyone of normal intelligence can be used as a test subject. In stage two, testers will recruit test subjects across a broad spectrum of abilities. For example, in one study, experienced users showed no problem using any design, from the first to the last, while naive user and self-identified power users both failed repeatedly. Later on, as the design smooths out, users should be recruited from the target population.
When the method is applied to a sufficient number of people over the course of a project, the objections raised above become addressed: The sample size ceases to be small and usability problems that arise with only occasional users are found. The value of the method lies in the fact that specific design problems, once encountered, are never seen again because they are immediately eliminated, while the parts that appear successful are tested over and over. While it's true that the initial problems in the design may be tested by only five users, when the method is properly applied, the parts of the design that worked in that initial test will go on to be tested by 50 to 100 people.
See also
- ISO 9241ISO 9241ISO 9241 is a multi-part standard from the International Organization for Standardization covering ergonomics of human-computer interaction. It is managed by the ISO...
- Software testingSoftware testingSoftware testing is an investigation conducted to provide stakeholders with information about the quality of the product or service under test. Software testing can also provide an objective, independent view of the software to allow the business to appreciate and understand the risks of software...
- Educational technologyEducational technologyEducational technology is the study and ethical practice of facilitating learning and improving performance by creating, using and managing appropriate technological processes and resources." The term educational technology is often associated with, and encompasses, instructional theory and...
- Universal usabilityUniversal usabilityUniversal usability refers to the design of information and communications products and services that are usable for every citizen. The concept has been advocated by Professor Ben Shneiderman, a computer scientist at the University of Maryland, College Park...
- Commercial eye tracking
- Don't Make Me ThinkDon't Make Me ThinkDon't Make Me Think is a book by Steve Krug about human-computer interaction and web usability. The book's premise is that a good software program or web site should let users accomplish their intended tasks as easily and directly as possible...
- Performance testingPerformance testingIn software engineering, performance testing is in general testing performed to determine how a system performs in terms of responsiveness and stability under a particular workload...
- System Usability Scale (SUS)System Usability ScaleIn systems engineering, the system usability scale is a simple, ten-item attitude Likert scale giving a global view of subjective assessments of usability...
- Test methodTest methodA test method is a definitive procedure that produces a test result.A test can be considered as technical operation that consists of determination of one or more characteristics of a given product, process or service according to a specified procedure. Often a test is part of an experiment.The test...
- Tree testing
- RITE MethodRITE MethodRITE Method, for Rapid Iterative Testing and Evaluation, typically referred to as "RITE" testing, is an iterative usability method. It was defined by Michael Medlock, Dennis Wixon, Bill Fulton, Mark Terrano and Ramon Romero. It has been publicly championed by Dennis Wixon while working in the...
- Component-Based Usability TestingComponent-Based Usability TestingComponent-based usability testing is a testing approach which aims at empirically testing the usability of an interaction component. The latter is defined as an elementary unit of an interactive system, on which behaviour-based evaluation is possible...
- Crowdsource testingCrowdsource testingCrowdsource testing is an emerging trend in software testing which exploits the benefits, effectiveness, and efficiency of crowdsourcing and the cloud platform. It differs from traditional testing methods in that the testing is carried out by a number of different testers from different places, and...

