
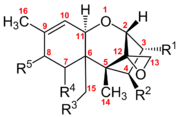
Trichothecene
Encyclopedia
Mycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s produced by various species of Fusarium
Fusarium
Fusarium is a large genus of filamentous fungi widely distributed in soil and in association with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health...
, Myrothecium, Trichoderma
Trichoderma
Trichoderma is a genus of fungi that is present in all soils, where they are the most prevalent culturable fungi. Many species in this genus can be characterized as opportunistic avirulent plant symbionts.-Species:...
, Trichothecium, Cephalosporium, Verticimonosporium, and Stachybotrys
Stachybotrys
Stachybotrys is a genus of molds, or asexually-reproducing, filamentous fungi. Closely related to the genus Memnoniella, most Stachybotrys species inhabit materials rich in cellulose. The genus has a widespread distribution, and contains about 50 species.The most infamous species, S. chartarum and S...
. Trichothecenes belong to sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be acyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations...
compounds.
The most important structural features causing the biological activities of trichothecenes are: the 12,13-epoxy ring, the presence of hydroxyl or acetyl groups at appropriate positions on the trichothecene nucleus and the structure and position of the side-chain. They are produced on many different grains like wheat, oats or maize by various Fusarium species such as F. graminearum, F. sporotrichioides, F. poae and F. equiseti.
Some molds that produce trichothecene mycotoxins, such as Stachybotrys chartarum, can grow in damp indoor environments. It has been found that macrocyclic trichothecenes produced by Stachybotrys chartarum can become airborne and thus contribute to health problems among building occupants.
The poisonous mushroom in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Podostroma cornu-damae
Podostroma cornu-damae
Podostroma cornu-damae is a species of fungus in the Hypocreaceae family. The fruit bodies of the fungus are highly toxic, and have been responsible for several fatalities in Japan...
contains six trichothecenes; satratoxin H, roridin E, verrucarin and others.
Toxicity mechanisms
This group of structurally related mycotoxinMycotoxin
A mycotoxin is a toxic secondary metabolite produced by organisms of the fungus kingdom, commonly known as molds. The term ‘mycotoxin’ is usually reserved for the toxic chemical products produced by fungi that readily colonize crops...
s has a strong impact on the health of animals and humans. Trichothecenes are powerful inhibitors of protein synthesis. They do this by reacting with components of the ribosomes: the structure within the cell where proteins are made. The specific site of action of T-2 toxin, which is a reaction with a critical site on the ribosomal RNA (rRNA), is known. Protein synthesis is an essential function in all tissues, but tissues where cells are actively and rapidly growing and dividing are very susceptible to the toxins.
Trichothecenes are different from most other potential weapons toxins because they can act through the skin. Compared with some of the other mycotoxins such as aflatoxin, the trichothecenes do not appear to require metabolic activation to exert their biological activity. After direct dermal application or oral ingestion, the trichothecene mycotoxins can cause rapid irritation to the skin or intestinal mucosa. In cell-free systems or single cells in culture, these mycotoxins cause a rapid inhibition of protein synthesis and polyribosomal disaggregation. Thus, we can postulate that the trichothecene mycotoxins have molecular capability of direct reaction with cellular components. Despite this direct effect, it is possible to measure the toxicokinetics and the metabolism of the trichothecene mycotoxins.
Regulatory issues
When it comes to animal and human food, type A trichothecenes (e.g. T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol) are of special interest because they are more toxic than the other foodborne trichothecenes i.e. type B group (e.g. deoxynivalenol, nivalenol, 3- and 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol). However, deoxynivalenol is of concern as it is the most prevalent trichothecene in Europe. The major effects of trichothecenes – related to their concentration in the commodity – are reduced feed uptake, vomiting and immuno-suppression.Only few countries (mostly EU) have recommended levels for these mycotoxins in food and animal feed but it is often tested for to prevent them from entering the food chain and to prevent losses in animal production.
Occurrence and outbreaks
Trihothecenes have been reported throughout the world. In modern history, incidences of emesis in animals and humans after consumption of cereals infected with Fusarium species have been described in early 1900s. Around 100,000 people in Soviet Union died due to alimentary toxic aleukia, a disease apparently caused by consuming grains infested with Fusarium sp. which are high producers of T-2 toxin. A disease of similar etiology, Akakabibyo (in case of equine, “bean-hulls poisoning”), has also been associated with trichothecene contaminated grains in Japan. Cereals or their products contaminated with trichothecenes including DON, T-2 toxin, and NIV, have also been associated with outbreaks of gastrointestinal disorders in China.Trichothecenes including DON, T-2 toxin, and diacetoxyscirpenol are also important from the view of biological warfare and controversial American allegations have described yellow rain
Yellow rain
Yellow rain was a political incident in which the United States Secretary of State Alexander Haig accused the Soviet Union of supplying T-2 mycotoxin to the Communist states in Vietnam and Laos for use in counterinsurgency warfare....
in southeast Asia as a Soviet bioweapon containing these toxins. These American "yellow rain" allegations are now regarded as discredited, as independent analyzes of the purported agent showed it to be bee feces rich in pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
.
Epoxitrichothecenes
Epoxitrichothecenes are a variation of the above, and were once explored for military use in East Germany, and possibly the whole Soviet bloc. There is no feasible treatment once symptoms of epoxithichothecene poisoning set in, though the effects can subside without leaving any permanent damage.The plans for use as a large-scale bioweapon were dropped, as the relevant epoxitrichothecenes degrade very quickly under UV light and heat, as well as chlorine exposure, making them useless for open attacks and the poisoning of water supplies.

