
Trihalomethane
Encyclopedia
Trihalomethanes are chemical compound
s in which three of the four hydrogen atoms of methane
(CH4) are replaced by halogen
atoms. Many trihalomethanes find uses in industry as solvent
s or refrigerant
s. THMs are also environmental pollutants, and many are considered carcinogen
ic. Trihalomethanes with all the same halogen atoms are called haloforms.
are both used as refrigerant
s in some applications. Trihalomethanes released to the environment break down faster than chlorofluorocarbons
(CFCs), thereby doing much less damage to the ozone layer
(if they contain chlorine). Chlorodifluoromethane is a refrigerant HCFC, or hydrochlorofluorocarbon, while fluoroform is an HFC, or hydrofluorocarbon. Fluoroform is not ozone depleting.
Unfortunately, the breakdown of trihalomethane HCFCs does still result in the creation of some free chlorine radicals in the upper atmosphere and subsequent ozone destruction. Ideally, HCFCs will be phased out entirely in favour of entirely nonchlorinated refrigerants.
used in organic chemistry. It is a significantly less polar
solvent than water, well-suited to dissolving many organic compound
s.
Although still toxic and potentially carcinogenic, chloroform is significantly less harmful than carbon tetrachloride
. Because of the health and regulatory issues associated with the use of carbon tetrachloride, in modern chemistry laboratories chloroform is used as a cheaper, cleaner alternative wherever possible.
is used to disinfect water
for drinking. They represent one group of chemicals generally referred to as disinfection by-product
s. They result from the reaction of chlorine and/or bromine with organic matter
present in the water being treated. The THMs produced have been associated through epidemiological studies with some adverse health effects. Many governments set limits on the amount permissible in drinking water. However, trihalomethanes are only one group of many hundreds of possible disinfection by-products—the vast majority of which are not monitored—and it has not yet been clearly demonstrated which of these are the most plausible candidate for causation of these health effects. In the United States
, the EPA
limits the total concentration of the four chief constituents (chloroform
, bromoform
, bromodichloromethane
, and dibromochloromethane
), referred to as total trihalomethanes (TTHM), to 80 parts per billion in treated water.
Chloroform
is also formed in swimming pools which are disinfected with chlorine
or hypochlorite
in the haloform reaction
with organic substances (e.g. urine
, sweat
, hair
and skin
particles). Some of the THMs are quite volatile and may easily vaporize into the air. This makes it possible to inhale THMs while showering, for example. The EPA, however, has determined that this exposure is minimal compared to that from consumption. In swimmers uptake of THMs is greatest via the skin with dermal absorption accounting for 80% of THM uptake. Exercising in a chlorinated pool increases the toxicity of a "safe" chlorinated pool atmosphere with toxic effects of chlorine byproducts greater in young swimmers than older swimmers.
Studies in adolescents have shown an inverse relationship between serum testosterone levels and the amount of time spent in a public pools. Chlorination by-products have been linked as a probable cause.
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
s in which three of the four hydrogen atoms of methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
(CH4) are replaced by halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
atoms. Many trihalomethanes find uses in industry as solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
s or refrigerant
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a substance used in a heat cycle usually including, for enhanced efficiency, a reversible phase change from a liquid to a gas. Traditionally, fluorocarbons, especially chlorofluorocarbons, were used as refrigerants, but they are being phased out because of their ozone depletion...
s. THMs are also environmental pollutants, and many are considered carcinogen
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that is an agent directly involved in causing cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes...
ic. Trihalomethanes with all the same halogen atoms are called haloforms.
Table of common trihalomethanes
| Molecular formula |
IUPAC name | CAS registry number CAS registry number CAS Registry Numbersare unique numerical identifiers assigned by the "Chemical Abstracts Service" toevery chemical described in the... |
Common name | Other names | Molecule |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHF3 | trifluoromethane | 75-46-7 | fluoroform Fluoroform Fluoroform is the chemical compound with the formula CHF3. It is one of the "haloforms", a class of compounds with the formula CHX3 . Fluoroform is used in diverse niche applications and is produced as a by-product of the manufacture of Teflon... |
Freon 23, R-23, HFC-23 |  |
| CHClF2 | chlorodifluoromethane | 75-45-6 | chlorodifluoromethane Chlorodifluoromethane Chlorodifluoromethane or difluoromonochloromethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon . This colorless gas is better known as HCFC-22, or R-22. It was once commonly used as a propellant and in air conditioning applications... |
R-22, HCFC-22 |  |
| CHCl3 | trichloromethane | 67-66-3 | chloroform Chloroform Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous... |
methyl trichloride | 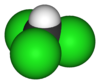 |
| CHBrCl2 | bromodichloromethane | 75-27-4 | dichlorobromomethane | BDCM | 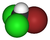 |
| CHBr2Cl | dibromochloromethane | 124-48-1 | chlorodibromomethane | CDBM | 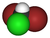 |
| CHBr3 | tribromomethane | 75-25-2 | bromoform Bromoform Bromoform is a pale yellowish liquid with a sweet odor similar to chloroform, a halomethane or haloform. Its refractive index is 1.595 . Bromoform is produced naturally by phytoplankton and seaweeds in the ocean and this is thought to be the predominant source to the environment... |
methyl tribromide | 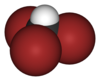 |
| CHI3 | triiodomethane | 75-47-8 | iodoform Iodoform Iodoform is the organoiodine compound with the formula CHI3. A pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, it has a penetrating odor and, analogous to chloroform, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant... |
methyl triiodide |  |
Refrigerants
Trifluoromethane and chlorodifluoromethaneChlorodifluoromethane
Chlorodifluoromethane or difluoromonochloromethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon . This colorless gas is better known as HCFC-22, or R-22. It was once commonly used as a propellant and in air conditioning applications...
are both used as refrigerant
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a substance used in a heat cycle usually including, for enhanced efficiency, a reversible phase change from a liquid to a gas. Traditionally, fluorocarbons, especially chlorofluorocarbons, were used as refrigerants, but they are being phased out because of their ozone depletion...
s in some applications. Trihalomethanes released to the environment break down faster than chlorofluorocarbons
Haloalkane
The haloalkanes are a group of chemical compounds derived from alkanes containing one or more halogens. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially and, consequently, are known under many chemical and...
(CFCs), thereby doing much less damage to the ozone layer
Ozone layer
The ozone layer is a layer in Earth's atmosphere which contains relatively high concentrations of ozone . This layer absorbs 97–99% of the Sun's high frequency ultraviolet light, which is potentially damaging to the life forms on Earth...
(if they contain chlorine). Chlorodifluoromethane is a refrigerant HCFC, or hydrochlorofluorocarbon, while fluoroform is an HFC, or hydrofluorocarbon. Fluoroform is not ozone depleting.
Unfortunately, the breakdown of trihalomethane HCFCs does still result in the creation of some free chlorine radicals in the upper atmosphere and subsequent ozone destruction. Ideally, HCFCs will be phased out entirely in favour of entirely nonchlorinated refrigerants.
Solvents
Chloroform is a very common solventSolvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
used in organic chemistry. It is a significantly less polar
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
solvent than water, well-suited to dissolving many organic compound
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s.
Although still toxic and potentially carcinogenic, chloroform is significantly less harmful than carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names is the organic compound with the formula CCl4. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, and as a cleaning agent...
. Because of the health and regulatory issues associated with the use of carbon tetrachloride, in modern chemistry laboratories chloroform is used as a cheaper, cleaner alternative wherever possible.
Water pollutants
Trihalomethanes are formed as a by-product predominantly when chlorineChlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
is used to disinfect water
Water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, materials, and biological contaminants from contaminated water. The goal is to produce water fit for a specific purpose...
for drinking. They represent one group of chemicals generally referred to as disinfection by-product
Disinfection by-product
Disinfection by-products result from reactions between organic and inorganic matter in water with chemical treatment agents during the water disinfection process.-Chlorination disinfection by-products:...
s. They result from the reaction of chlorine and/or bromine with organic matter
Organic matter
Organic matter is matter that has come from a once-living organism; is capable of decay, or the product of decay; or is composed of organic compounds...
present in the water being treated. The THMs produced have been associated through epidemiological studies with some adverse health effects. Many governments set limits on the amount permissible in drinking water. However, trihalomethanes are only one group of many hundreds of possible disinfection by-products—the vast majority of which are not monitored—and it has not yet been clearly demonstrated which of these are the most plausible candidate for causation of these health effects. In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, the EPA
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
limits the total concentration of the four chief constituents (chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
, bromoform
Bromoform
Bromoform is a pale yellowish liquid with a sweet odor similar to chloroform, a halomethane or haloform. Its refractive index is 1.595 . Bromoform is produced naturally by phytoplankton and seaweeds in the ocean and this is thought to be the predominant source to the environment...
, bromodichloromethane
Bromodichloromethane
Bromodichloromethane is a trihalomethane with formula CHBrCl2.It has been formerly used as a flame retardant, solvent for fats and waxes and because of its high density for mineral separation. Now it is only used as a reagent or intermediate in organic chemistry.-External links:* * *...
, and dibromochloromethane
Dibromochloromethane
Dibromochloromethane is a compound with formula CHBr2Cl. It is a trihalomethane.Dibromochloromethane was formerly used as a flame retardant and as an intermediate in chemicals manufacturing. Today it is used only as a laboratory reagent....
), referred to as total trihalomethanes (TTHM), to 80 parts per billion in treated water.
Chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
is also formed in swimming pools which are disinfected with chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
or hypochlorite
Hypochlorite
The hypochlorite ion, also known as chlorate anion is ClO−. A hypochlorite compound is a chemical compound containing this group, with chlorine in oxidation state +1.Hypochlorites are the salts of hypochlorous acid...
in the haloform reaction
Haloform reaction
The haloform reaction is a chemical reaction where a haloform is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of a methyl ketone in the presence of a base. R may be , alkyl or aryl...
with organic substances (e.g. urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
, sweat
SWEAT
SWEAT is an OLN/TSN show hosted by Julie Zwillich that aired in 2003-2004.Each of the 13 half-hour episodes of SWEAT features a different outdoor sport: kayaking, mountain biking, ice hockey, beach volleyball, soccer, windsurfing, rowing, Ultimate, triathlon, wakeboarding, snowboarding, telemark...
, hair
Hair
Hair is a filamentous biomaterial, that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Found exclusively in mammals, hair is one of the defining characteristics of the mammalian class....
and skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
particles). Some of the THMs are quite volatile and may easily vaporize into the air. This makes it possible to inhale THMs while showering, for example. The EPA, however, has determined that this exposure is minimal compared to that from consumption. In swimmers uptake of THMs is greatest via the skin with dermal absorption accounting for 80% of THM uptake. Exercising in a chlorinated pool increases the toxicity of a "safe" chlorinated pool atmosphere with toxic effects of chlorine byproducts greater in young swimmers than older swimmers.
Studies in adolescents have shown an inverse relationship between serum testosterone levels and the amount of time spent in a public pools. Chlorination by-products have been linked as a probable cause.

