
Toda lattice
Encyclopedia
The Toda lattice, named after Morikazu Toda, is a simple model for a one-dimensional crystal
in solid state physics. It is given by a chain of particles with nearest neighbor interaction
described by the equations of motion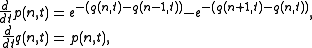
where is the displacement of the
is the displacement of the  -th particle from its equilibrium position,
-th particle from its equilibrium position,
and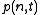 is its momentum (mass
is its momentum (mass 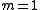 ).
).
The Toda lattice is a prototypical example of a completely integrable system with soliton
solutions. To see this one uses Flaschka
's variables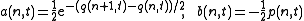
such that the Toda lattice reads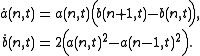
Then one can verify that the Toda lattice is equivalent to the Lax equation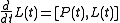
where [L,P] = L P - P L is the commutator
of two operators. The operators L and P, the Lax pair
, are linear operators in the Hilbert space
of square summable sequences given by
given by
In particular, the Toda lattice can be solved by virtue of the inverse scattering transform
for the Jacobi operator
L. The main result implies that arbitrary (sufficiently fast) decaying initial conditions asymptotically for large t split into a sum of solitons and a decaying dispersive
part.
in solid state physics. It is given by a chain of particles with nearest neighbor interaction
described by the equations of motion
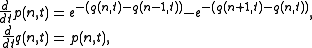
where
 is the displacement of the
is the displacement of the  -th particle from its equilibrium position,
-th particle from its equilibrium position,and
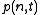 is its momentum (mass
is its momentum (mass 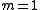 ).
).The Toda lattice is a prototypical example of a completely integrable system with soliton
Soliton
In mathematics and physics, a soliton is a self-reinforcing solitary wave that maintains its shape while it travels at constant speed. Solitons are caused by a cancellation of nonlinear and dispersive effects in the medium...
solutions. To see this one uses Flaschka
Hermann Flaschka
Herman Flaschka is a well-known Austrian born mathematical physicist and Professor of Mathematics at the University of Arizona, known for his important contributions in completely integrable systems .- Childhood :...
's variables
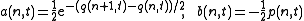
such that the Toda lattice reads
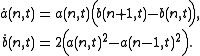
Then one can verify that the Toda lattice is equivalent to the Lax equation
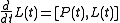
where [L,P] = L P - P L is the commutator
Commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.-Group theory:...
of two operators. The operators L and P, the Lax pair
Lax pair
In mathematics, in the theory of integrable systems, a Lax pair is a pair of time-dependent matrices or operators that describe the corresponding differential equations. They were introduced by Peter Lax to discuss solitons in continuous media...
, are linear operators in the Hilbert space
Hilbert space
The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions...
of square summable sequences
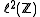 given by
given by
In particular, the Toda lattice can be solved by virtue of the inverse scattering transform
Inverse scattering transform
In mathematics, the inverse scattering transform is a method for solving some non-linear partial differential equations. It is one of the most important developments in mathematical physics in the past 40 years...
for the Jacobi operator
Jacobi operator
A Jacobi operator, named after Carl Gustav Jakob Jacobi, is a symmetric linear operator acting on sequences which is given by a tridiagonal matrix in the standard basis given by Kronecker deltas.- Self-adjoint Jacobi operators :...
L. The main result implies that arbitrary (sufficiently fast) decaying initial conditions asymptotically for large t split into a sum of solitons and a decaying dispersive
Dispersion
Dispersion may refer to:In physics:*The dependence of wave velocity on frequency or wavelength:**Dispersion , for light waves**Dispersion **Acoustic dispersion, for sound waves...
part.
External links
- E. W. Weisstein, Toda Lattice at ScienceWorld
- G. Teschl, The Toda Lattice

