
The ABC Model of Flower Development
Encyclopedia
Elliot Meyerowitz
Elliot Meyerowitz is an American biologist.He is George W. Beadle Professor of Biology, Division of Biology at the California Institute of Technology, he served as Chair of the Biology Division from 2000 to 2010....
in 1991. This model is built on the observation of mutants with defects in floral organ development. The ABC model summarizes how the presence or absence of different classes of transcription factors in the different parts of the flower
Flower
A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
regulates the development of floral organs.
Two key observations have led to the ABC model. First, the discovery of homeotic
Homeotic gene
Hox genes are a group of related genes that determine the basic structure and orientation of an organism.Hox genes are critical for the proper placement of segment structures of animals during early embryonic development Hox genes are a group of related genes that determine the basic structure and...
mutations in which one organ develops in a location normally occupied by a different organ. Wild rose
Rose
A rose is a woody perennial of the genus Rosa, within the family Rosaceae. There are over 100 species. They form a group of erect shrubs, and climbing or trailing plants, with stems that are often armed with sharp prickles. Flowers are large and showy, in colours ranging from white through yellows...
s, for example, have only five petal
Petal
Petals are modified leaves that surround the reproductive parts of flowers. They often are brightly colored or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. Together, all of the petals of a flower are called a corolla. Petals are usually accompanied by another set of special leaves called sepals lying...
s but many stamen
Stamen
The stamen is the pollen producing reproductive organ of a flower...
s. Garden roses have a homeotic gene that causes some of the potential stamens to develop into petals instead. Second, each of the genes that affect the identity of organs in flowers has an effect on two groups of flower organs, affecting petals and sepals or affecting petals and stamens.
Floral organ identity gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s are therefore divided into three classes, depending on which organs they affect. Mutations in class A genes affect sepal
Sepal
A sepal is a part of the flower of angiosperms . Collectively the sepals form the calyx, which is the outermost whorl of parts that form a flower. Usually green, sepals have the typical function of protecting the petals when the flower is in bud...
s and petals. Mutations in class B genes affect petals and stamens, while those in class C affect stamens and carpels. All three classes of genes are homeotic gene
Homeotic gene
Hox genes are a group of related genes that determine the basic structure and orientation of an organism.Hox genes are critical for the proper placement of segment structures of animals during early embryonic development Hox genes are a group of related genes that determine the basic structure and...
s, which are translated into protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. Each protein coded by these genes contains a MADS-box
MADS-box
The MADS box is a conserved sequence motif found in genes which comprise the MADS-box gene family. The MADS box encodes the DNA-binding MADS domain. The MADS domain binds to DNA sequences of high similarity to the motif CC[A/T]6GG termed the CArG-box. MADS-domain proteins are generally...
region that allows the protein to bind to DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and to function as a regulator in DNA transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
. It is believed that these genes are master controlling genes, regulating the action of other genes that will control organ development.
| Antirrhinum Antirrhinum majus Antirrhinum majus is a species of plants belonging to the genus Antirrhinum... |
Arabidopsis Arabidopsis thaliana Arabidopsis thaliana is a small flowering plant native to Europe, Asia, and northwestern Africa. A spring annual with a relatively short life cycle, arabidopsis is popular as a model organism in plant biology and genetics... |
|
|---|---|---|
| Class A | SQUAMOSA (SQUA) LIPLESS1 (LIP1) LIPLESS2 (LIP2) | APETALA2 Apetala 2 Apetala 2 ' is a gene coding for a member of a large family of transcription factors, the AP2/EREBP family. In Arabidopsis thaliana which plays a role in the ABC model of flower development... (AP2) APETALA1 (AP1) |
| Class B | DEFICIENS (DEF) GLOBOSA (GLO) | APETALA3 (AP3) PISTILLATA (PI) |
| Class C | PLENA (PLE) FARINELLI (FAR) | AGAMOUS (AG) |
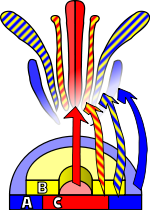
The ABC model proposes that class A genes alone are responsible for the development of sepals, but act together with class B genes to effect petal development. Class C genes alone are responsible for initiating the development of carpels, but act together with class B genes to determine the development of stamens. Support for a dual gene interaction with class B genes comes from the nature of class B mutants. A defective B gene leads to the absence of petals and stamens; in their places develop additional sepals and carpels. Similar organ replacement occurs when other classes of genes undergo mutation.
Summary:
- The expression of A genes induces the development of sepals.
- The expression of B genes together with A genes induces the development of petals.
- The expression of B genes together with C genes induces the development of stamens.
- The expression of C genes induces the development of carpels.
The characterization of sepallata1,2,3 triple mutant in Arabidopsis has led to the formulation of the ABCE model, which consider the importance of class E genes for the development of the floral organs.
See also
- FlowerFlowerA flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants . The biological function of a flower is to effect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs...
- MADS-boxMADS-boxThe MADS box is a conserved sequence motif found in genes which comprise the MADS-box gene family. The MADS box encodes the DNA-binding MADS domain. The MADS domain binds to DNA sequences of high similarity to the motif CC[A/T]6GG termed the CArG-box. MADS-domain proteins are generally...
- MutationMutationIn molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
- Plant evolutionary developmental biologyPlant evolutionary developmental biologyEvolutionary developmental biology refers to the study of developmental programs and patterns from an evolutionary perspective. It seeks to understand the various influences shaping the form and nature of life on the planet. Evo-devo arose as a separate branch of science rather recently. An early...
- Superman (gene)Superman (gene)Superman is a plant gene in Arabidopsis thaliana that plays a role in controlling the boundary between stamen and carpel development in a flower. It is named for the comic book character Superman, and the related genes kryptonite and clark kent were named accordingly...

