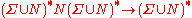Terminal and nonterminal symbols
Encyclopedia
In computer science
, terminal and nonterminal symbols are the lexical elements used in specifying the production rules that constitute a formal grammar
. The terminals and nonterminals of a particular grammar are two disjoint sets.
has a as a terminal symbol because no rule exists that would change it to something else. (On the other hand, x has two rules that can change it, so it is nonterminal.) A formal language
defined (or generated) by a particular grammar is the set of strings that can be produced by the grammar and that consist only of terminal symbols; nonterminals that do not consist entirely of terminals may not appear in the lexemes that are said to belong to the language.
In the context of syntax analysis, as opposed to the theory of programming language
s and compiler
s, the terms "terminal symbol" and "token" are often treated as synonymous. Quoting the so-called Dragon Book (a standard reference on the latter subject):
Terminal symbols, or just terminals, are the elementary symbols of the language
defined by a formal grammar
.
Context-free grammar
s are those grammars in which the left-hand side of each production rule consists of only a single nonterminal symbol. This restriction is non-trivial; not all languages can be generated by context-free grammars. Those that can are called context-free languages.
These are exactly the languages that can be recognized by a non-deterministic pushdown automaton
. Context-free languages are the theoretical basis for the syntax of most programming languages.
 ; e.g., the rule z0 → z1 specifies that z0 can be replaced by z1.
; e.g., the rule z0 → z1 specifies that z0 can be replaced by z1.
In the classic formalization of generative grammars first proposed by Noam Chomsky
in the 1950s, a grammar G consists of the following components:
A grammar is formally defined as the ordered quadruple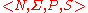 . Such a formal grammar is often called a rewriting system or a phrase structure grammar
. Such a formal grammar is often called a rewriting system or a phrase structure grammar
in the literature.
:
::= ['-'] {}
::= '0' | '1' | '2' | '3' | '4' | '5' | '6' | '7' | '8' | '9'
In this example, the symbols (-,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) are terminal symbols and and are nonterminal symbols.
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, terminal and nonterminal symbols are the lexical elements used in specifying the production rules that constitute a formal grammar
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
. The terminals and nonterminals of a particular grammar are two disjoint sets.
Terminal symbols
Terminal symbols are literal characters that can appear in the inputs to or outputs from the production rules of a formal grammar and that cannot be broken down into "smaller" units. To be precise, terminal symbols cannot be changed using the rules of the grammar. For example, a grammar that is defined by two rules:- x can become xa
- x can become ax
has a as a terminal symbol because no rule exists that would change it to something else. (On the other hand, x has two rules that can change it, so it is nonterminal.) A formal language
Formal language
A formal language is a set of words—that is, finite strings of letters, symbols, or tokens that are defined in the language. The set from which these letters are taken is the alphabet over which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar...
defined (or generated) by a particular grammar is the set of strings that can be produced by the grammar and that consist only of terminal symbols; nonterminals that do not consist entirely of terminals may not appear in the lexemes that are said to belong to the language.
In the context of syntax analysis, as opposed to the theory of programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
s and compiler
Compiler
A compiler is a computer program that transforms source code written in a programming language into another computer language...
s, the terms "terminal symbol" and "token" are often treated as synonymous. Quoting the so-called Dragon Book (a standard reference on the latter subject):
In a compiler, the lexical analyzer reads the characters of the source program, groups them into lexically meaningful units called lexemes, and produces as output tokens representing these lexemes. A token consists of two components, a token name and an attribute value. The token names are abstract symbols that are used by the parser for syntax analysis. Often, we shall call these token names terminals, since they appear as terminal symbols in the grammar for a programming language. The attribute value, if present, is a pointer to the symbol table that contains additional
information about the token. This additional information is not part of the grammar, so in our discussion of syntax analysis, often we refer to tokens and terminals synonymously.
Terminal symbols, or just terminals, are the elementary symbols of the language
Formal language
A formal language is a set of words—that is, finite strings of letters, symbols, or tokens that are defined in the language. The set from which these letters are taken is the alphabet over which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar...
defined by a formal grammar
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of formation rules for strings in a formal language. The rules describe how to form strings from the language's alphabet that are valid according to the language's syntax...
.
Nonterminal symbols
Nonterminal symbols, or just nonterminals, are the symbols which can be replaced; thus there are strings composed of some combination of terminal and nonterminal symbols. They may also be called simply syntactic variables. A formal grammar includes a start symbol, a designated member of the set of nonterminals from which all the strings in the language may be derived by successive applications of the production rules. In fact, the language defined by a grammar is precisely the set of terminal strings that can be so derived.Context-free grammar
Context-free grammar
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar is a formal grammar in which every production rule is of the formwhere V is a single nonterminal symbol, and w is a string of terminals and/or nonterminals ....
s are those grammars in which the left-hand side of each production rule consists of only a single nonterminal symbol. This restriction is non-trivial; not all languages can be generated by context-free grammars. Those that can are called context-free languages.
These are exactly the languages that can be recognized by a non-deterministic pushdown automaton
Pushdown automaton
In automata theory, a pushdown automaton is a finite automaton that can make use of a stack containing data.- Operation :Pushdown automata differ from finite state machines in two ways:...
. Context-free languages are the theoretical basis for the syntax of most programming languages.
Production rules
A grammar is defined by production rules that specify which lexemes may replace which other lexemes; these rules may be used to generate strings, or to parse them. Each such rule has a head, or left-hand side, which consists of the string that may be replaced, and a body, or right-hand side, which consists of a string that may replace it. Rules are often written in the form ; e.g., the rule z0 → z1 specifies that z0 can be replaced by z1.
; e.g., the rule z0 → z1 specifies that z0 can be replaced by z1.In the classic formalization of generative grammars first proposed by Noam Chomsky
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, and activist. He is an Institute Professor and Professor in the Department of Linguistics & Philosophy at MIT, where he has worked for over 50 years. Chomsky has been described as the "father of modern linguistics" and...
in the 1950s, a grammar G consists of the following components:
- A finite set
 of nonterminal symbols.
of nonterminal symbols. - A finite set
 of terminal symbols that is disjoint from
of terminal symbols that is disjoint from  .
. - A finite set
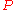 of production rules, each rule of the form
of production rules, each rule of the form
-
-
- where
 is the Kleene starKleene starIn mathematical logic and computer science, the Kleene star is a unary operation, either on sets of strings or on sets of symbols or characters. The application of the Kleene star to a set V is written as V*...
is the Kleene starKleene starIn mathematical logic and computer science, the Kleene star is a unary operation, either on sets of strings or on sets of symbols or characters. The application of the Kleene star to a set V is written as V*...
operator and denotes set unionUnion (set theory)In set theory, the union of a collection of sets is the set of all distinct elements in the collection. The union of a collection of sets S_1, S_2, S_3, \dots , S_n\,\! gives a set S_1 \cup S_2 \cup S_3 \cup \dots \cup S_n.- Definition :...
denotes set unionUnion (set theory)In set theory, the union of a collection of sets is the set of all distinct elements in the collection. The union of a collection of sets S_1, S_2, S_3, \dots , S_n\,\! gives a set S_1 \cup S_2 \cup S_3 \cup \dots \cup S_n.- Definition :...
, so represents zero or more symbols, and
represents zero or more symbols, and  means one nonterminal symbol. That is, each production rule maps from one string of symbols to another, where the first string contains at least one nonterminal symbol. In the case that the body consists solely of the empty stringEmpty stringIn computer science and formal language theory, the empty string is the unique string of length zero. It is denoted with λ or sometimes Λ or ε....
means one nonterminal symbol. That is, each production rule maps from one string of symbols to another, where the first string contains at least one nonterminal symbol. In the case that the body consists solely of the empty stringEmpty stringIn computer science and formal language theory, the empty string is the unique string of length zero. It is denoted with λ or sometimes Λ or ε....
—i.e., that it contains no symbols at all—it may be denoted with a special notation (often ,
,  or
or  ) in order to avoid confusion.
) in order to avoid confusion.
- A distinguished symbol
 that is the start symbol.
that is the start symbol.
- A distinguished symbol
A grammar is formally defined as the ordered quadruple
 . Such a formal grammar is often called a rewriting system or a phrase structure grammar
. Such a formal grammar is often called a rewriting system or a phrase structure grammarPhrase structure grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammars as defined by phrase structure rules, i.e. rewrite rules of the type studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue...
in the literature.
Example
For instance, the following represents an integer (which may be signed) expressed in a variant of Backus–Naur formBackus–Naur form
In computer science, BNF is a notation technique for context-free grammars, often used to describe the syntax of languages used in computing, such as computer programming languages, document formats, instruction sets and communication protocols.It is applied wherever exact descriptions of...
:
In this example, the symbols (-,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) are terminal symbols and