.gif)
Tree of life (science)
Encyclopedia
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
proposed that phylogeny, the evolutionary relatedness among species through time, was expressible as a metaphor he termed the Tree of Life. The modern development of this idea is called the Phylogenetic tree
Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics...
.
Early Trees of Life
Although the mutability of species may have appeared in paintings and trees have been used as a metaphor for other purposes (Porphyrian treeArbor porphyriana
An arbor porphyriana or Porphyrian tree, created by Porphyry, is a hierarchical ontology, construction in logic consisting of three rows or columns of words; the middlemost whereof contains the series of genus and species, and bears some analogy to the trunk...
) earlier than 1800, the combination of the concept of branching evolution and the tree image did not appear before 1800. The earliest tree of life was published by the French botanist Augustin Augier in 1801. It shows the relationships between members of the plant kingdom.
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, Chevalier de la Marck , often known simply as Lamarck, was a French naturalist...
(1744–1829) produced the first branching tree of animals in his Philosophie Zoologique
Philosophie Zoologique
Philosophie zoologique ou exposition des considérations relatives à l'histoire naturelle des animaux is an 1809 book by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in which he outlines his theory of evolution now known as Lamarckism.Lamarck proposed that :“as new modifications will necessarily continue...
(1809). It was an upside-down tree starting with worms and ending with mammals. However, Lamarck did not believe in common descent of all life. Instead, he believed that life consists of separate parallel lines advancing from simple to complex.
The American geologist Edward Hitchcock
Edward Hitchcock
Edward Hitchcock was a noted American geologist and the third President of Amherst College .-Life:...
(1763–1864) published in 1840 the first Tree of Life based on paleontology in his Elementary Geology. On the vertical axis are paleontological periods. Hitchcock made a separate tree for plants (left) and animals (right). The plant and the animal tree are not connected at the bottom of the chart. Furthermore, each tree starts with multiple origins. Hitchcock's tree was more realistic than Darwin's 1859 theoretical tree (see below) because Hitchcock used real names in his trees. It is also true that Hitchcock's trees were branching trees. However, they were not real evolutionary trees, because Hitchcock believed that a deity was the agent of change. That was an important difference with Darwin.
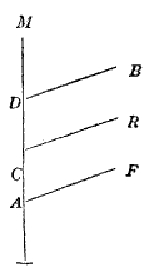
The first edition of Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation
Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation
Vestiges of the Natural History of Creation is a unique work of speculative natural history published anonymously in England in 1844. It brought together various ideas of stellar evolution with the progressive transmutation of species in an accessible narrative which tied together numerous...
, which was published anonymously in 1844 in England, contained a tree like diagram (p. 212) in the chapter 'Hypothesis of the development of the vegetable and animal kingdoms'. It shows a model of embryological development where fish (F), reptiles (R), and birds (B) represent branches from a path leading to mammals (M). In the text this branching tree idea is tentatively applied to the history of life on earth: "there may be branching" (p. 191), but the branching diagram is not displayed again specifically for this purpose. However, the image of a branching tree could easily have inspired others to use it explicitly as a representation of the history of life on earth.
In 1858, a year before Darwin's Origin, the paleontologist Heinrich Georg Bronn
Heinrich Georg Bronn
Heinrich Georg Bronn was a German geologist and paleontologist.Bronn was born at Ziegelhausen near Heidelberg. Studying at the university of Heidelberg he took his doctor's degree in the faculty of medicine in 1821, and in the following year was appointed professor of natural history...
(1800–1862) published a hypothetical tree labeled with letters. Although not a creationist, Bronn did not propose a mechanism of change.
Darwin's Tree of Life
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
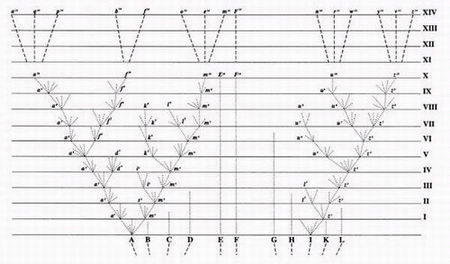
(see figure). On the horizontal base line hypothetical species within this genus are labelled A – L and are spaced irregularly to indicate how distinct they are from each other, and are above broken lines at various angles suggesting that they have diverged from one or more common ancestors. On the vertical axis divisions labelled I – XIV each represent a thousand generations. From A, diverging lines show branching descent producing new varieties, some of which go extinct, so that after ten thousand generations descendants of A have become distinct new varieties or even sub-species a10, f10, and m10. Similarly, the descendants of I have diversified to become the new varieties w10 and z10. The process is extrapolated for a further four thousand generations so that the descendants of A and I become fourteen new species labelled a14 to z14. While F has continued for fourteen thousand generations relatively unchanged, species B,C,D,E,G,H,K and L have gone extinct. In Darwin's own words: "Thus the small differences distinguishing varieties of the same species, will steadily tend to increase till they come to equal the greater differences between species of the same genus, or even of distinct genera.". This is a branching pattern with no names given to species, unlike the more linear tree Ernst Haeckel made years later (figure below) which includes the names of species and shows a more linear development from "lower" to "higher" species. In his summary to the section as revised in the 6th edition of 1872, Darwin explains his views on the Tree of Life:

Haeckel's Tree of Life
 |
Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Haeckel
The "European War" became known as "The Great War", and it was not until 1920, in the book "The First World War 1914-1918" by Charles à Court Repington, that the term "First World War" was used as the official name for the conflict.-Research:...
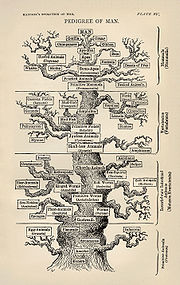
(1834–1919) constructed several Trees of Life. Left is shown the first sketch of the famous Haeckel's Tree of Life in the 1860s which shows "Pithecanthropus alalus" as the ancestor of Homo sapiens. In the middle is the Tree of Life from Generelle Morphologie der Organismen (1866) with three kingdoms Plantae, Protista and Animalia. On the right is the 'Pedigree of Man' published in The Evolution of Man (1879).
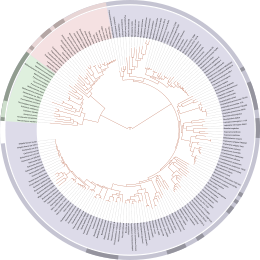
The tree of life today

Biologists now recognize that the prokaryotes, the bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
and archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
have the ability to transfer genetic information between unrelated organisms through horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer , also lateral gene transfer , is any process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism...
(HGT). Recombination, gene loss, duplication, and gene creation are a few of the processes by which genes can be transferred within and between bacterial and archaeal species, causing variation that is not due to vertical transfer.
There is emerging evidence of HGT occurring within the prokaryotes at the single and multicell level and the view is now emerging that the tree of life gives an incomplete picture of life's evolution. It was a useful tool in understanding the basic processes of evolution for prokaryotes, but cannot explain the full complexity of the situation.
See also
- Common descentCommon descentIn evolutionary biology, a group of organisms share common descent if they have a common ancestor. There is strong quantitative support for the theory that all living organisms on Earth are descended from a common ancestor....
- Phylogenetic treePhylogenetic treeA phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics...
- Tree of Life Web ProjectTree of Life Web ProjectThe Tree of Life Web Project is an ongoing Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world....
- History of evolutionary thoughtHistory of evolutionary thoughtEvolutionary thought, the conception that species change over time, has roots in antiquity, in the ideas of the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Chinese as well as in medieval Islamic science...
- Horizontal gene transferHorizontal gene transferHorizontal gene transfer , also lateral gene transfer , is any process in which an organism incorporates genetic material from another organism without being the offspring of that organism...
- CladisticsCladisticsCladistics is a method of classifying species of organisms into groups called clades, which consist of an ancestor organism and all its descendants . For example, birds, dinosaurs, crocodiles, and all descendants of their most recent common ancestor form a clade...
- Bacterial phylaBacterial phylaThe bacterial phyla are the major lineages of the domain Bacteria.In the scientific classification established by Carl von Linné, each bacterial strain has to be assigned to a species , which is a lower level of a hierarchy of ranks...
- Last universal ancestorLast universal ancestorThe last universal ancestor , also called the last universal common ancestor , or the cenancestor, is the most recent organism from which all organisms now living on Earth descend. Thus it is the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth...
- HolismHolismHolism is the idea that all the properties of a given system cannot be determined or explained by its component parts alone...
External links
- Tree of Life Web Project - explore complete phylogenetic tree interactively
- Tree of Life illustration - A modern illustration of the complete tree of life.
- Science Magazine Tree of Life - Sample tree of life from Science journal.
- Science journal issue - Issue devoted to the tree of life.
- http://www.geneticstimes.com/Research/Tiny_Genetic_Differences_Have_Huge_Consequences.asp-Report on recent paper on "pruning" of the tree of life model.
- The Tree of Life by Garrett Neske, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project: "presents an interactive tree of life that allows you to explore the relationships between many different kinds of organisms by allowing you to select an organism and visualize the clade to which it belongs."
- The Green Tree of Life - Hyperbolic tree The University and Jepson Herbaria

