
Transistor count
Encyclopedia
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s in the device.
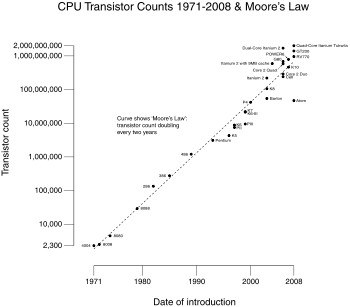
Transistor count is the most common measure of integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
complexity. According to Moore's Law
Moore's Law
Moore's law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware: the number of transistors that can be placed inexpensively on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years....
, the transistor count of the integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s doubles every two years. On most modern microprocessors, the majority of transistors are contained in caches
CPU cache
A CPU cache is a cache used by the central processing unit of a computer to reduce the average time to access memory. The cache is a smaller, faster memory which stores copies of the data from the most frequently used main memory locations...
.
Microprocessors
| Processor | Transistor count | Date of introduction | Manufacturer | Process | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intel 4004 Intel 4004 The Intel 4004 was a 4-bit central processing unit released by Intel Corporation in 1971. It was the first complete CPU on one chip, and also the first commercially available microprocessor... |
2,300 | 1971 | Intel | 10 µm | 12 mm² |
| Intel 8008 Intel 8008 The Intel 8008 was an early byte-oriented microprocessor designed and manufactured by Intel and introduced in April 1972. It was an 8-bit CPU with an external 14-bit address bus that could address 16KB of memory... |
3,500 | 1972 | Intel | 10 µm | 14 mm² |
| MOS Technology 6502 MOS Technology 6502 The MOS Technology 6502 is an 8-bit microprocessor that was designed by Chuck Peddle and Bill Mensch for MOS Technology in 1975. When it was introduced, it was the least expensive full-featured microprocessor on the market by a considerable margin, costing less than one-sixth the price of... |
3,510 | 1975 | MOS Technology MOS Technology MOS Technology, Inc., also known as CSG , was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor, and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.-History:MOS Technology, Inc... |
21 mm² | |
| Motorola 6800 Motorola 6800 The 6800 was an 8-bit microprocessor designed and first manufactured by Motorola in 1974. The MC6800 microprocessor was part of the M6800 Microcomputer System that also included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips... |
4,100 | 1974 | Motorola | 16 mm² | |
| Intel 8080 Intel 8080 The Intel 8080 was the second 8-bit microprocessor designed and manufactured by Intel and was released in April 1974. It was an extended and enhanced variant of the earlier 8008 design, although without binary compatibility... |
4,500 | 1974 | Intel | 6 μm | 20 mm² |
| RCA 1802 RCA 1802 The RCA CDP1802, also known as the COSMAC , is an 8-bit CMOS microprocessor introduced by RCA in early 1976. It is being by Intersil Corporation as a high-reliability microprocessor... |
5,000 | 1974 | RCA | 5 μm | 27 mm² |
| Intel 8085 Intel 8085 The Intel 8085 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Intel in 1977. It was binary-compatible with the more-famous Intel 8080 but required less supporting hardware, thus allowing simpler and less expensive microcomputer systems to be built.... |
6,500 | 1976 | Intel | 3 μm | 20 mm² |
| Zilog Z80 Zilog Z80 The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog and sold from July 1976 onwards. It was widely used both in desktop and embedded computer designs as well as for military purposes... |
8,500 | 1976 | Zilog | 4 μm | 18 mm² |
| Motorola 6809 Motorola 6809 The Motorola 6809 is an 8-bit microprocessor CPU from Motorola, designed by Terry Ritter and Joel Boney and introduced 1978... |
9,000 | 1978 | Motorola | 5 μm | 21 mm² |
| Intel 8086 Intel 8086 The 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and mid-1978, when it was released. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture of Intel's future processors... |
29,000 | 1978 | Intel | 3 μm | 33 mm² |
| Intel 8088 Intel 8088 The Intel 8088 microprocessor was a variant of the Intel 8086 and was introduced on July 1, 1979. It had an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range were unchanged, however... |
29,000 | 1979 | Intel | 3 μm | 33 mm² |
| Intel 80186 Intel 80186 The 80188 is a version with an 8-bit external data bus, instead of 16-bit. This makes it less expensive to connect to peripherals. The 80188 is otherwise very similar to the 80186. It has a throughput of 1 million instructions per second.... |
55,000 | 1982 | Intel | ||
| Motorola 68000 Motorola 68000 The Motorola 68000 is a 16/32-bit CISC microprocessor core designed and marketed by Freescale Semiconductor... |
68,000 | 1979 | Motorola | 4 μm | 44 mm² |
| Intel 80286 Intel 80286 The Intel 80286 , introduced on 1 February 1982, was a 16-bit x86 microprocessor with 134,000 transistors. Like its contemporary simpler cousin, the 80186, it could correctly execute most software written for the earlier Intel 8086 and 8088... |
134,000 | 1982 | Intel | 1.5 µm | 49 mm² |
| Intel 80386 Intel 80386 The Intel 80386, also known as the i386, or just 386, was a 32-bit microprocessor introduced by Intel in 1985. The first versions had 275,000 transistors and were used as the central processing unit of many workstations and high-end personal computers of the time... |
275,000 | 1985 | Intel | 1.5 µm | 104 mm² |
| Intel 80486 Intel 80486 The Intel 80486 microprocessor was a higher performance follow up on the Intel 80386. Introduced in 1989, it was the first tightly pipelined x86 design as well as the first x86 chip to use more than a million transistors, due to a large on-chip cache and an integrated floating point unit... |
1,180,000 | 1989 | Intel | 1 µm | 160 mm² |
| Pentium | 3,100,000 | 1993 | Intel | 0.8 µm | 294 mm² |
| AMD K5 AMD K5 The K5 was AMD's first x86 processor to be developed entirely in-house. Introduced in March 1996, its primary competition was Intel's Pentium microprocessor. The K5 was an ambitious design, closer to a Pentium Pro than a Pentium regarding technical solutions and internal architecture... |
4,300,000 | 1996 | AMD | 0.5 µm | |
| Pentium II Pentium II The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million... |
7,500,000 | 1997 | Intel | 0.35 µm | 195 mm² |
| AMD K6 AMD K6 The K6 microprocessor was launched by AMD in 1997. The main advantage of this particular microprocessor is that it was designed to fit into existing desktop designs for Pentium branded CPUs. It was marketed as a product which could perform as well as its Intel Pentium II equivalent but at a... |
8,800,000 | 1997 | AMD | 0.35 µm | |
| Pentium III Pentium III The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors... |
9,500,000 | 1999 | Intel | 0.25 µm | |
| AMD K6-III AMD K6-III The K6-III, code-named "Sharptooth", was an x86 microprocessor manufactured by AMD, released on 22 February 1999, with 400 and 450 MHz models. It was the last Socket 7 desktop processor. For an extremely short time after its release, the fastest available desktop processor from Intel was the... |
21,300,000 | 1999 | AMD | 0.25 µm | |
| AMD K7 | 22,000,000 | 1999 | AMD | 0.25 µm | |
| Pentium 4 Pentium 4 Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the... |
42,000,000 | 2000 | Intel | 180 nm Nm NM, nm, nM, or Nm are common abbreviations for various terms.nm may stand for:* nanometer, an SI unit of length, equal to 10−9 m * nm , a computer program used as an aid for debugging... |
|
| Atom Intel Atom Intel Atom is the brand name for a line of ultra-low-voltage x86 and x86-64 CPUs from Intel, designed in 45 nm CMOS and used mainly in netbooks, nettops, embedded application ranging from health care to advanced robotics and Mobile Internet devices... |
47,000,000 | 2008 | Intel | 45 nm | |
| Barton | 54,300,000 | 2003 | AMD | 130 nm | |
| AMD K8 AMD K8 The AMD K8 is a computer processor microarchitecture designed by AMD as the successor to the AMD K7 microarchitecture. The K8 was the first implementation of the AMD64 64-bit extension to the x86 processor architecture.Processors based on the K8 core include:... |
105,900,000 | 2003 | AMD | 130 nm | |
| Itanium 2 | 220,000,000 | 2003 | Intel | 130 nm | |
| Cell Cell (microprocessor) Cell is a microprocessor architecture jointly developed by Sony, Sony Computer Entertainment, Toshiba, and IBM, an alliance known as "STI". The architectural design and first implementation were carried out at the STI Design Center in Austin, Texas over a four-year period beginning March 2001 on a... |
241,000,000 | 2006 | Sony Sony , commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues.... /IBM IBM International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas... /Toshiba Toshiba is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and... |
90 nm | |
| Core 2 Duo | 291,000,000 | 2006 | Intel | 65 nm | |
| AMD K10 AMD K10 The AMD Family 10h is a microprocessor microarchitecture by AMD. Though there were once reports that the K10 had been canceled, the first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom processors for desktops following and launching on November... |
463,000,000 | 2007 | AMD | 65 nm | |
| AMD K10 AMD K10 The AMD Family 10h is a microprocessor microarchitecture by AMD. Though there were once reports that the K10 had been canceled, the first third-generation Opteron products for servers were launched on September 10, 2007, with the Phenom processors for desktops following and launching on November... |
758,000,000 | 2008 | AMD | 45 nm | |
| Itanium 2 with 9MB cache | 592,000,000 | 2004 | Intel | 130 nm | |
| Core i7 (Quad) | 731,000,000 | 2008 | Intel | 45 nm | 263 mm² |
| Six-Core Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... 7400 |
1,900,000,000 | 2008 | Intel | 45 nm | |
| POWER6 POWER6 The POWER6 is a microprocessor developed by IBM that implemented the Power ISA v.2.03. When it became available in systems in 2007, it succeeded the POWER5+ as IBM's flagship Power microprocessor... |
789,000,000 | 2007 | IBM | 65 nm | 341 mm² |
| Six-Core Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... 2400 |
904,000,000 | 2009 | AMD | 45 nm | 346 mm² |
| 16-Core SPARC T3 | 1,000,000,000 | 2010 | Sun Sun Microsystems Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982... /Oracle Oracle Corporation Oracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation that specializes in developing and marketing hardware systems and enterprise software products – particularly database management systems... |
40 nm | 377 mm² |
| Six-Core Core i7 Gulftown (microprocessor) Gulftown or Westmere-EP is the codename of a six-core hyperthreaded Intel processor able to run up to 12 threads in parallel. It is based on Westmere microarchitecture, the 32 nm shrink of Nehalem. Originally rumored to be called the Intel Core i9, it is sold as an Intel Core i7... (Gulftown) |
1,170,000,000 | 2010 | Intel | 32 nm | 240 mm² |
| 8-core POWER7 POWER7 POWER7 is a Power Architecture microprocessor released in 2010 that succeeded the POWER6. POWER7 was developed by IBM at several sites including IBM's Rochester, MN; Austin, TX; Essex Junction, Vermont; T. J. Watson Research Center, NY; Bromont, QC and Böblingen, Germany laboratories... |
1,200,000,000 | 2010 | IBM | 45 nm | 567 mm² |
| Quad-core z196 IBM z196 (microprocessor) The z196 microprocessor is a chip made by IBM for their zEnterprise 196 mainframe computers, announced on July 22, 2010. The processor was developed over a three year time span by IBM engineers from Poughkeepsie, New York; Austin, Texas; and Böblingen, Germany at a cost of US$1.5 billion... |
1,400,000,000 | 2010 | IBM | 45 nm | 512 mm² |
| Dual-Core Itanium 2 | 1,700,000,000 | 2006 | Intel | 90 nm | 596 mm² |
| Quad-Core Itanium Tukwila Tukwila (processor) Tukwila is the code-name for the generation of Intel's Itanium processor family following Itanium 2 and Montecito. It was released on 8 February 2010 as the Itanium 9300 Series. While its features have not been publicly disclosed in detail, it utilizes both multiple processor cores and SMT... |
2,000,000,000 | 2010 | Intel | 65 nm | 699 mm² |
| Six-Core Core i7 (Sandy Bridge-E) | 2,270,000,000 | 2011 | Intel | 32 nm | 434 mm² |
| 8-Core Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... Nehalem-EX |
2,300,000,000 | 2010 | Intel | 45 nm | 684 mm² |
| 10-Core Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... Westmere-EX |
2,600,000,000 | 2011 | Intel | 32 nm | 512 mm² |
GPUs
| Processor | Transistor count | Date of introduction | Manufacturer | Process | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G80 | 681,000,000 | 2006 | NVIDIA NVIDIA Nvidia is an American global technology company based in Santa Clara, California. Nvidia is best known for its graphics processors . Nvidia and chief rival AMD Graphics Techonologies have dominated the high performance GPU market, pushing other manufacturers to smaller, niche roles... |
90 nm | 480 mm² |
| RV770 Radeon R700 The Radeon R700 is the engineering codename for a graphics processing unit series developed by Advanced Micro Devices under the ATI brand name. The foundation chip, codenamed RV770, was announced and demonstrated on June 16, 2008 as part of the FireStream 9250 and Cinema 2.0 initiative launch media... |
956,000,000 | 2008 | AMD | 55 nm | 260 mm² |
| GT200 GeForce 200 Series The GeForce 200 Series is the 10th generation of Nvidia's GeForce graphics processing units. The series also represents the continuation of the company's unified shader architecture introduced with the GeForce 8 Series and the GeForce 9 Series. Its primary competition came from ATI's Radeon HD 4000... |
1,400,000,000 | 2008 | NVIDIA | 55 nm | 576 mm² |
| RV870 | 2,154,000,000 | 2009 | AMD | 40 nm | 334 mm² |
| Cayman Northern Islands (GPU family) The Northern Islands series is a family of GPUs developed by Advanced Micro Devices for its Radeon line, based on the 40 nm process.Starting with this family, the former ATI brand was officially discontinued in favor of making a correlation between the graphics products and the AMD branding for... |
2,640,000,000 | 2010 | AMD | 40 nm | 389 mm² |
| GF100 | 3,000,000,000 | 2010 | NVIDIA | 40 nm | 529 mm² |
FPGA
| FPGA | Transistor count | Date of introduction | Manufacturer | Process | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virtex Virtex * Virtex , a series of FPGAs produced by Xilinx* Virtex, a series of comic books published by Oktomica Comics* Virtex L, otherwise known as sodium dithionite... |
~70,000,000 | 1997 | Xilinx Xilinx Xilinx, Inc. is a supplier of programmable logic devices. It is known for inventing the field programmable gate array and as the first semiconductor company with a fabless manufacturing model.... |
||
| Virtex-E | ~200,000,000 | 1998 | Xilinx | ||
| Virtex-II | ~350,000,000 | 2000 | Xilinx | 130 nm | |
| Virtex-II PRO | ~430,000,000 | 2002 | Xilinx | ||
| Virtex-4 | 1,000,000,000 | 2004 | Xilinx | 90 nm | |
| Virtex-5 | 1,100,000,000 | 2006 | Xilinx | 65 nm | |
| Stratix IV | 2,500,000,000 | 2008 | Altera Altera Altera Corporation is a Silicon Valley manufacturer of PLDs . The company offered its first programmable logic device in 1984. PLDs can be reprogrammed during the design cycle as well as in the field to perform multiple functions, and they support a fairly fast design process... |
40 nm | |
| Stratix V | 3,800,000,000 | 2011 | Altera Altera Altera Corporation is a Silicon Valley manufacturer of PLDs . The company offered its first programmable logic device in 1984. PLDs can be reprogrammed during the design cycle as well as in the field to perform multiple functions, and they support a fairly fast design process... |
28 nm | n/a mm² |
| Virtex-7 | 6,800,000,000 | 2011 | Xilinx | 28 nm |
Logic Functions
Transistor count for generic logic functions is based on CMOSCMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits...
implementation.
| Function | Transistor count |
|---|---|
| NOT | 2 |
| BUF | 4 |
| NAND 2-input NAND gate The Negated AND, NO AND or NAND gate is the opposite of the digital AND gate, and behaves in a manner that corresponds to the opposite of AND gate, as shown in the truth table on the right. A LOW output results only if both the inputs to the gate are HIGH... |
4 |
| NOR 2-input NOR gate The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW . If one or both input is HIGH , a LOW output results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator... |
4 |
| AND 2-input AND gate The AND gate is a basic digital logic gate that implements logical conjunction - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results only if both the inputs to the AND gate are HIGH . If neither or only one input to the AND gate is HIGH, a LOW output results... |
6 |
| OR 2-input OR gate The OR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical disjunction - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results if one or both the inputs to the gate are HIGH . If neither input is HIGH, a LOW output results... |
6 |
| NAND 3-input NAND gate The Negated AND, NO AND or NAND gate is the opposite of the digital AND gate, and behaves in a manner that corresponds to the opposite of AND gate, as shown in the truth table on the right. A LOW output results only if both the inputs to the gate are HIGH... |
6 |
| NOR 3-input NOR gate The NOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements logical NOR - it behaves according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results if both the inputs to the gate are LOW . If one or both input is HIGH , a LOW output results. NOR is the result of the negation of the OR operator... |
6 |
| XOR 2-input XOR gate The XOR gate is a digital logic gate that implements an exclusive or; that is, a true output results if one, and only one, of the inputs to the gate is true . If both inputs are false or both are true , a false output results. Its behavior is summarized in the truth table shown on the right... |
6 |
| XNOR 2-input XNOR gate The XNOR gate is a digital logic gate whose function is the inverse of the exclusive OR gate. The two-input version implements logical equality, behaving according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output results if both of the inputs to the gate are the same... |
8 |
| MUX 2-input with TG | 6 |
| MUX 4-input with TG | 18 |
| NOT MUX 2-input | 8 |
| MUX 4-input | 24 |
| Adder full | 28 |
| Latch, D gated | 8 |
| Flip-flop, edge triggered dynamic D with reset | 12 |
Parallel systems
Historically, each processing element in earlier parallel systems—like all CPUs of that time—was a serial computerSerial computer
A serial computer is typified by internally operating on one bit or digit for each clock cycle. Machines with serial main storage devices such as acoustic or magnetostrictive delay lines and rotating magnetic devices were usually serial computers....
built out of multiple chips.
As transistor counts per chip increases, each processing element could be built out of fewer chips, and then later each multi-core processor chip could contain more processing elements.
Goodyear MPP:
(1983?)
8 pixel processors per chip,
3,000 to 8,000 transistors per chip.
Brunel University Scape (single-chip array-processing element):
(1983)
256 pixel processors per chip,
120,000 to 140,000 transistors per chip.
Cell Broadband Engine:
(2006)
9 cores per chip,
234 million transistors per chip.

