
Twin prime
Encyclopedia
A twin prime is a prime number
that differs from another prime number by two. Except for the pair (2, 3), this is the smallest possible difference between two primes. Some examples of twin prime pairs are (3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13), (17, 19), (29, 31) and (41, 43). Sometimes the term twin prime is used for a pair of twin primes; an alternative name for this is prime twin.
for many years. This is the content of the twin prime conjecture, which states There are infinitely many primes p such that p + 2 is also prime. In 1849 de Polignac
made the more general conjecture that for every natural number k, there are infinitely many prime pairs p and p′ such that p′ − p = 2k. The case k = 1 is the twin prime conjecture.
A stronger form of the twin prime conjecture, the Hardy–Littlewood conjecture, postulates a distribution law for twin primes akin to the prime number theorem
.
showed that the sum of reciprocals of the twin primes was convergent. This famous result, called Brun's theorem
, was the first use of the Brun sieve
and helped initiate the development of modern sieve theory
. The modern version of Brun's argument can be used to show that the number of twin primes less than N does not exceed
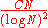
for some absolute constant C > 0.
In 1940, Paul Erdős
showed that there is a constant
c < 1 and infinitely many primes p such that (p′ − p) < (c ln p) where p′ denotes the next prime after p. This result was successively improved; in 1986 Helmut Maier
showed that a constant c < 0.25 can be used. In 2004 Daniel Goldston
and Cem Yıldırım
showed that the constant could be improved further to c = 0.085786… In 2005, Goldston, János Pintz
and Yıldırım established that c can be chosen to be arbitrarily small
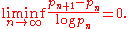
In fact, by assuming the Elliott–Halberstam conjecture or a slightly weaker version, they were able to show that there are infinitely many n such that at least two of n, n + 2, n + 6, n + 8, n + 12, n + 18, or n + 20 are prime. Under a stronger hypothesis they showed that for infinitely many n at least two of n, n + 2, n + 4, and n + 6 are prime.
Every twin prime pair except (3, 5) is of the form (6n − 1, 6n + 1) for some natural number
n, and with the exception of n = 1, n must end in 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, or 8.
It has been proven that the pair (m, m+2) is a twin prime if and only if

If m − 4 or m + 6 is also prime then the 3 primes are called a prime triplet
.
projects, Twin Prime Search
and PrimeGrid
found the largest known twin primes, 2003663613 · 2195000 ± 1. The numbers have 58711 decimal
digits
. Their discoverer was Eric Vautier of France
.
On August 6, 2009 those same two projects announced that a new record twin prime had been found. It is 65516468355 · 2333333 ± 1. The numbers have 100355 decimal digits.
An empirical analysis of all prime pairs up to 4.35 · 1015 shows that if the number of such pairs less than x is f(x)·x/(log x)2 then f(x) is about 1.7 for small x and decreases towards about 1.3 as x tends to infinity.
There are 808,675,888,577,436 twin prime pairs below 1018.
The limiting value of f(x) is conjectured to equal twice the twin prime constant (not to be confused with Brun's constant)
this conjecture would imply the twin prime conjecture, but remains unresolved.
The twin prime conjecture would give a better approximation, as with the prime counting function
, by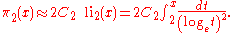
Since every third odd number is divisible by 3, no three successive odd numbers can be prime unless one of them is 3, thus 5 is the only prime which is part of two pairs. Also, along the same lines, other than the first pair, the number centered between the twin primes must always be divisible by 6. The lower member of a pair is by definition a Chen prime
.
and John Littlewood
) is a generalization of the twin prime conjecture. It is concerned with the distribution of prime constellations, including twin primes, in analogy to the prime number theorem
. Let π2(x) denote the number of primes p ≤ x such that p + 2 is also prime. Define the twin prime constant C2 as

(here the product extends over all prime numbers p ≥ 3). Then the conjecture is that
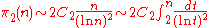
in the sense that the quotient of the two expressions tends to
1 as n approaches infinity. (The second ~ is not part of the conjecture and is proved by integration by parts
.)
This conjecture can be justified (but not proven) by assuming that 1 / ln t describes the density function of the prime distribution, an assumption suggested by the prime number theorem.
from 1849 states that for every even natural number k, there are infinitely many consecutive prime pairs p and p′ such that p′ − p = k (i.e. there are infinitely many prime gaps of size k). The case k = 2 is the twin prime conjecture. The conjecture has not been proved or disproved for any value of k.
.
The first few isolated primes are
Prime number
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
that differs from another prime number by two. Except for the pair (2, 3), this is the smallest possible difference between two primes. Some examples of twin prime pairs are (3, 5), (5, 7), (11, 13), (17, 19), (29, 31) and (41, 43). Sometimes the term twin prime is used for a pair of twin primes; an alternative name for this is prime twin.
History
The question of whether there exist infinitely many twin primes has been one of the great open questions in number theoryNumber theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers as well...
for many years. This is the content of the twin prime conjecture, which states There are infinitely many primes p such that p + 2 is also prime. In 1849 de Polignac
Alphonse de Polignac
Alphonse de Polignac was a French mathematician. In 1849 he made Polignac's conjecture:The case k = 1 is the twin prime conjecture.-References:...
made the more general conjecture that for every natural number k, there are infinitely many prime pairs p and p′ such that p′ − p = 2k. The case k = 1 is the twin prime conjecture.
A stronger form of the twin prime conjecture, the Hardy–Littlewood conjecture, postulates a distribution law for twin primes akin to the prime number theorem
Prime number theorem
In number theory, the prime number theorem describes the asymptotic distribution of the prime numbers. The prime number theorem gives a general description of how the primes are distributed amongst the positive integers....
.
Brun's theorem
In 1915, Viggo BrunViggo Brun
Viggo Brun was a Norwegian mathematician.He studied at the University of Oslo and began research at the University of Göttingen in 1910. In 1923, Brun became a professor at the Technical University in Trondheim and in 1946 a professor at the University of Oslo...
showed that the sum of reciprocals of the twin primes was convergent. This famous result, called Brun's theorem
Brun's theorem
In number theory, Brun's theorem was proved by Viggo Brun in 1919. It states that the sum of the reciprocals of the twin primes is convergent with a finite value known as Brun's constant, usually denoted by B2...
, was the first use of the Brun sieve
Brun sieve
In the field of number theory, the Brun sieve is a technique for estimating the size of "sifted sets" of positive integers which satisfy a set of conditions which are expressed by congruences...
and helped initiate the development of modern sieve theory
Sieve theory
Sieve theory is a set of general techniques in number theory, designed to count, or more realistically to estimate the size of, sifted sets of integers. The primordial example of a sifted set is the set of prime numbers up to some prescribed limit X. Correspondingly, the primordial example of a...
. The modern version of Brun's argument can be used to show that the number of twin primes less than N does not exceed
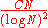
for some absolute constant C > 0.
In 1940, Paul Erdős
Paul Erdos
Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. Erdős published more papers than any other mathematician in history, working with hundreds of collaborators. He worked on problems in combinatorics, graph theory, number theory, classical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory...
showed that there is a constant
Mathematical constant
A mathematical constant is a special number, usually a real number, that is "significantly interesting in some way". Constants arise in many different areas of mathematics, with constants such as and occurring in such diverse contexts as geometry, number theory and calculus.What it means for a...
c < 1 and infinitely many primes p such that (p′ − p) < (c ln p) where p′ denotes the next prime after p. This result was successively improved; in 1986 Helmut Maier
Helmut Maier
Helmut Maier is a German mathematician. Specializing in number theory, he has made significant progress in the study of the twin prime conjecture. He proved Maier's theorem....
showed that a constant c < 0.25 can be used. In 2004 Daniel Goldston
Daniel Goldston
Daniel Alan Goldston is an American mathematician who specializes in number theory. He is currently a professor of mathematics at San Jose State University....
and Cem Yıldırım
Cem Yildirim
Cem Yalçın Yıldırım is a Turkish mathematician who specializes in number theory. He obtained his PhD from the University of Toronto in 1990. His advisor was John Friedlander...
showed that the constant could be improved further to c = 0.085786… In 2005, Goldston, János Pintz
János Pintz
János Pintz is a Hungarian mathematician working in analytic number theory. He is a fellow of the Rényi Mathematical Institute and is also a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.-Mathematical results:...
and Yıldırım established that c can be chosen to be arbitrarily small
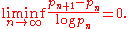
In fact, by assuming the Elliott–Halberstam conjecture or a slightly weaker version, they were able to show that there are infinitely many n such that at least two of n, n + 2, n + 6, n + 8, n + 12, n + 18, or n + 20 are prime. Under a stronger hypothesis they showed that for infinitely many n at least two of n, n + 2, n + 4, and n + 6 are prime.
Every twin prime pair except (3, 5) is of the form (6n − 1, 6n + 1) for some natural number
Natural number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the ordinary whole numbers used for counting and ordering . These purposes are related to the linguistic notions of cardinal and ordinal numbers, respectively...
n, and with the exception of n = 1, n must end in 0, 2, 3, 5, 7, or 8.
It has been proven that the pair (m, m+2) is a twin prime if and only if

If m − 4 or m + 6 is also prime then the 3 primes are called a prime triplet
Prime triplet
In mathematics, a prime triplet is a set of three prime numbers of the form or...
.
Largest known twin prime pair
On January 15, 2007 two distributed computingDistributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system consists of multiple autonomous computers that communicate through a computer network. The computers interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal...
projects, Twin Prime Search
Twin Prime Search
Twin Prime Search is a distributed computing project that looks for large twin primes. It uses the programs LLR and NewPGen . It was founded on April 13, 2006 by Michael Kwok...
and PrimeGrid
PrimeGrid
PrimeGrid is a distributed computing project for searching for prime numbers of world-record size. It makes use of the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing platform...
found the largest known twin primes, 2003663613 · 2195000 ± 1. The numbers have 58711 decimal
Decimal
The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
digits
Numerical digit
A digit is a symbol used in combinations to represent numbers in positional numeral systems. The name "digit" comes from the fact that the 10 digits of the hands correspond to the 10 symbols of the common base 10 number system, i.e...
. Their discoverer was Eric Vautier of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
.
On August 6, 2009 those same two projects announced that a new record twin prime had been found. It is 65516468355 · 2333333 ± 1. The numbers have 100355 decimal digits.
An empirical analysis of all prime pairs up to 4.35 · 1015 shows that if the number of such pairs less than x is f(x)·x/(log x)2 then f(x) is about 1.7 for small x and decreases towards about 1.3 as x tends to infinity.
There are 808,675,888,577,436 twin prime pairs below 1018.
The limiting value of f(x) is conjectured to equal twice the twin prime constant (not to be confused with Brun's constant)

this conjecture would imply the twin prime conjecture, but remains unresolved.
The twin prime conjecture would give a better approximation, as with the prime counting function
Prime counting function
In mathematics, the prime-counting function is the function counting the number of prime numbers less than or equal to some real number x. It is denoted by \scriptstyle\pi .-History:...
, by
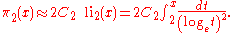
Properties
The first few twin prime pairs are:, (5, 7), (11, 13), (17, 19), (29, 31), (41, 43), (59, 61), (71, 73), (101, 103), (107, 109), (137, 139), … .Since every third odd number is divisible by 3, no three successive odd numbers can be prime unless one of them is 3, thus 5 is the only prime which is part of two pairs. Also, along the same lines, other than the first pair, the number centered between the twin primes must always be divisible by 6. The lower member of a pair is by definition a Chen prime
Chen prime
A prime number p is called a Chen prime if p + 2 is either a prime or a product of two primes. The even number 2p + 2 therefore satisfies Chen's theorem....
.
First Hardy–Littlewood conjecture
The Hardy–Littlewood conjecture (after G. H. HardyG. H. Hardy
Godfrey Harold “G. H.” Hardy FRS was a prominent English mathematician, known for his achievements in number theory and mathematical analysis....
and John Littlewood
John Edensor Littlewood
John Edensor Littlewood was a British mathematician, best known for the results achieved in collaboration with G. H. Hardy.-Life:...
) is a generalization of the twin prime conjecture. It is concerned with the distribution of prime constellations, including twin primes, in analogy to the prime number theorem
Prime number theorem
In number theory, the prime number theorem describes the asymptotic distribution of the prime numbers. The prime number theorem gives a general description of how the primes are distributed amongst the positive integers....
. Let π2(x) denote the number of primes p ≤ x such that p + 2 is also prime. Define the twin prime constant C2 as

(here the product extends over all prime numbers p ≥ 3). Then the conjecture is that
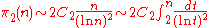
in the sense that the quotient of the two expressions tends to
Limit of a function
In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input....
1 as n approaches infinity. (The second ~ is not part of the conjecture and is proved by integration by parts
Integration by parts
In calculus, and more generally in mathematical analysis, integration by parts is a rule that transforms the integral of products of functions into other integrals...
.)
This conjecture can be justified (but not proven) by assuming that 1 / ln t describes the density function of the prime distribution, an assumption suggested by the prime number theorem.
Polignac's conjecture
Polignac's conjecturePolignac's conjecture
In number theory, Polignac's conjecture was made by Alphonse de Polignac in 1849 and states:The conjecture has not been proven or disproven for any value of n....
from 1849 states that for every even natural number k, there are infinitely many consecutive prime pairs p and p′ such that p′ − p = k (i.e. there are infinitely many prime gaps of size k). The case k = 2 is the twin prime conjecture. The conjecture has not been proved or disproved for any value of k.
Isolated prime
An isolated prime is a prime number p such that neither p − 2 nor p + 2 is prime. In other words, p is not part of a twin prime pair. For example, 23 is an isolated prime since 21 and 25 are both compositeComposite number
A composite number is a positive integer which has a positive divisor other than one or itself. In other words a composite number is any positive integer greater than one that is not a prime number....
.
The first few isolated primes are
- 2, 2323 (number)23 is the natural number following 22 and preceding 24.- In mathematics :Twenty-three is the ninth prime number, the smallest odd prime that is not a twin prime. Twenty-three is also the fifth factorial prime, the third Woodall prime...
, 3737 (number)37 is the natural number following 36 and preceding 38.-In mathematics:It is a prime number, the fifth lucky prime, the first irregular prime, the third unique prime and the third cuban prime of the form...
, 4747 (number)47 is the natural number following 46 and preceding 48.-In mathematics:Forty-seven is the fifteenth prime number, a safe prime, the thirteenth supersingular prime, and the sixth Lucas prime. Forty-seven is a highly cototient number...
, 5353 (number)53 is the natural number following 52 and preceding 54.-In mathematics:Fifty-three is the 16th prime number. It is also an Eisenstein prime....
, 6767 (number)67 is the natural number following 66 and preceding 68. It is an odd number.-In mathematics:Sixty-seven is the 19th prime number , an irregular prime, a lucky prime, the sum of five consecutive primes , and a Heegner number.Since 18! + 1 is divisible by 67 but 67 is not one more than a multiple of...
, 7979 (number)Seventy-nine is the natural number following 78 and preceding 80.79 may represent:-In mathematics:*An odd number*The smallest number that can't be represented as a sum of fewer than 19 fourth powers*A strictly non-palindromic number...
, 8383 (number)83 is the natural number following 82 and preceding 84.-In mathematics:Eighty-three is the sum of three consecutive primes as well as the sum of five consecutive primes ....
, 89, 9797 (number)97 is the natural number following 96 and preceding 98.-In mathematics:97 is the 25th prime number , following 89 and preceding 101. 97 is a Proth prime as it is 3 × 25 + 1.The numbers 97, 907, 9007, 90007 and 900007 are happy primes...
… .
Further reading
- Neil SloaneNeil SloaneNeil James Alexander Sloane is a British-U.S. mathematician. His major contributions are in the fields of combinatorics, error-correcting codes, and sphere packing...
and Simon PlouffeSimon PlouffeSimon Plouffe is a Quebec mathematician born on June 11, 1956 in Saint-Jovite, Quebec. He discovered the formula for the BBP algorithm which permits the computation of the nth binary digit of π, in 1995...
, The encyclopedia of integer sequences, Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1995.
External links
- Top-20 Twin Primes at Chris Caldwell's Prime PagesPrime pagesThe Prime Pages is a website about prime numbers maintained by Chris Caldwell at the University of Tennessee at Martin.The site maintains the list of the "5,000 largest known primes", selected smaller primes of special forms, and many "top twenty" lists for primes of various forms...
. - Xavier Gourdon, Pascal Sebah: Introduction to Twin Primes and Brun's Constant
- "Official press release" of 58711-digit twin prime record.
- The 20 000 first twin primes

