Thermal contact conductance
Overview
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, thermal contact conductance is the study of heat conduction
Heat conduction
In heat transfer, conduction is a mode of transfer of energy within and between bodies of matter, due to a temperature gradient. Conduction means collisional and diffusive transfer of kinetic energy of particles of ponderable matter . Conduction takes place in all forms of ponderable matter, viz....
between solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
bodies in thermal contact
Thermal contact
In heat transfer and thermodynamics, a thermodynamic system is said to be in thermal contact with another system if it can exchange energy with it through the process of heat...
. The thermal contact conductance coefficient,
 , is a property indicating the thermal conductivity
, is a property indicating the thermal conductivityThermal conductivity
In physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
, or ability to conduct heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
, between two bodies in contact. The inverse of this property is termed thermal contact resistance.
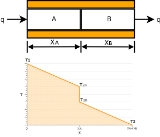
When two solid bodies come in contact, such as A and B in Figure 1, heat flows from the hotter body to the colder body.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

