
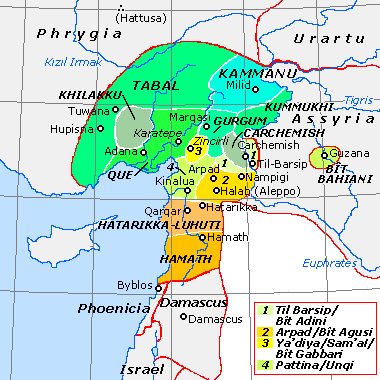
Tabal
Encyclopedia
Luwian language
Luwian is an extinct language of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Luwian is closely related to Hittite, and was among the languages spoken during the second and first millennia BC by population groups in central and western Anatolia and northern Syria...
speaking Neo-Hittite
Neo-Hittite
The states that are called Neo-Hittite, or more recently Syro-Hittite, were Luwian, Aramaic and Phoenician-speaking political entities of the Iron Age northern Syria and southern Anatolia that arose following the collapse of the Hittite Empire around 1180 BC and lasted until roughly 700 BC...
kingdom of South Central Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
. According to archaeologist Kurt Bittel, the kingdom of Tabal first appeared after the collapse of the Hittite Empire.
The Assyria
Assyria
Assyria was a Semitic Akkadian kingdom, extant as a nation state from the mid–23rd century BC to 608 BC centred on the Upper Tigris river, in northern Mesopotamia , that came to rule regional empires a number of times through history. It was named for its original capital, the ancient city of Assur...
n king Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III was king of Assyria , and son of the previous ruler, Ashurnasirpal II....
records that he received gifts from their 24 kings in 837 BC and the following year. A century later, their king Burutash is mentioned in an inscription of king Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III was a prominent king of Assyria in the eighth century BC and is widely regarded as the founder of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Tiglath-Pileser III seized the Assyrian throne during a civil war and killed the royal family...
. The kings of Tabal have left a number of inscriptions from the 9th
9th century BC
The 9th century BC started the first day of 900 BC and ended the last day of 801 BC.- Overview :The 9th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Africa, Carthage is founded by the Phoenicians...
-8th centuries BC
8th century BC
The 8th century BC started the first day of 800 BC and ended the last day of 701 BC.-Overview:The 8th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Egypt, the 23rd and 24th dynasties led to rule from Nubia in the 25th Dynasty...
in hieroglyphic-Luwian
Luwian language
Luwian is an extinct language of the Anatolian branch of the Indo-European language family. Luwian is closely related to Hittite, and was among the languages spoken during the second and first millennia BC by population groups in central and western Anatolia and northern Syria...
in the Turkish villages of Çalapverdi and Alişar
Alisar
Alişar is a village in the Yozgat Province, Turkey. Near the village is the archaeological site of Alişar Höyük.-Alişar Höyük:The site was settled from the Chalcolithic period in the fourth millennium BC until the Phrygian period in the first millennium BC. During the Early and Middle Bronze Age in...
.
Tabal and its people are often identified with the tribe of the Tibareni
Tibareni
The Tibareni were a people referred to in Herodotus, Xenophon, Strabo and other classical authors. In classical times, they and other related tribes, the Chalybes and the Mossynoeci, were considered the founders of metallurgy...
(Tibarenoi in Greek, Thobeles in Josephus) who lived near the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
. They are mentioned in the works of Hecataeus
Hecataeus
Hecataeus of Miletus , named after the Greek goddess Hecate, was an early Greek historian of a wealthy family. He flourished during the time of the Persian invasion. After having travelled extensively, he settled in his native city, where he occupied a high position, and devoted his time to the...
, Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
, Xenophon
Xenophon
Xenophon , son of Gryllus, of the deme Erchia of Athens, also known as Xenophon of Athens, was a Greek historian, soldier, mercenary, philosopher and a contemporary and admirer of Socrates...
and Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
. On this ground, the Georgian historian Ivane Javakhishvili
Ivane Javakhishvili
Ivane Javakhishvili was a Georgian historian whose voluminous works heavily influenced the modern scholarship of the history and culture of Georgia...
considered Tabal, Tubal, Jabal and Jubal to be ancient Georgian
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
tribal designations, and argued that they spoke a non-Indo-European language. Whether there is really any connection between the Tibareni of the Black Sea coast and the Tabal kingdom of Southern Anatolia is uncertain, ancient authors may have already confused the two.
The known later rulers of Tabal are:
- Ambaris (until ca. 713)
- Hidi (ca. 690)
- Mugallu (ca. 670)
- x-ussi (ca. 650)

