
Threshold potential
Encyclopedia
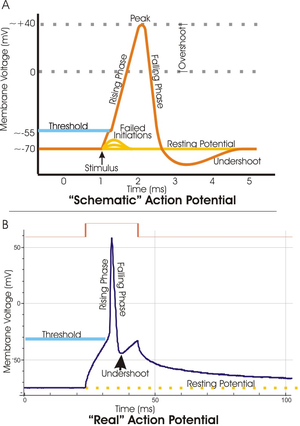
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
to which a membrane must be depolarized
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
to initiate an action potential
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
.
It often can be between −40 and -55 mV
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
, but it can vary based upon several factors. If ion channel
Ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells...
s are available, that will move the potential in the direction of the equilibrium potential for that ion:
- sodium ion channelSodium ion channelSodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions through a cell's plasma membrane. They are classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e...
: Na+ is approximately +55mV - potassium channelPotassium channelIn the field of cell biology, potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel and are found in virtually all living organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes...
: K+ is approximately -95mV - chloride channelChloride channelChloride channels are a superfamily of poorly understood ion channels consisting of approximately 13 members.Chloride channels display a variety of important physiological and cellular roles that include regulation of pH, volume homeostasis, organic solute transport, cell migration, cell...
: Cl- is approximately -90mV
Therefore, resting ion channel for sodium will depolarize
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
and thus excite, while channels for potassium or chloride will hyperpolarize
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization.Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g...
and thus inhibit.

